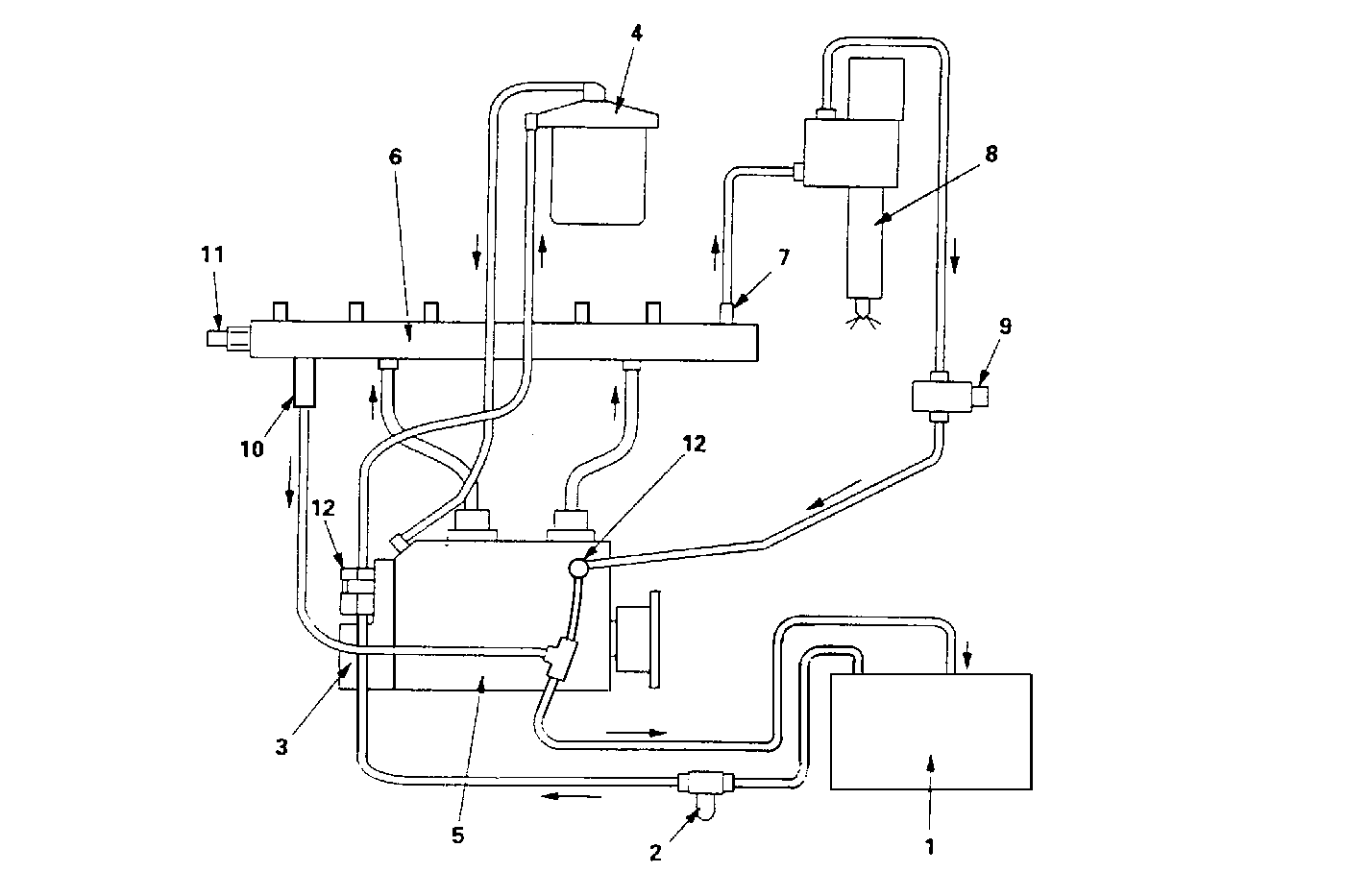
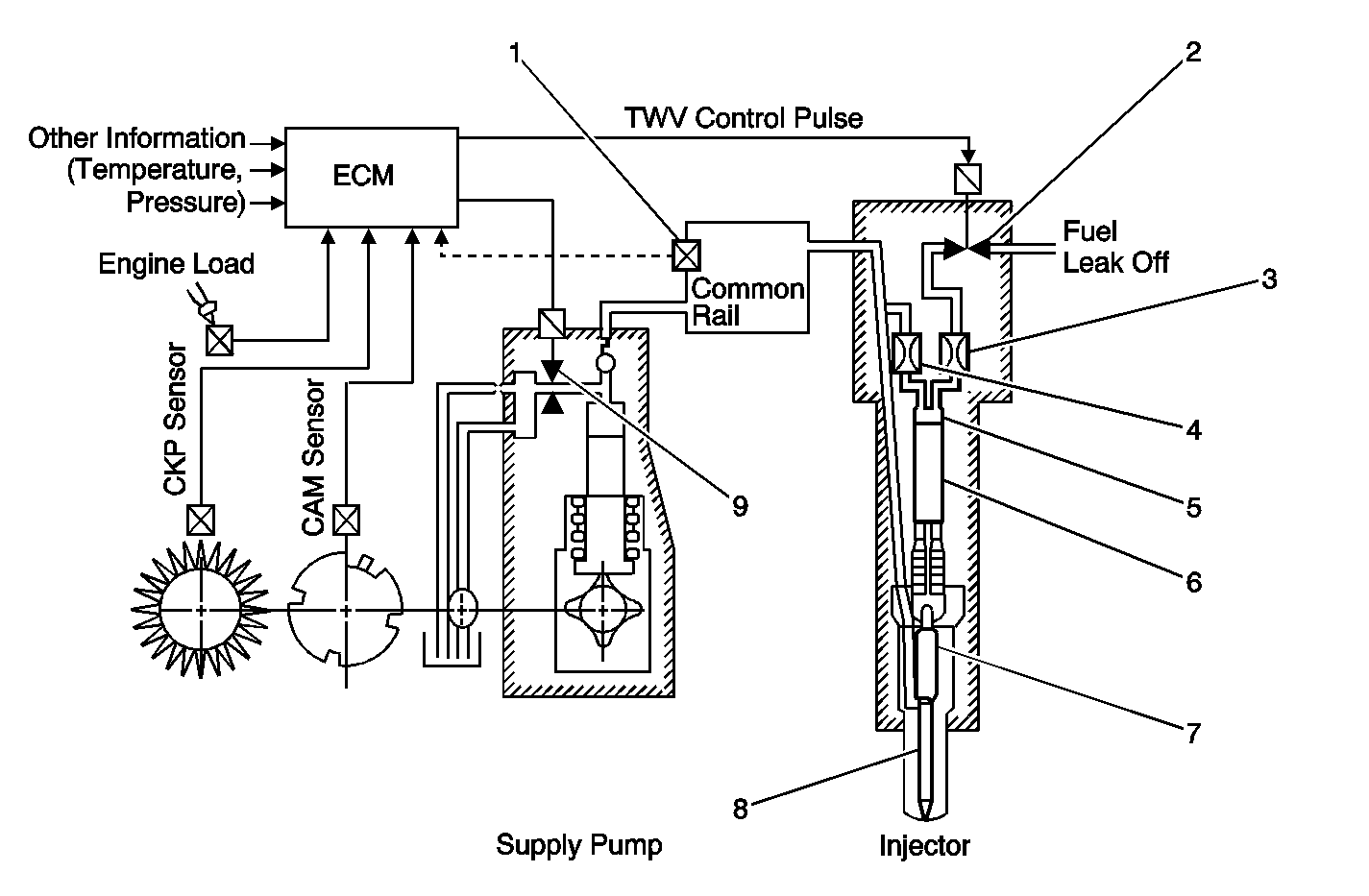
Fuel is drawn from the fuel tank (1) through the fuel pre-filter (2)
by the fuel feed pump (3). The fuel feed pump, sends the fuel into the fuel
filter (4) and then into the fuel supply pump (5). The fuel supply pump
then pressurizes and supplies the fuel to the fuel common rail (6).
The pressurized fuel is distributed through the fuel injector lines
(7) to the fuel injectors (8). The high pressure fuel enters the fuel injector
and forces the needle off the seat. At the same time, the fuel enters the
control chambers of the fuel injectors. The fuel injection timing is controlled
by the ECM. The ECM is commanded to open the fuel return line of the solenoid
valve (TWV) on top of the injector, then the fuel is forced out of the
fuel injector into the cylinder.
