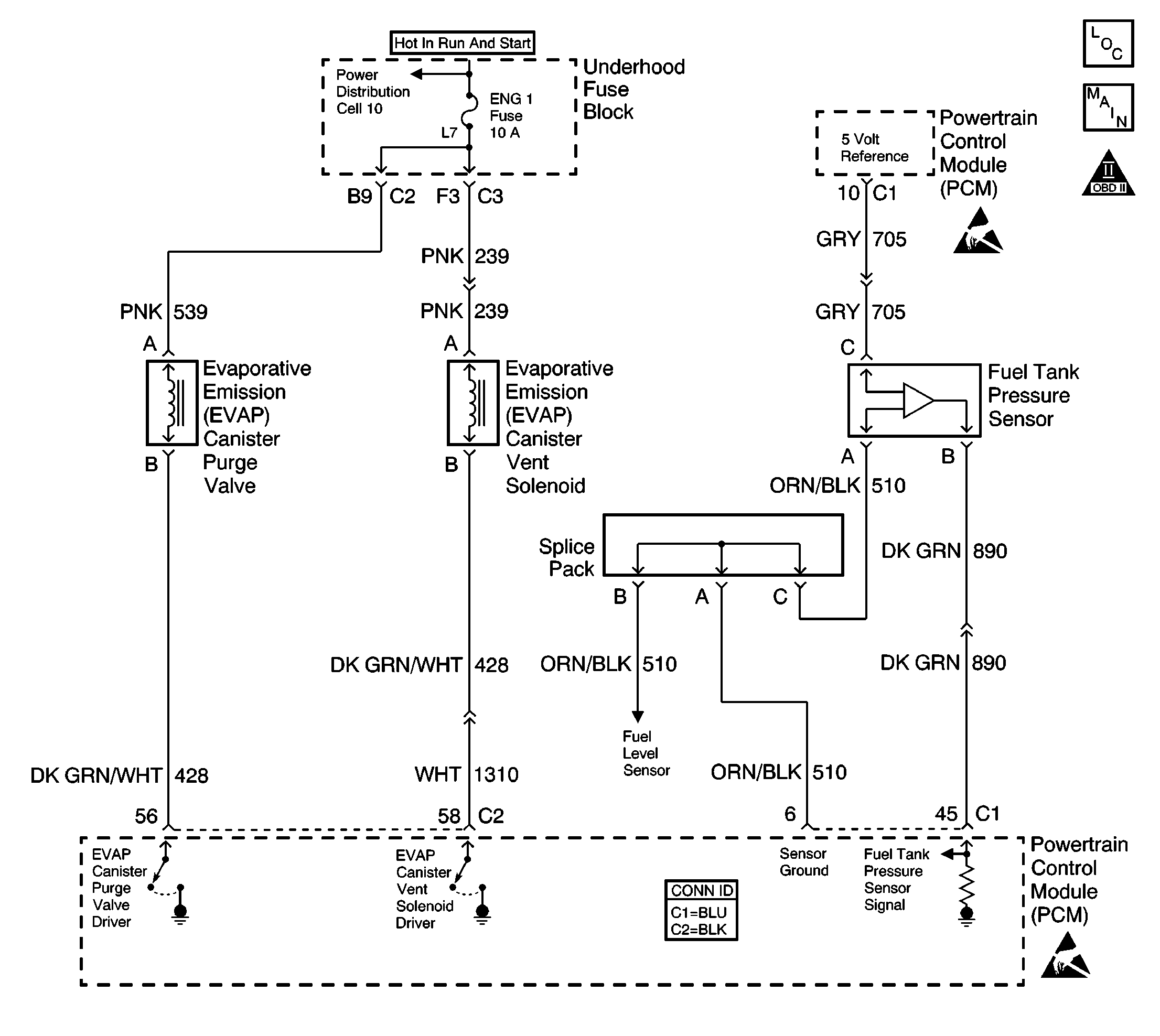
System Description
The powertrain control module (PCM) supplies a ground to energize the EVAP purge valve (purge ON). The EVAP purge valve control is pulse width modulated (PWM) or turned ON and OFF several times a second. The duty cycle (pulse width) is determined by engine operating conditions including load, throttle position, coolant temperature and ambient temperature. The duty cycle is calculated by the PCM and the output is commanded when the appropriate conditions have been met. The system checks for conditions that cause the EVAP system to purge continuously by commanding the EVAP vent valve ON (closed) and the EVAP canister purge valve OFF (closed). If vacuum level in the fuel tank increases during the test, a continuous purge flow condition is indicated. This can be caused by any of the following conditions:
Conditions for Running the DTC
All conditions for DTC P0440, P0442 and P0446 diagnostic tests have been met and passed.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
A continuous open purge flow condition is detected during the diagnostic test (fuel tank pressure decreases to less than -11 inches H2O).
