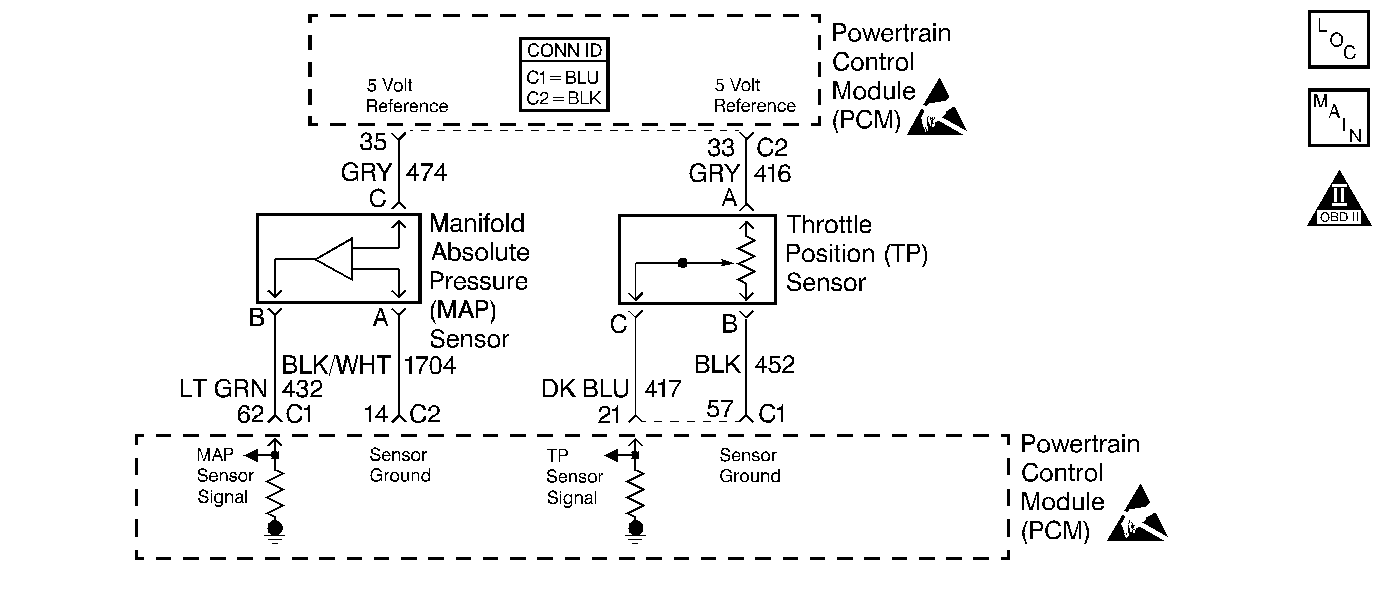
Circuit Description
The powertrain control module (PCM) supplies a 5.0 volt reference signal and a ground to both the throttle position (TP) sensor and the manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor. The TP sensor sends a voltage signal back to the PCM relative to the throttle plate opening and the MAP sensor sends a voltage signal back to the PCM relative to the intake manifold pressure. The PCM can detect if the TP sensor or the manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor is out of range by comparing the two values against the high and low limits against engine speed defined within the engine calibration. If the TP sensor or the MAP sensor are not within the expected limits of the engine calibration, a DTC P0105 is set. During the DTC P0105 test, the actual MAP value is compared to a high limit threshold and low limit threshold for any speed and load that the vehicle is operated in. If the actual MAP value is greater than the high limit, or less than the low limit, a malfunction is indicated.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | No active MAP DTCs |
| • | No active ECT DTCs |
| • | No active TP DTCs |
| • | No active oxygen sensor DTCs |
| • | No active fuel trim DTCs |
| • | No active injector control DTCs |
| • | No active misfire DTCs |
| • | No active knock sensor DTCs |
| • | No active CMP DTCs |
| • | No active EVAP DTCs |
| • | No active VSS DTCs |
| • | No active IAC DTCs |
| • | No active PCM memory DTCs |
| • | The engine run time is more than 40 seconds. |
| • | Engine speed is between 900 RPM and 6,375 RPM. |
| • | Torque converter clutch (TCC) is stable to within 2.5 percent. |
| • | The change in engine speed is less than 50 RPM. |
| • | The change in the IAC valve is less than 5 counts. |
| • | The above conditions are present for 1.5 seconds. |
| • | The change in the TP sensor is less than 2 percent. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The MAP sensor is out of an expected range defined on the engine calibration for 10 seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The control module illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) if a failure is detected during 2 consecutive key cycles. |
| • | The control module sets the DTC and records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic failed. The failure information is stored in the scan tools Freeze Frame and Failure Records. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The control module turns OFF the MIL after 3 consecutive drive trips when the test has Run and Passed |
| • | A history DTC will clear if no fault conditions have been detected for 40 warm-up cycles. A warm up cycle occurs when the coolant temperature has risen 22°C (40°F) from the startup coolant temperature and the engine coolant reaches a temperature that is more than 70°C (158°F) during the same ignition cycle. |
| • | Use a scan tool to clear the DTCs. |
Diagnostic Aids
| • | With the ignition ON, and the engine OFF, the manifold pressure is equal to atmospheric pressure and the signal voltage will be high. This information is used by the PCM as an indication of the vehicle barometric pressure. Comparison of this reading with a known good vehicle with the same sensor is a good way to verify the accuracy of a suspect sensor. Readings should be the same +/-0.4 volts. |