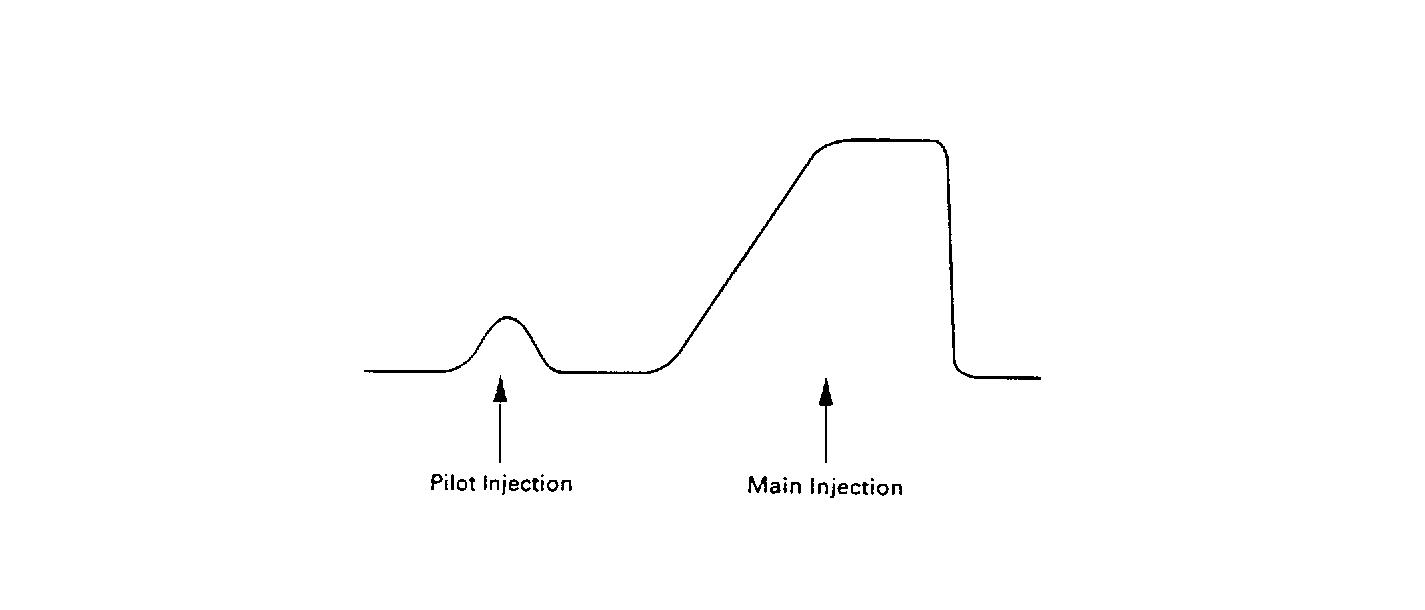
The Main Injection is the same as the conventional system.
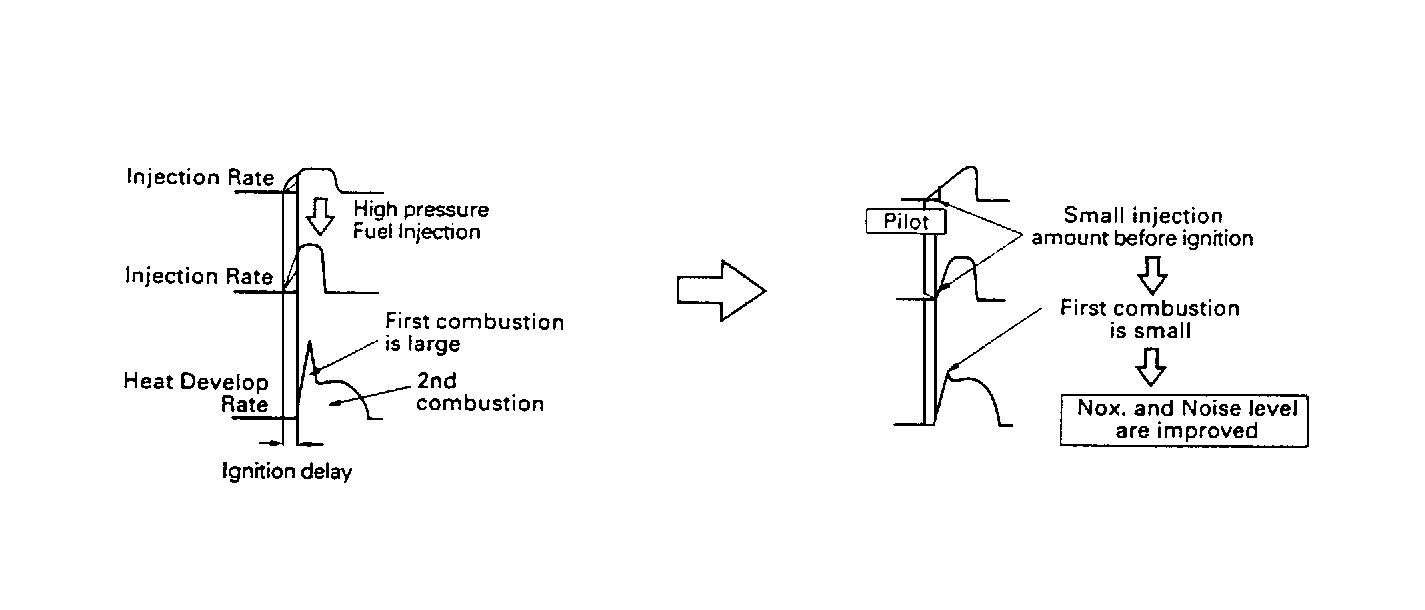
There is a small amount of fuel injected prior to the conventional
fuel injection, main injection, which is know as the Pilot Injection. The
injection rate is increased as there is a rising tide of high pressure
injection. However, there is a time lag from fuel injection to a combustion
start, ignition delay, which cannot be shortened over a certain value.
