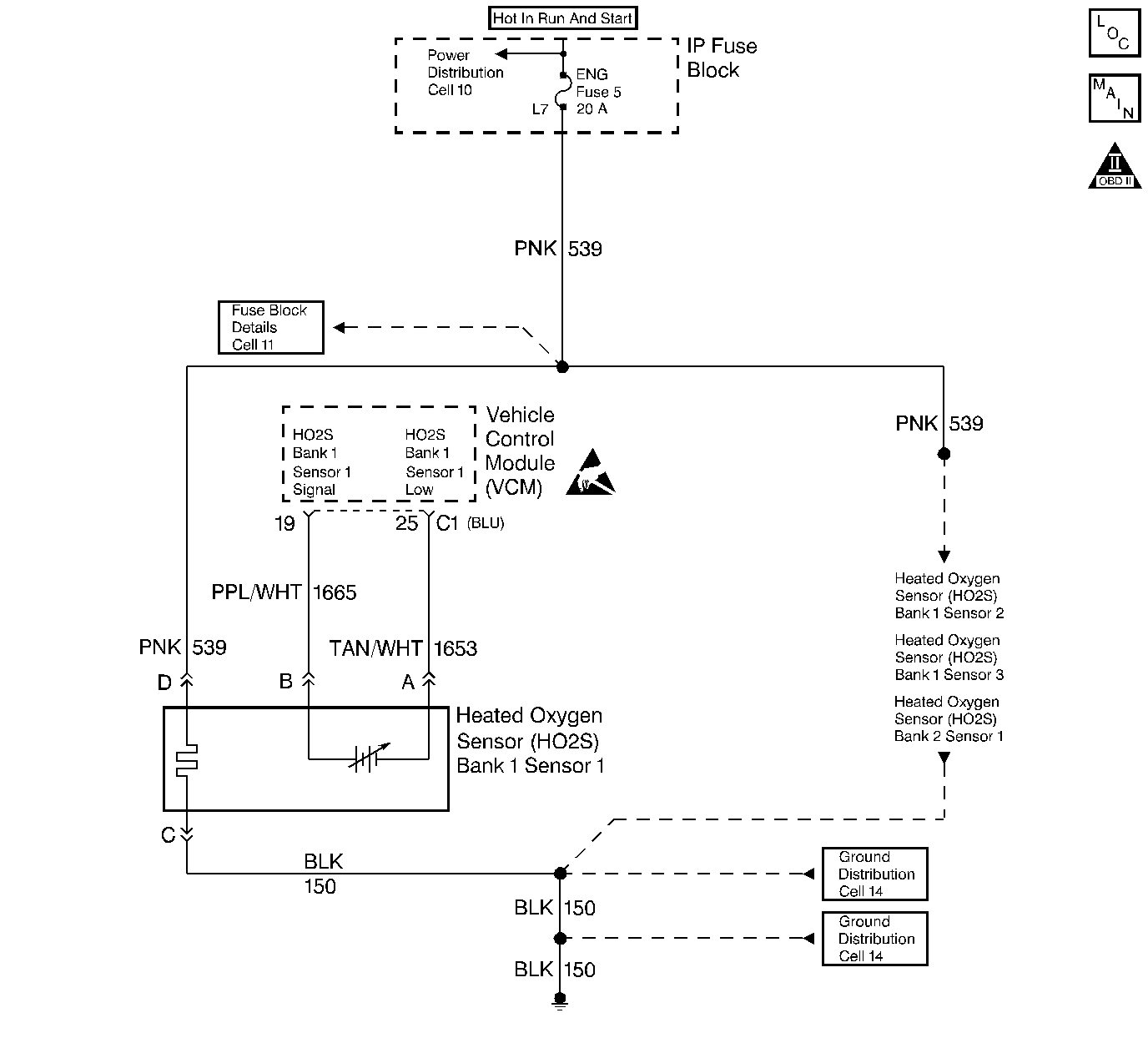
Circuit Description
Important: If the voltage is measured with a 10 Megaohm Digital Voltmeter, the voltage may read as low as 0.32 volt (320 mV).
The VCM supplies a voltage of approximately 0.45 volt (450 mV) between the HO2S High and HO2S Low circuits. The Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S) varies the voltage from approximately 1.0 volt (1000 mV) during rich conditions to 0.10 volt (100 mV) during lean conditions.