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) during the second consecutive trip in which the diagnostic test has been run and failed. |
| • | The PCM will store conditions which were present when the DTC set as Freeze Frame/Failure Records data. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The PCM will turn the MIL OFF during the first trip in which the diagnostic has been run and passed. |
| • | The history DTC will clear when the PCM turns OFF the MIL. |
| • | The DTC can be cleared by using a scan tool. |
Diagnostic Aids
The following conditions will set a DTC P1441.
| • | EVAP canister purge valve leaking internally. |
| • | EVAP purge and engine vacuum lines switched at the EVAP canister purge valve. |
| • | EVAP canister purge valve control circuit grounded. |
Check for the following conditions:
Important: If charcoal release is detected, replace the EVAP canister. Refer to Evaporative Emission Canister Replacement .
| • | Incorrect vacuum line routing. |
| Verify that the source vacuum line routing to the EVAP purge valve is correct and that the EVAP purge and source vacuum lines to the EVAP canister purge valve are not switched. |
| • | Malfunctioning or damaged canister. |
| • | Inspect for carbon release in the EVAP system. |
Important: : Remove any debris from the connector surfaces before servicing a component. Inspect the connector gaskets when diagnosing or replacing a component. Ensure that the gaskets are installed correctly. The gaskets prevent contaminate intrusion.
| • | Poor terminal connection--Inspect the harness connectors for backed out terminals, improper mating, broken locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals and faulty terminal to wire connection. Use a corresponding mating terminal to test for proper tension. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections and Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems. |
| • | Damaged harness--Inspect the wiring harness for damage. If the harness appears to be OK, observe the sensor display on the scan tool while moving connectors and wiring harnesses related to the sensor. A change in the sensor display may indicate the location of the fault. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. |
| • | Inspect the PCM and the engine grounds for clean and secure connections. |
If the DTC is determined to be intermittent, reviewing the Failure Records can be useful in determining when the DTC was last set.
Reviewing the Fail Records vehicle mileage since the diagnostic test last failed may help determine how often the condition that caused the DTC to set occurs. This may assist in diagnosing the condition.
If the harness appears to be OK, connect the J 41413 EVAP pressure/purge diagnostic station to the EVAP service port, pressurize the EVAP system to 10 inches H2O and observe the fuel tank pressure parameter on the scan tool while moving connectors and wiring harnesses related to the EVAP purge valve. A sudden change in the display will indicate the location of the malfunction.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table:
-
The Powertrain On Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check prompts you to complete some of the basic check and store the Freeze Frame and Failure Records data on the scan tool if applicable.
-
Determines if the EVAP canister purge valve is leaking.
-
Determines if the EVAP canister purge valve driver circuit is shorted to ground.
-
Determines if the EVAP canister purge valve driver circuit wiring or PCM are a fault.
Step | Action | Values | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | |||
2 | Did any other EVAP DTCs codes store in history? | -- | Go to Evaporative Emission Control System Operation Description | |
Does the scan tool indicate vacuum above the specified value? | 0 Hg (0 H2O) | Go to Diagnostic Aids | ||
Does the scan tool indicate vacuum above the specified value? | 0 Hg (0 H2O) | |||
Did the test lamp illuminate? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | ||
6 | Test the purge valve control circuit for a short to ground. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||
7 |
Important: Check for carbon release into the EVAP system. Replace the EVAP canister purge valve. Refer to Evaporative Emission Canister Purge Solenoid Valve Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | -- | |
8 |
Important: The replacement PCM must be programmed. Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement/Programming . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
9 |
Does the scan tool indicate FTP near the specified value? | 0 Hg (0 H2O) | System OK |
