DTC P0502 Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS) Circuit Low Input Manual Trans Only
Circuit Description
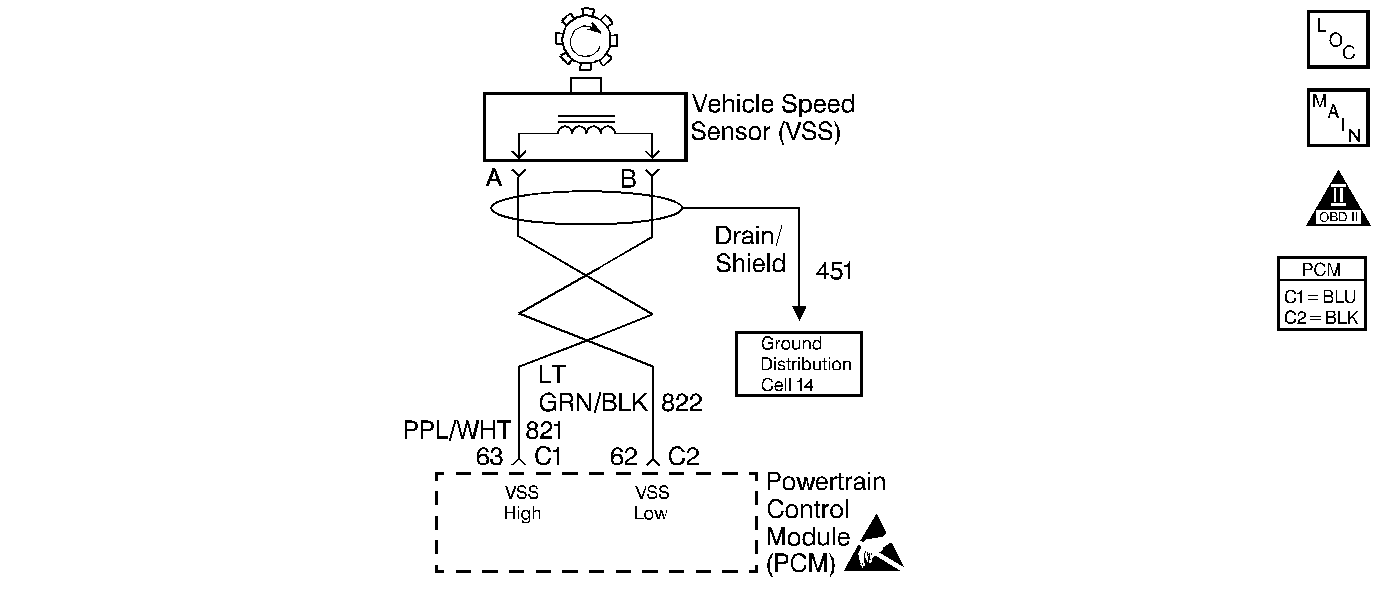
The Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS) provides the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) with the vehicle speed information. The VSS is a permanent magnet generator that is mounted in the transmission. The VSS produces a pulsing voltage whenever the vehicle speed is greater than 3 mph (5 km/h). The AC voltage level and the number of pulses increases with the vehicle speed. The PCM then supplies the signal to the instrument panel for the speedometer, the odometer, the electronic transmission (if equipped) and the cruise control operation. The PCM converts the pulsing voltage into mph the technician can use for calculations.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | No active MAP DTC's |
| • | No active TP DTC's |
| • | Engine speed is between 1700 and 3600 RPM. |
| • | Throttle Position (TP) is less than 1 percent. |
| • | Engine vacuum is between 80 and 70 kPa. |
| • | Above conditions met for 5 seconds. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
Vehicle speed is less than 2 mph (3 km/h).
