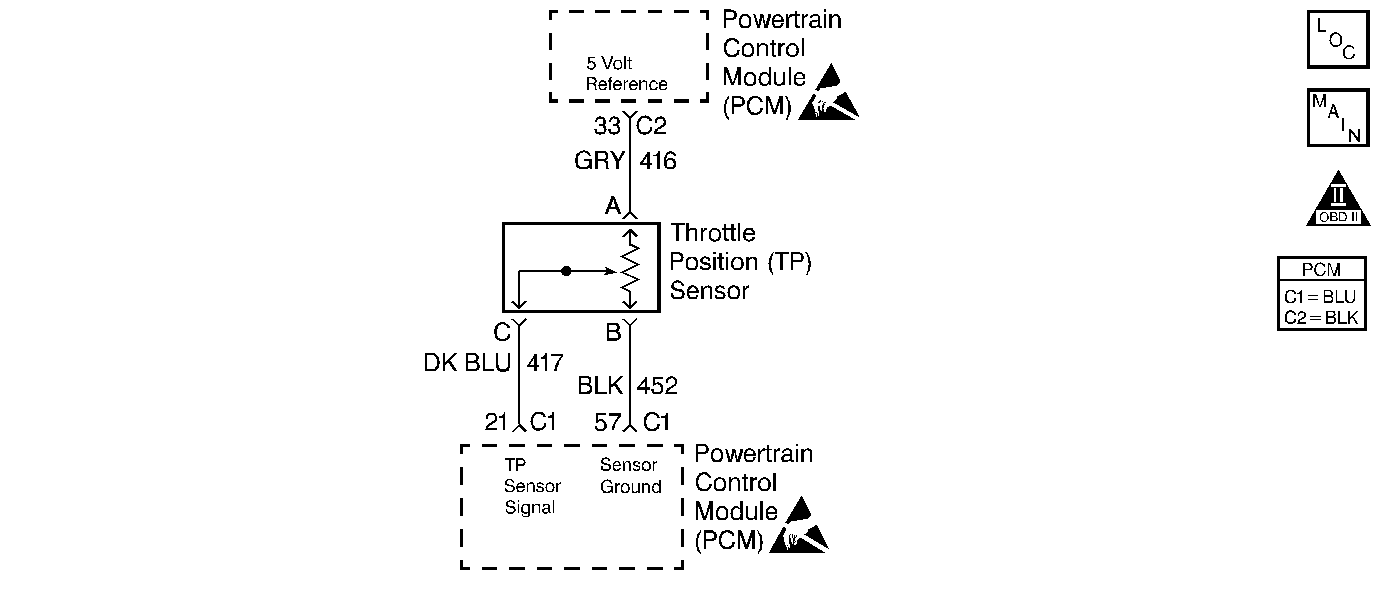
Circuit Description
The Throttle Position (TP) sensor is a potentiometer. The Control Module (PCM/VCM) supplies the TP sensor a reference voltage, signal, and ground circuits. When the throttle is depressed, the TP sensor signal rises to near the reference voltage. When the throttle is released, the TP sensor signal decreases from the reference voltage. The Control Module monitors the TP sensor signal circuit voltage to determine the throttle blade's angle (or opening).
This DTC determines if the TP sensor signal input to the PCM does not closely match what the predicted value for the TP sensor should be. The PCM calculates what the TP signal voltage should be based on engine RPM. If the TP sensor voltage and the predicted TP sensor values do not closely match, this DTC will be set.
Conditiions for Running the DTC
| • | No active MAP DTC's |
| • | The engine is running. |
| • | MAP is less than 60 kPa when the engine speed is less than 1500 RPM. |
| • |
| or |
| • | No active MAP DTC's |
| • | The engine is running. |
| • | MAP is moe than 60 kPa when the engine speed is more than 1500 RPM. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The TP sensor voltage is more than 3.9 volts for 13.75 seconds when the engine speed is less than 1500 RPM.
Or
TP sensor voltage is more than 4.8 volts when the engine speed is more than 1500 RPM.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The control module illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) if a failure is detected during 2 consecutive key cycles. |
| • | The control module sets the DTC and records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic failed. The failure information is stored in the scan tool Freeze Frame/Failure Records. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL or DTC
| • | The control module turns OFF the MIL after 3 consecutive drive trips when the test has run and passed. |
| • | A history DTC will clear if no fault conditions have been detected for 40 warm-up cycles. A warm-up cycle occurs when the coolant temperature has risen 22°C (40°F) from the startup coolant temperature and the engine coolant reaches a temperature that is more than 70°C (158°F) during the same ignition cycle. |
| • | Use a scan tool in order to clear the DTCs. |
Diagnostic Aids
With the ignition ON and the throttle at closed position, the voltage should read between 0.20 Volts and 0.90 Volts and increase steadily to over 4.5 Volts at wide open throttle.
An intermittent may be caused by any of the following conditions:
| • | A poor connection |
| • | Rubbed through wire insulation |
| • | A broken wire inside the insulation |
Thoroughly check any circuitry that is suspected of causing the intermittent complaint. Refer to Intermittents and Poor Connections Diagnosis in Wiring Systems.
If a repair is necessary, refer to Wiring Repairs or Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the Diagnostic Table.
-
The Powertrain OBD System Check prompts you to complete some of the basic checks and to store the freeze frame and failure records data on the scan tool if applicable. This creates an electronic copy of the data captured when the malfunction occurred. The scan tool stores this data for later reference.
-
With the throttle closed, the TP sensor voltage should read less than 0.80 volts. If the TP sensor voltage does not read less than 0.80 volts, check for a binding or a sticking throttle cable.
-
The PCM and the wiring are OK if the TP sensor voltage is less than 0.3 volts with the TP sensor electrical connector disconnected.
-
Probing the ground circuit with a test light checks the circuit for high resistance which will cause a DTC P0123 to set.
-
Important: The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) uses a single internal 5.0 volt power supply to supply power to all the engine control components. If one component shorts its 5.0 volt reference circuit to ground or battery voltage, the other 5.0 volt reference circuits will also have a low or high voltage.
A shorted 5.0 volt reference circuit will also set additional DTCs.
-
Program the replacement PCM and perform the Crankshaft Position System Variation Learn Procedure. Refer to the latest Techline information for PCM programming.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | |||
Is the TP sensor voltage more than the specified value? | 0.8 V | |||
3 |
Is the TP sensor voltage more than the specified value? | 3.9 V | ||
Is the TP sensor voltage less than the specified value? | 0.3 V | |||
Probe the TP sensor ground circuit at the TP sensor harness connector with a test lamp connected to B+. Is the test lamp ON? | -- | |||
6 |
Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||
|
Important: The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) uses a single internal 5.0 volt power supply to supply power to all the engine control components. If one component shorts its 5.0 volt reference circuit to ground or voltage, the other 5.0 volt reference circuits will also have a low or high voltage.
Was a repair necessary? | -- | |||
8 |
Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||
9 |
Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||
10 | Replace the TP sensor. Refer to the Throttle Position Sensor Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
Was a repair necessary? | -- | |||
12 |
Important:: The replacement PCM must be programmed. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement/Programming . Replace the PCM Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
13 |
Does the scan tool indicate that the diagnostic ran and passed? | -- | ||
14 | Check to see if any additional DTCs are set. Does the scan tool display any DTCs that you have not diagnosed? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | System OK |
