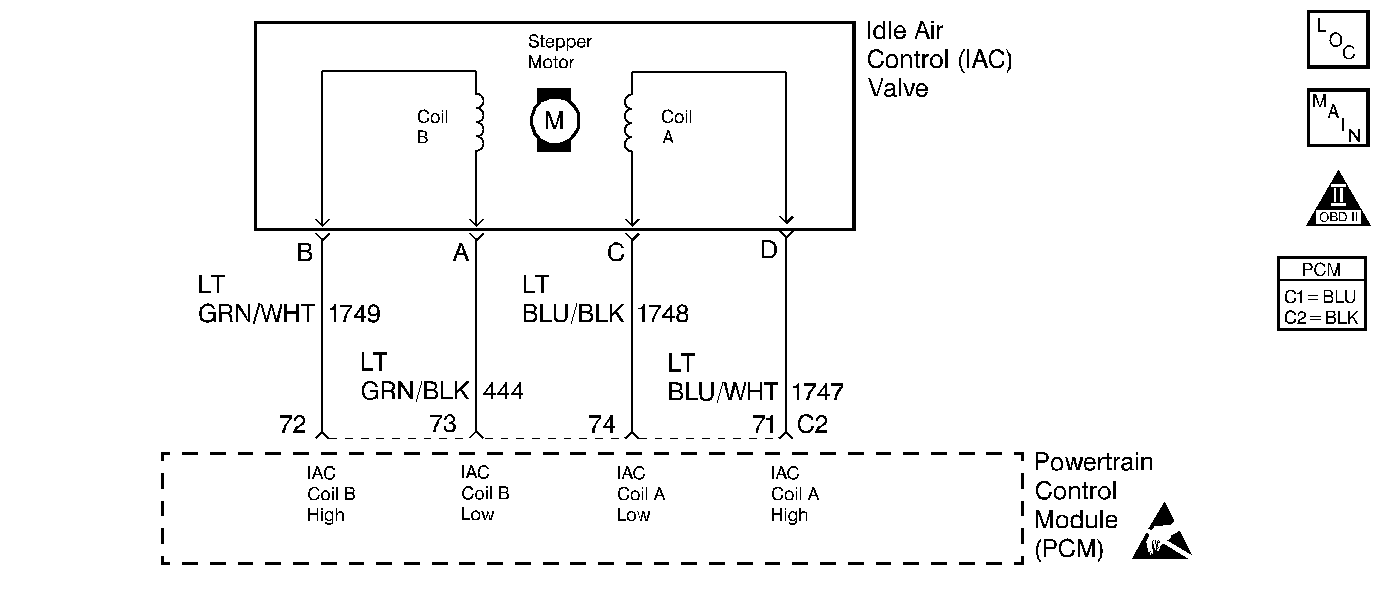
Circuit Description
The powertrain control module (PCM) controls the air entering into the engine with an idle air control (IAC) valve. In order to increase the idle RPM, the PCM commands the pintle inside the IAC valve away from the throttle body seat. This allows more air to bypass through the throttle blade. In order to decrease the RPM the PCM commands the pintle towards the throttle body seat. This reduces the amount of air bypassing the throttle blade. A scan tool will read the IAC valve pintle position in counts. The higher the counts, the more air that is allowed to bypass the throttle blade.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | DTCs P0105, P0107, P0108, P0112, P0113, P0117, P0118, P0122, P0123, P0125, P0131, P0132, P0133, P0134, P0200, P0335, P0341, P0342, P0440, P0442, P0446, P0480, P0502, P0503, P0601, P0602, P1133 and P1441 are not set. |
| • | BARO is more than 72 kPa. |
| • | The engine coolant temperature (ECT) is more than 40°C (104°F). |
| • | Engine has been running more than 20 seconds. |
| • | The throttle position (TP) angle is less than 1 percent. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | Engine RPM is below desired RPM by more than 100 RPM for 19 seconds. |
| • | IAC command is more than 145 counts. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) will illuminate after two consecutive ignition cycles in which the diagnostic runs with the malfunction present. |
| • | The PCM will record the operating conditions at the time that the diagnostic fails. This information will store in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records buffers. |
| • | A history DTC stores. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The MIL will turn OFF after 3 consecutive ignition cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault. |
| • | A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm up cycles without a fault. |
| • | A scan tool can clear the DTCs. |
Diagnostic Aids
| • | Inspect the IAC valve electrical connection for proper mating. |
| • | Inspect the wiring harness for damage. |
| • | Inspect the throttle stop screw for signs of tampering. |
| • | Inspect the throttle linkage for signs of binding or excessive wear. |
| • | A slow or unstable idle may be the cause of one of the following conditions: |
| - | Fuel system too rich or too lean. |
| - | Foreign material in the throttle body bore or in the Air Induction System. |
| - | A leaking or restricted intake manifold. |
| - | An excessive engine overloading: Check for seized pulleys, pumps, or motors on the accessory drive. |
| - | Too high a viscosity engine oil |
| • | Refer to Rough, Unstable, or Incorrect Idle and Stalling . |
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
The Powertrain OBD System Check prompts you to complete some of the basic checks and to store the Freeze Frame and Failure Records data on the scan tool if applicable. This creates an electronic copy of the data captured when the malfunction occurred. The scan tool stores this data for later reference.
-
A normally operating IAC can be extended and retracted by a scan tool to change the engine idle RPM. Valve movement is verified by an engine RPM change.
Step | Action | Values | Yes | No | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | |||||||||
Does the engine RPM change smoothly when the engine is commanded by the scan tool? | 900-2000 RPM | Go to Diagnostic Aids | ||||||||
3 |
Does the engine RPM change smoothly when commanded by the IAC driver? | - | ||||||||
4 |
Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||||||||
5 |
Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||||||||
6 |
Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||||||||
7 | Replace the IAC valve. Refer to Idle Air Control Valve Replacement Is the action complete? | -- | - | |||||||
8 |
Important: The replacement PCM must be programmed. Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement/Programming . Is the action complete? | -- | - | |||||||
9 |
Does the scan tool indicate that this diagnostic has Ran and Passed? | -- | ||||||||
10 | Check to see if any additional DTCs are set. Does the scan tool display any DTCs that you have not diagnosed? | -- | Go to applicable DTC table | System OK |
