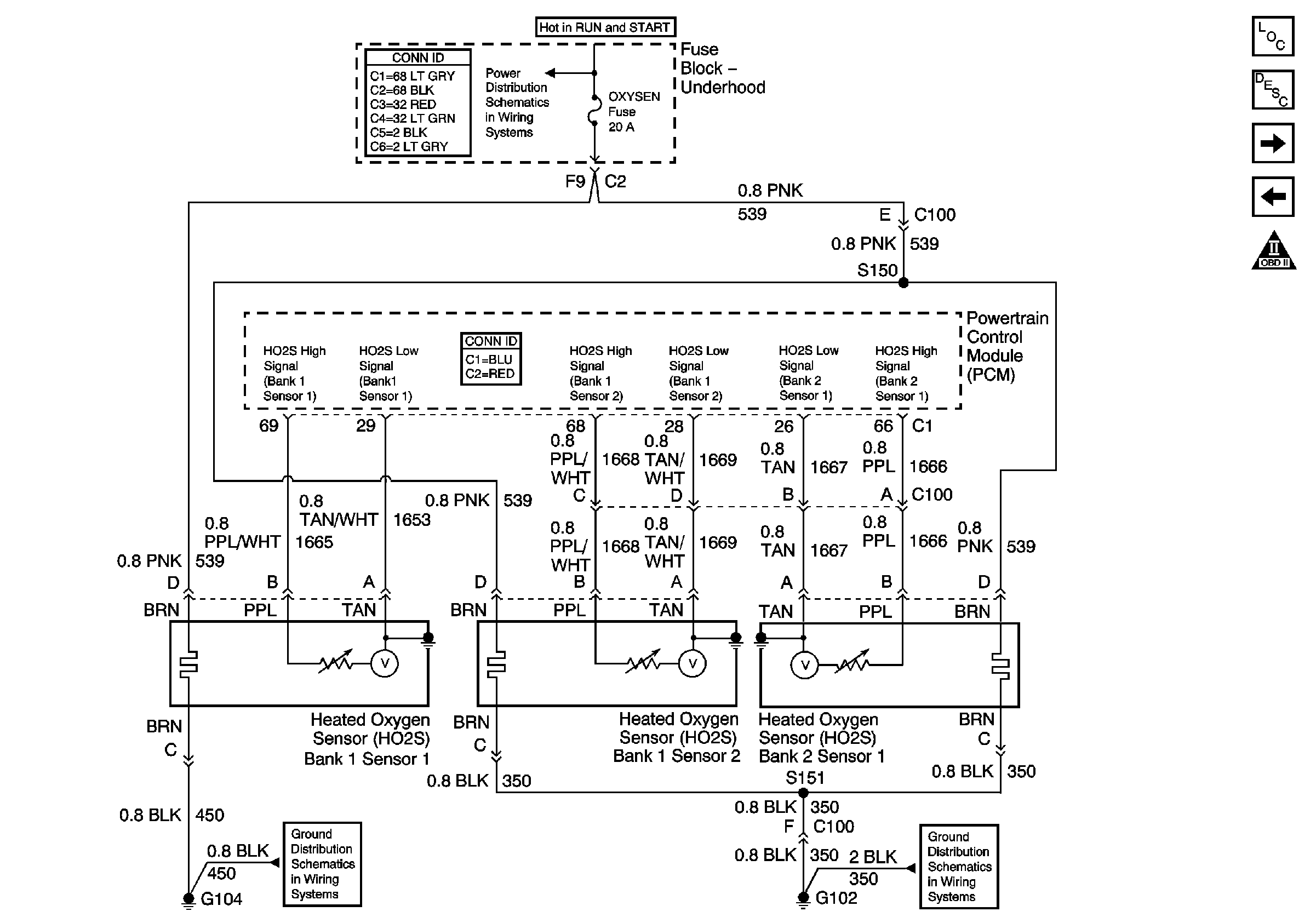
Circuit Description
The heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) is a sensor designed to create a voltage relative to the oxygen content in the engine exhaust stream. The control module supplies the HO2S with signal high and low circuits. Ignition voltage and ground are supplied to the HO2S heater by independent circuits. The oxygen content of the exhaust indicates when the engine is operating lean or rich. When the HO2S detects that the engine is operating rich, the signal voltage is high, and decreases the signal voltage as the engine runs leaner. This oscillation above and below the bias voltage, sometimes referred to as activity or switching, can be monitored with the HO2S signal voltage.
The HO2S contains a heater that is necessary in order to quickly warm the sensor to operating temperature. The heater also maintains the operating temperature during extended idle conditions. The HO2S needs to be at a high temperature in order to produce a voltage. When the HO2S reaches operating temperature, the control module monitors the HO2S bias, or reference, voltage. The control module also monitors the HO2S signal voltage for Closed Loop fuel control. During normal Closed Lop fuel control operation, the control module will add fuel, or enrich the mixture, when the HO2S detects a lean exhaust content. The control module will subtract fuel, or "lean out" the mixture when the HO2S detects a rich exhaust condition.
