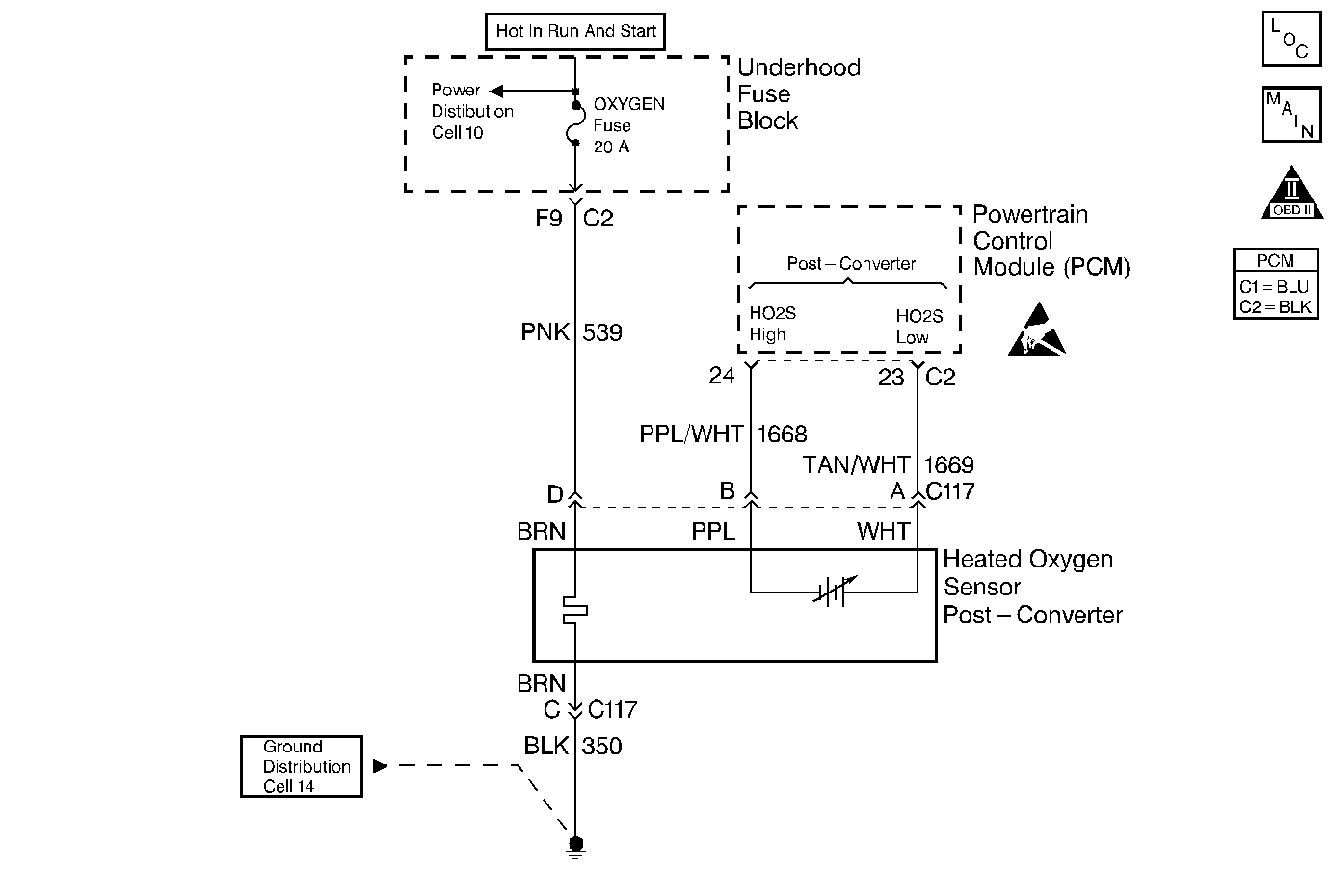
Circuit Description
The PCM has the ability to monitor this process by using a rear Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S 2). The rear HO2S 2, located in the exhaust stream past the catalytic converter, produces an output signal relative to the oxygen storage capacity of the catalytic converter. The PCM then calculates the ability of the catalytic converter to convert the exhaust emissions effectively. Whenever the catalytic converter is functioning properly, the rear HO2S 2 signal will be far less active than the signal produced by the front Oxygen Sensor 1(O2S 1).