When the HO2S temperature measures below 360°C (600°F) the sensor will not produce any voltage and will behave like an open circuit. This will result in an Open Loop operation.
The HO2S heater provides for a faster sensor warm-up which allows the sensor to become active in a shorter period of time. The sensor will remain active during a long extended idle. The DTC P0135 determines if the HO2S is functioning properly by checking the response time of the sensor. This is a type B DTC.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| Important: If the voltage remains outside this range for more than 4 seconds, the test is void for this cold start |
| • | The system voltage is greater than 9.0 volts but less than 17.0 volts |
| • | The MAF is less than 27 grams per second |
| • | The engine run time is greater than 2 seconds |
| • | The ECT sensor is less than 32°C |
| • | The IAT is less than 32°C |
| • | The deference between the ECT and the IAT is no more than 5°C |
| • | The elapsed time in order to obtain the ±0.150 volts from the average HO2S bias voltage (0.299-0.598 volts) is greater than 130 seconds |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The VCM turns the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) ON after 2 consecutive test failures.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL or DTC
| • | The control module turns OFF the MIL after 3 consecutive drive trips when the test has run and passed. |
| • | A history DTC will clear if no fault conditions have been detected for 40 warm-up cycles. A warm-up cycle occurs when the coolant temperature has risen 22°C (40°F) from the startup coolant temperature and the engine coolant reaches a temperature that is more than 70°C (158°F) during the same ignition cycle. |
| • | Use a scan tool in order to clear the DTCs. |
Diagnostic Aids
Important: Never solder the HO2S wires. For proper wire and connection repairs, refer to Wiring Repairs in Engine Electrical.
| • | Check for a poor connection or a damaged harness. |
| • | Inspect the harness for the following conditions: |
| - | Backed out terminals |
| - | Improper mating |
| - | Broken locks |
| - | Improperly formed or damaged terminals |
| - | A poor terminal to wire connection |
| - | A damaged harness |
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the Diagnostic Table.
-
The HO2S should be allowed to cool before performing this test. If the HO2S heater is functioning, the signal voltage will gradually increase or decrease as the sensor element warms. If the heater is not functioning, the HO2S signal will remain near the 450mv bias voltage.
-
This step determines if the ignition feed circuit to the HO2S is not open or shorted. The test light should be connected to a known good chassis ground, in case the HO2S low or HO2S heater ground circuit is faulty.
-
This step checks the HO2S heater ground circuit.
-
This step checks for an open or shorted HO2S heater element. The heater element resistance will vary according to HO2S temperature (a hot HO2S heater element will measure a much higher resistance than a HO2S heater element at room temperature). It is important to allow the HO2S to cool before measuring the HO2S heater element resistance.
-
This step checks for an open HO2S signal or low circuit which can cause the HO2S heater to appear not to be operating correctly. It is important to check these circuits before replacing the sensor.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Important: Before clearing the DTCs, use the scan tool in order to record the Freeze Frame and the Failure Records for reference. This data will be lost when the Clear DTC Information function is used. Was the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check performed? | -- | ||
|
Important: If engine has just been operating, allow the engine to cool for about one half hour before proceeding.
Does the H02S voltage displayed gradually decrease by the specified value? | 0.150V (150 mV) | Go to Diagnostic Aids | ||
3 | Inspect the fuse for the HO2S ignition feed. Is the fuse open? | -- | ||
Is the test light ON? | -- | |||
Use a test light in order to connect the HO2S ignition feed and the HO2S heater ground. Is the test light ON? | -- | |||
Is the HO2S heater resistance within the specified values? | 3-10 ohms | |||
7 | Repair the open in the HO2S ignition feed circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Electrical Diagnosis. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
8 | Repair the open in the HO2S heater ground circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Electrical Diagnosis. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
9 |
Was a poor connection found? | -- | ||
Is the H02S resistance above the specified value? | 5 ohms | |||
11 | Replace the HO2S. Refer to Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S) Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
12 |
Is action complete? | -- | -- | |
13 | Repair the open or poor connection in the H02S signal or H02S low circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Electrical Diagnosis. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
14 |
Important: If the engine has just been operating, allow the engine to cool for about one half hour before proceeding.
Does the H02S voltage displayed gradually decrease by the specified value? | 0.150V 150mV | ||
15 | Use the scan tool in order to display the Capture Info and the Review Capture Info function. Are there any DTCs displayed that have not been diagnosed? | -- | Go to the Applicable DTC Table | System OK |