This diagnostic trouble code (DTC) monitors the HO2S voltage and detects if the voltage goes out of the bias range (400-475 mV). If the (PCM) does not detect the voltage went out of the bias range, a DTC sets
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | DTCs P0101, P0102, P0103, P0106, P0107, P0108, P0112, P0113, P0117, P0118, P0121, P0122, P0123, P0300, P0351, P0401, P0404, P0405, P0440, P0442, P0446, P0452, P0453, P1258, P1404, or P1441 are not set. |
| • | The engine run time is more than 409 seconds. |
| • | The loop status is closed. |
| • | The ignition 1 signal is between 9-18 volts. |
| • | Intrusive tests are not in progress |
| • | The scan tool output controls are not active. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | The HO2S signal voltage is between 400-475 mV for 150 seconds. |
| • | The throttle position (TP) changes more than 5 percent within 1 second, 6 times. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The control module illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) on the second consecutive ignition cycle that the diagnostic runs and fails. |
| • | The control module records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The first time the diagnostic fails, the control module stores this information in the Failure Records. If the diagnostic reports a failure on the second consecutive ignition cycle, the control module records the operating conditions at the time of the failure. The control module writes the operating conditions to the Freeze Frame and updates the Failure Records. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The control module turns OFF the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) after 3 consecutive ignition cycles that the diagnostic runs and does not fail. |
| • | A current DTC, Last Test Failed, clears when the diagnostic runs and passes. |
| • | A history DTC clears after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles, if no failures are reported by this or any other emission related diagnostic. |
| • | Clear the MIL and the DTC with a scan tool. |
Diagnostic Aids
Important: Before you service the PCM, remove any debris from the PCM connector surfaces. Inspect the PCM connector gaskets when diagnosing or replacing the PCM. Ensure that the gaskets are installed correctly. The gaskets prevent water intrusion into the PCM.
| • | An oxygen supply inside the HO2S is necessary for proper operation. The HO2S wires provides the supply of oxygen. Inspect the HO2S wires and connections for breaks or contamination. Refer to Heated Oxygen Sensor Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. |
| • | For an intermittent condition, refer to Intermittent Conditions . |
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
After the ignition is turned ON, the HO2S heater heats up causing the HO2S signal voltage to either increase or decrease. This indicates that the HO2S heater is OK.
-
If the HO2S voltage is varying outside the specified range, the condition is not present.
-
If the voltage is below the specified value, the high signal circuit, the low signal circuit, and the PCM are OK.
-
If the voltage is above the specified value, the low signal circuit is OK.
-
All oxygen sensors must be disconnected to isolate a short to ground in the HO2S heater ignition 1 voltage circuit.
-
Resistance within the specified range indicates the HO2S heater is OK.
Step | Action | Values | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Schematic Reference:
| ||||
1 | Did you perform the Diagnostic System Check-Engine Controls? | -- | Go to Step 2 | |
|
Important: Allow the engine to cool for one-half hour before proceeding with this diagnostic. This allows the HO2S signal voltage to return to bias voltage, approximately 447 mV.
Does the HO2S voltage go from bias voltage to more than or less than the specified range? | 350-550 mV | Go to Step 3 | Go to Step 5 | |
Is the HO2S voltage varying outside the specified range? | 400-475 mV | Go to Step 4 | Go to Step 5 | |
4 |
Does the DTC fail this ignition? | -- | Go to Step 5 | Go to Intermittent Conditions |
Is the HO2S voltage less than the specified value? | 200 mV | Go to Step 9 | Go to Step 6 | |
Is the voltage above the specified value? | 4.5 V | Go to Step 7 | Go to Step 8 | |
7 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 21 | Go to Step 16 |
8 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 21 | Go to Step 16 |
9 | Remove the jumpers from the previous step. Is the OXYSEN fuse open? | -- | Go to Step 12 | Go to Step 10 |
10 |
Does the test lamp illuminate? | -- | Go to Step 11 | Go to Step 17 |
11 |
Does the test lamp illuminate? | -- | Go to Step 15 | Go to Step 18 |
Did you find and correct a short to ground in the ignition 1 voltage circuit? | -- | Go to Step 21 | Go to Step 13 | |
13 |
Important: Perform the following test on all oxygen sensors. A condition in any sensor will cause this DTC to set. Test the HO2S ignition 1 voltage circuit, sensor side, for a short to the HO2S body. Refer to Circuit Testing in Wiring Systems. Did you find the condition? | -- | Go to Step 19 | Go to Step 14 |
|
Important: Perform the following test on all oxygen sensors. A condition in any sensor will cause this DTC to set. Measure the resistance between the HO2S ignition 1 voltage circuit, sensor side, and the HO2S heater ground circuit, sensor side. Refer to Circuit Testing in Wiring Systems. Does the resistance of any sensor measure above or below the specified range? | 2-50 ohms | Go to Step 19 | Go to Intermittent Conditions | |
15 | Inspect for poor connections at the harness connector of the affected HO2S. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections and Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 19 | |
16 | Inspect for poor connections at the harness connector of the PCM. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections and Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 21 | Go to Step 20 |
17 | Repair the open in the ignition 1 voltage circuit. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you complete the repair? | -- | Go to Step 21 | -- |
18 | Repair the open in the HO2S heater ground circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you complete the repair? | -- | Go to Step 21 | -- |
19 | Replace the affected HO2S. Refer to Heated Oxygen Sensor Replacement - Bank 1 Sensor 1 , Heated Oxygen Sensor Replacement - Bank 2 Sensor 1 , or Heated Oxygen Sensor Replacement - Bank 1 Sensor 2 . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | Go to Step 21 | -- |
20 | Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | Go to Step 21 | -- |
21 |
Does the DTC run and pass? | -- | Go to Step 22 | Go to Step 2 |
22 | With a scan tool, observe the stored information, Capture Info. Does the scan tool display any DTCs that you have not diagnosed? | -- | System OK | |