| • | The MAP sensor vacuum source should be thoroughly inspected for restrictions at the intake manifold. |
| • | If a DTC P0105 cannot be duplicated, the information included in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records data can be useful. Use the scan tool DTC information data in order to determine the status of the DTC. |
| • | A DTC P0105 may set due to any condition that may cause an unreasonably high or low map value including the following engine conditions: |
| • | Incorrect cam timing |
| • | Restricted exhaust |
| • | Worn piston rings |
| • | Using a DMM in order to test 5.0 volt reference circuits may not detect small amounts of resistance within the malfunctioning circuit. Connecting a jumper wire from the 5.0 volt reference circuit to the signal circuit can detects the small amounts of resistance. |
| • | The MAP sensor needs a dedicated vacuum source. Inspect the MAP sensor and the MAP sensor vacuum source for the following conditions: |
| - | Vacuum leaks |
| - | Split vacuum hose |
| - | Shared vacuum source |
An intermittent may be caused by any of the following conditions:
| • | A poor connection |
| • | Rubbed through wire insulation |
| • | A broken wire inside the insulation |
Thoroughly test any circuitry that is suspected of causing the intermittent complaint. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections in Wiring Systems.
If a repair is necessary, refer to Wiring Repairs or Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table:
-
A DTC P0507 may also set if a vacuum leak is present. Refer to DTC P0507 Idle Speed High.
-
A normal MAP sensor will react as quickly to the throttle changes as they can be made. A MAP sensor should not appear to be lazy or catch up with the throttle movements.
-
The MAP sensor vacuum source should be thoroughly inspected for restrictions. A drill bit can be used to clean out any casting flash that may exist in the vacuum port.
-
The replacement PCM must be programmed and the Crankshaft Position System Variation Learn procedure must be preformed.
Step | Action | Values | Yes | No | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||||||||
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | |||||||||
3 |
Does the MAP sensor voltage change when the engine speed increased? | 2000 RPM | ||||||||
4 |
Does the TP sensor voltage change from below the first specified value to above the second specified value? | 1.0 V to 4.0 V | ||||||||
Does the MAP sensor perform correctly through the ranges? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | ||||||||
6 |
Does the MAP sensor voltage read near the specified value? | 0.0 V | ||||||||
7 |
Does the MAP sensor voltage change? | 15 in Hg | ||||||||
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | |||||||||
9 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||
10 | Replace MAP sensor. Refer to Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | -- | |||||||
11 |
Does the TP sensor voltage read the specified value? | 0.0 V | ||||||||
12 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||
13 | Replace TP sensor. Refer to Throttle Position Sensor Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | ||||||||
14 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||
|
Important:: The replacement PCM must be programmed. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement/Programming . Replace the PCM. Did you complete the replacement? | -- | -- | ||||||||
16 |
Does the DTC reset? | -- | System OK |