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | No actice MAP DTC's |
| • | No active IAT DTC's |
| • | No active ECT DTC's |
| • | No active TP DTC's |
| • | No active Fuel Trim DTC's |
| • | No active Injector Control DTC's |
| • | No active Misfire DTC's |
| • | No active CKP DTC's |
| • | No active Evap DTC's |
| • | No active IAC DTC's |
| • | No active PCM Memory DTC's |
| • | Air flow is more than 5.5 grams per second. |
| • | Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) is more than 40°C (104°F). |
| • | The above conditions are met for 140 seconds. |
| • | Throttle Position (TP) angle is between 5 percent and 50 percent for 4 seconds. |
Conditions For Setting The DTC
HO2S 2 voltage is more than 1042 mV for 50 seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The control module illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) if a failure is detected during 2 consecutive key cycles. |
| • | The control module sets the DTC and records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic failed. The failure information is stored in the scan tool Freeze Frame/Failure Records. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL or DTC
| • | The control module turns OFF the MIL after 3 consecutive drive trips when the test has run and passed. |
| • | A history DTC will clear if no fault conditions have been detected for 40 warm-up cycles. A warm-up cycle occurs when the coolant temperature has risen 22°C (40°F) from the startup coolant temperature and the engine coolant reaches a temperature that is more than 70°C (158°F) during the same ignition cycle. |
| • | Use a scan tool in order to clear the DTCs. |
Diagnostic Aids
Whenever the oxygen sensor pigtail wiring, connector or terminal are damaged, the entire oxygen sensor assembly must be replaced. Do not attempt to repair the wiring, connector or terminals. In order for the sensor to function properly, the O2S must have a clean air reference. This clean air reference is obtained by way of the oxygen sensor wires. Any attempt to repair the wires, connectors or terminals could result in the obstruction of the air reference and degrade the performance of the oxygen sensor.
Check for the following conditions:
| • | A rich exhaust - An overly rich exhaust may load the catalytic converter causing high rear HO2S 2 signal voltages. |
| • | A silicone contamination - A silicone contamination of the rear HO2S 2 may cause a false rich condition. A powdery white deposit on the rear HO2S 2 will indicate this condition. |
| • | A faulty HO2S 2 - Whenever the rear HO2S 2 is internally shorted, the rear HO2S 2 voltage displayed on a scan tool will be over 1.0 volt. Disconnect the rear HO2S 2 . Jumper the rear HO2S low circuit to the engine ground. Whenever the rear HO2S 2 voltage goes from 100 mV to around 450 mV, replace the rear HO2S 2. |
| • | An intermittent test - Observe the rear HO2S 2 on a scan tool while moving the related connectors and wiring harness with the key ON. Whenever the fault is induced, the rear HO2S 2 display will change. This may help isolate the location of the malfunction. |
| • | A damaged harness - Inspect the PCM harness for a short to voltage in the rear HO2S 2 low circuit. |
An intermittent may be caused by any of the following conditions:
| • | A poor connection |
| • | Rubbed through wire insulation |
| • | A broken wire inside the insulation |
Thoroughly check any circuitry that is suspected of causing the intermittent complaint. Refer to Intermittents and Poor Connections Diagnosis in Wiring Systems.
If a repair is necessary, refer to Wiring Repairs or Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems.
Test Description
The number below refers to the step number on the diagnostic table.
-
In order to determine if the engine is rich during De-acceleration Fuel Cut-Off (DFCO) operate the vehicle up to highway speed conditions and release the accelerator pedal allowing the vehicle to coast in gear. Monitor the scan tool HO2S voltage and the DFCO parameter. A rich condition will cause HO2S voltage to be above 468 mV during DFCO.
An HO2S contaminated by silicon will have a white, powdery deposit on the portion of the HO2S that is exposed to the exhaust stream. The usual cause of silica contamination is the use of un-approved silicon RTV engine gasket material or the use of silicon based sprays or fluids within the engine. If the cause of this contamination is not corrected, the replacement HO2S will also get contaminated.
-
Monitor the HO2S voltage of the opposite bank sensor. If the voltage activity of the opposite bank sensor is similar to the voltage activity of the suspect sensor check for rich conditions that would affect both cylinder banks. An opposite bank sensor with normal HO2S voltage activity indicates the suspect HO2S is defective or a rich condition exists only on the suspect HO2S cylinder bank.
-
This step checks the HO2S HIGH signal circuit for a short to voltage.
-
An HO2S contaminated by silicon will have a white, powdery deposit on the portion of the HO2S that is exposed to the exhaust stream. The usual cause of silica contamination is the use of un-approved silicon RTV engine gasket material or the use of silicon based sprays or fluids within the engine. If the cause of this contamination is not corrected, the replacement HO2S will also get contaminated.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||||||||||||||||||
Is the HO2S voltage fixed more than the value specified? | 994 mV | |||||||||||||||||||
3 | This DTC is intermittent. Are any additional DTCs stored? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | Go to Diagnostic Aids | ||||||||||||||||
4 |
Is the HO2S voltage within the value range specified? | 351 - 551 mV | ||||||||||||||||||
The HO2S is detecting a rich exhaust condition or may be contaminated. Check for one of the following conditions:
Repair any of the above or similar engine conditions as necessary. Did you find a problem? | -- | |||||||||||||||||||
Is the voltage more than the specified value? | 20 mV | |||||||||||||||||||
7 | Repair the short to voltage in the HO2S HIGH signal circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||||||||
|
Important: Before replacing a contaminated HO2S determine and repair the cause of the contamination. Replace the HO2S. Refer to Heated Oxygen Sensor Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | ||||||||||||||||||
9 |
Important: The replacement PCM must be programmed. Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement/Programming . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||||||||
10 |
Does the scan tool indicate the diagnostic Passed? | -- | ||||||||||||||||||
11 | Does the scan tool display any additional undiagnosed DTCs? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | System OK |
