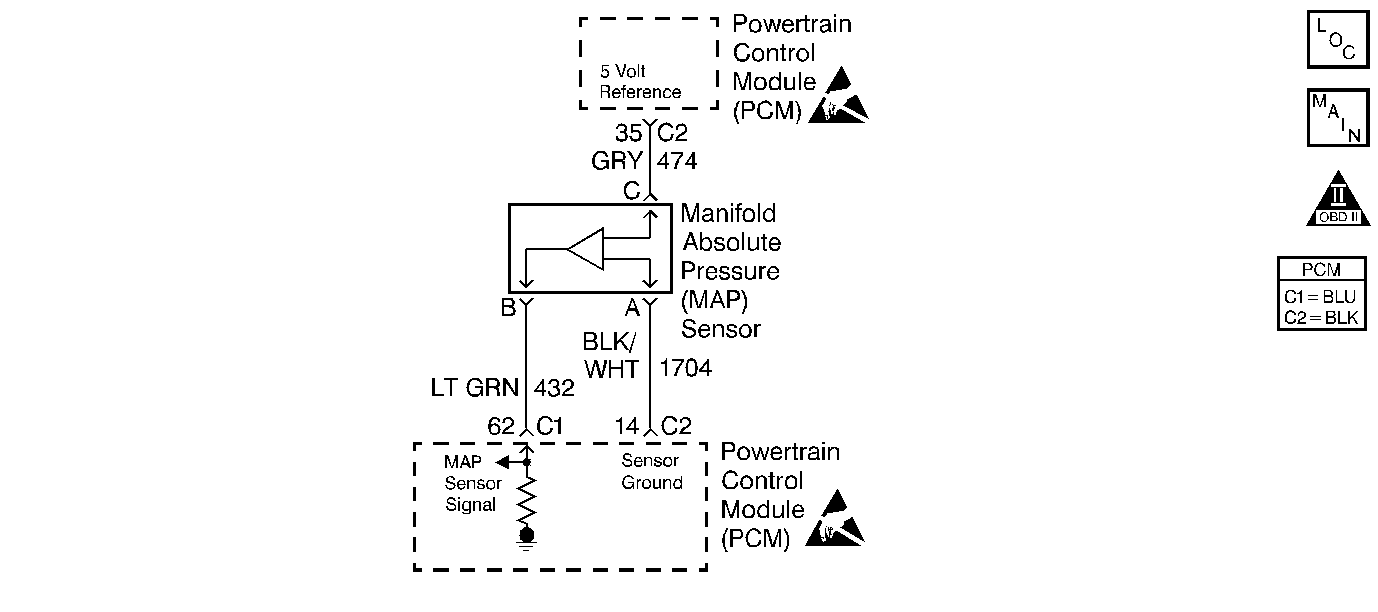
Circuit Description
The manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor measures the changes in the intake manifold pressure which results from the engine load, intake manifold vacuum and the RPM changes then converts these into a voltage output. The powertrain control module (PCM) supplies a 5 volt reference voltage to the MAP sensor. As the manifold pressure changes, the output voltage of the sensor also changes. By monitoring the sensor output voltage, the PCM knows the manifold pressure. A lower pressure--low voltage--output voltage will be about 1.0 volts to 1.5 volts at idle. While high pressure--high voltage--output voltage will be about 4.5 volts to 4.8 volts at wide open throttle (WOT). The MAP sensor is also used, under certain conditions, to measure barometric pressure, allowing the PCM to make adjustment for different altitudes. The PCM uses the MAP sensor in order to control the fuel delivery and the ignition timing.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table:
-
Applying 34 kPa (10 inches of Hg) vacuum to the MAP sensor should cause the voltage to be 1.5 volts to 2.1 volts less than the voltage at step 3. Upon applying vacuum to the sensor, the change in voltage should be instantaneous. A slow voltage change indicates a malfunctioning sensor.
-
Check sensor for leaking sealing gasket or restriction of the sensor port.
-
Move sensor electrical connector by hand only while watching scan tool to check for intermittent connection. Output changes more than 0.10 volts indicate a bad connection. If OK, replace sensor.
Step | Action | Values | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | Go to | |
2 | Install scan tool and check for MAP DTCs. Were any MAP DTCs set? | -- | Go to applicable DTC tables | |
3 |
Important: Be sure to use the same diagnostic test equipment for all measurements. Are the voltage readings between the 2 vehicles within the specified value? | ± 0.4 V | ||
Is the difference more than the specified value? | 34 kPa (10 in of Hg) 1.5V | |||
5 | Replace MAP sensor. Refer to Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
Check the MAP sensor sealing gasket for a damaged or missing seal or a restricted/damaged sensor port. Was a condition found? | -- | |||
Was a repair necessary? | -- | |||
8 | Replace the MAP sensor seal or MAP sensor if the port is damaged. Is the action complete? | -- |
| |
9 | Operate vehicle within the conditions under which the original symptom was noted. Does the system now operate properly? | -- | System OK |