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The control module illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) if a failure is detected during 2 consecutive key cycles. |
| • | The control module sets the DTC and records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic failed. The failure information is stored in the scan tool Freeze Frame/Failure Records. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL or DTC
| • | The control module turns OFF the MIL after 3 consecutive drive trips when the test has run and passed. |
| • | A history DTC will clear if no fault conditions have been detected for 40 warm-up cycles. A warm-up cycle occurs when the coolant temperature has risen 22°C (40°F) from the startup coolant temperature and the engine coolant reaches a temperature that is more than 70°C (158°F) during the same ignition cycle. |
| • | Use a scan tool in order to clear the DTCs. |
Diagnostic Aids
| • | A scan tool should indicate a vehicle speed whenever the drive wheels are turning more than 3 mph (5 km/h). A DTC P0502 can be falsely set if the engine is braked-torqued in gear. Disregard if the DTC set while the drive wheels are not turning. |
| • | Thoroughly check the VSS high and VSS low circuits for backed out terminals, broken locks, and for proper routing. |
| • | Refer to Symptoms . |
An intermittent may be caused by any of the following conditions:
| • | A poor connection |
| • | Rubbed through wire insulation |
| • | A broken wire inside the insulation |
Thoroughly check any circuitry that is suspected of causing the intermittent complaint. Refer to Intermittents and Poor Connections Diagnosis in Wiring Systems.
If a repair is necessary, refer to Wiring Repairs or Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the Diagnostic Table.
-
The Powertrain OBD System Check prompts the technician to complete some basic checks and store the freeze frame and failure records data on the scan tool if applicable. This creates an electronic copy of the data taken when the malfunction occurred. The information is then stored on the scan tool for later reference.
-
The permanent magnet generator only produces a signal if the drive wheels are turning greater than 3 mph (5 km/h). This step determines if DTC P0502 is the result of a hard malfunction or an intermittent condition.
-
Proper engine loads cannot be achieved in a shop environment to properly run the vehicle within the Freeze Frame data conditions. It will be necessary to drive the vehicle on the road to obtain the proper engine loads.
-
This step verifies that the PCM is receiving a signal from the vehicle speed sensor.
-
Refer to service bulletin information for the latest calibration update.
-
Refer to the latest Techline information for programming procedures.
-
A resistance reading that is higher than the specified value indicates that the VSS circuitry is open.
-
If the displayed resistance were less than the 1300 ohms, the VSS high and low circuits are shorted together. If the resistance value within the specified value, check the VSS high and low circuits for a short to ground.
-
This checks the resistance of the VSS if no opens or shorts were found on the VSS high and low circuits.
-
Replacement PCMs must be programmed and the Crankshaft Position System Variation Learn Procedure must be performed. Refer to the latest Techline information for PCM programming.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | |||
Does the scan tool display vehicle speed above the specified value? | 0 mph | |||
Does the scan tool display the vehicle speed above the specified value? | 0 mph | |||
Is the AC voltage more than or equal to the specified value? | 0.5V | |||
Check for the most current calibration ID number. Is the latest calibration ID in the vehicle? | -- | |||
Update the PCM with the latest calibration ID number. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | ||
7 | Measure the resistance between the VSS high circuit and VSS low circuit at the PCM harness connector. Is the resistance more than the specified value? | 1950ohms | ||
Check the VSS high circuit for an open and repair as necessary. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Was a repair necessary? | -- | |||
9 | Was the resistance value within or equal to the specified value? | 1300-1950ohms | ||
Check the VSS high circuit for a short to ground or for being shorted to the low circuit and repair as necessary. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Was a repair necessary? | -- | |||
Is the resistance value within the specified value? | 1300-1950ohms | |||
12 | Replace the Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS). Refer to Vehicle Speed Sensor in Manual Transmission. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
|
Important:: The replacement PCM must be programmed. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement/Programming . Replace the PCM. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | ||
14 |
Does the scan tool indicate that this diagnostic has ran and passed? | -- | ||
15 | Check if any additional DTCs are set. Are any DTCs displayed that have not been diagnosed? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | System OK |