As a result, the fuel injected could be increased until ignition which
will cause an instantaneous explosive combustion. This combustion increases
NOx and noise. Pilot injection cuts down the initial injection rate to
a minimum to lessen the explosive combustion so that NOx and noise can
be reduced.
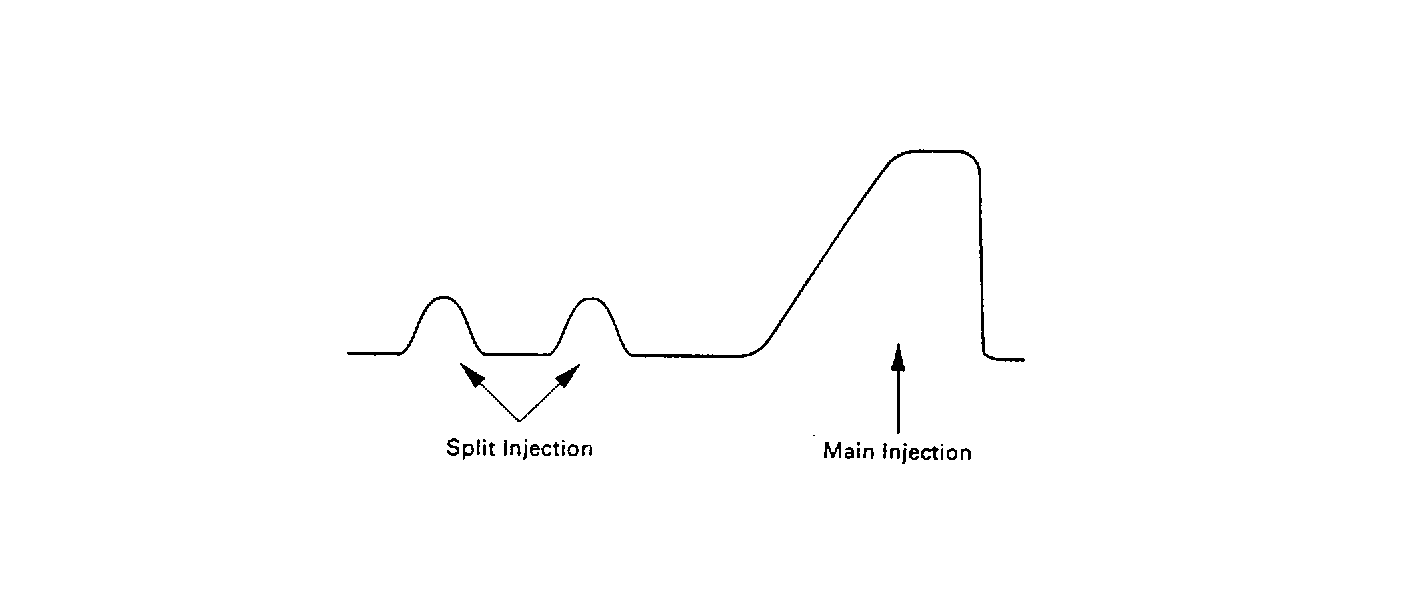
Split injection occurs when 2 or more small amounts of fuel are injected
prior to the conventional fuel injection, main injection, for easy engine
starts during cold weather.