Special Tools
| • | J 8089 Carbon Removal Brush
|
| • | J 9666 Valve Spring Tester
|
| • | J 8001 Dial Indicator Set
|
Cleaning Procedure
Warning: Refer to Safety Glasses Warning in the Preface section.
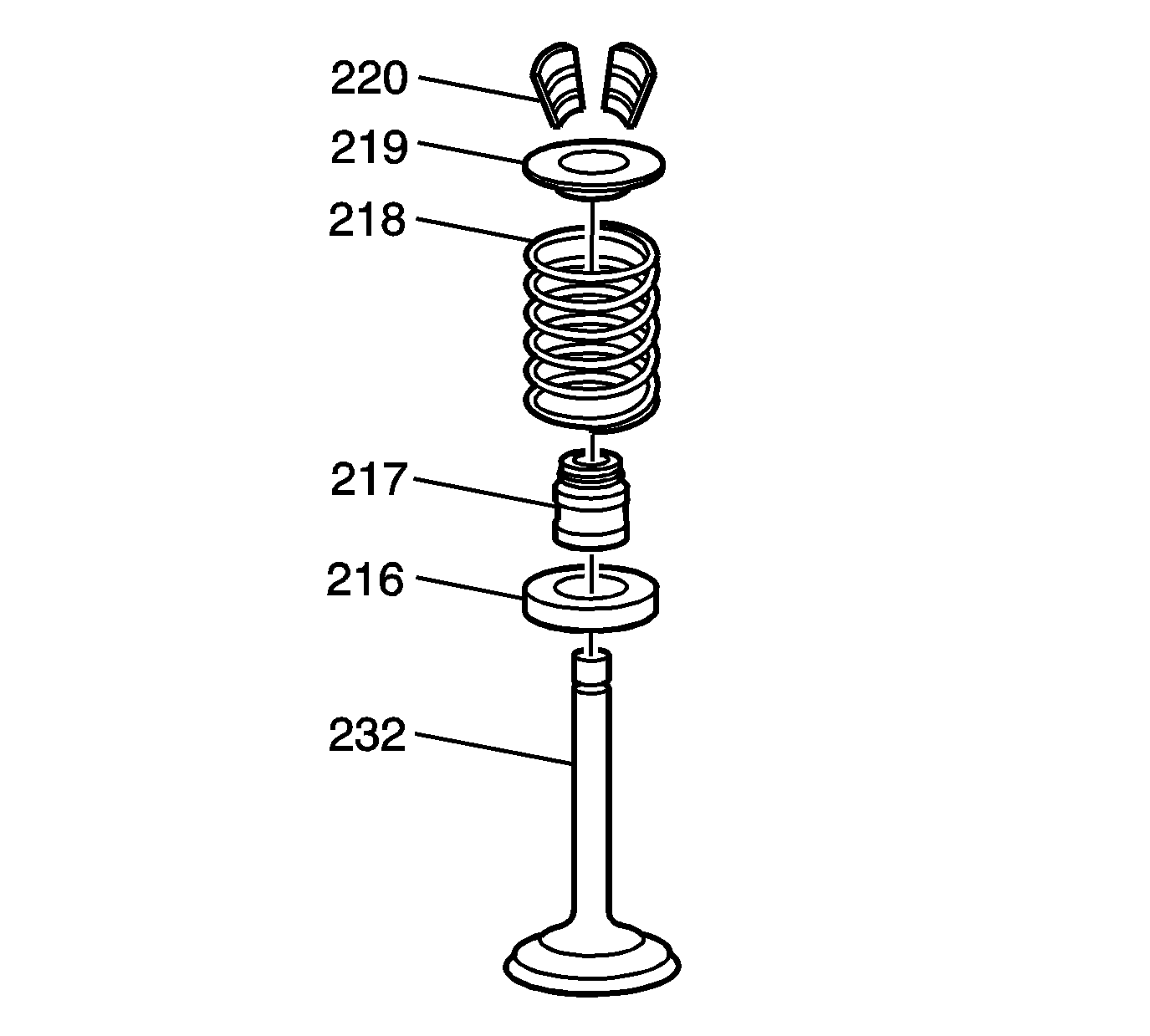
Note: Mark, sort, or organize components for return to their original locations.
- Clean the valve stems and heads on a buffing wheel.
- Clean the following components in solvent:
Warning: Refer to Safety Glasses Warning in the Preface section.
- Dry the components with compressed air.
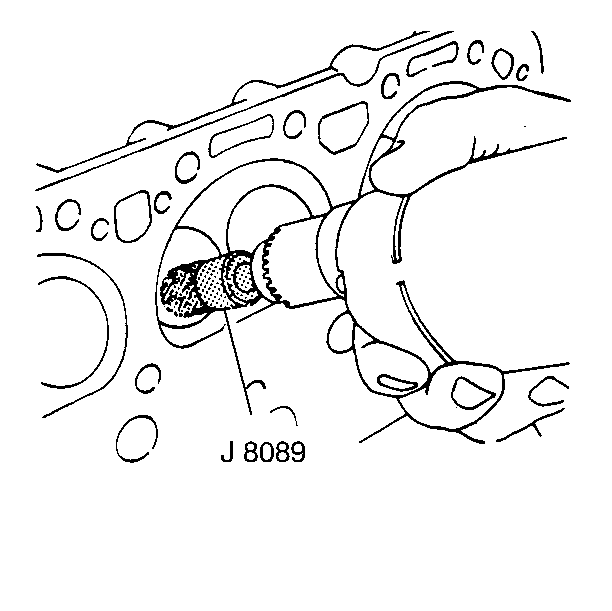
Note: Do not damage the chamber or the valve seat.
- Use the
J 8089 brush
in order to clean the carbon from the combustion chambers.
Visual Inspection Procedure
Inspect the cylinder head for the following conditions:
| • | Damaged gasket surfaces |
| • | Damage to threaded bolt holes |
| • | Burnt or eroded areas in the combustion chamber |
| • | Cracks in the exhaust ports and combustion chambers |
| • | External cracks in the water chamber |
| • | Restrictions in the intake or exhaust passages |
| • | Restrictions in the cooling system passages |
Flatness Measurement Procedure
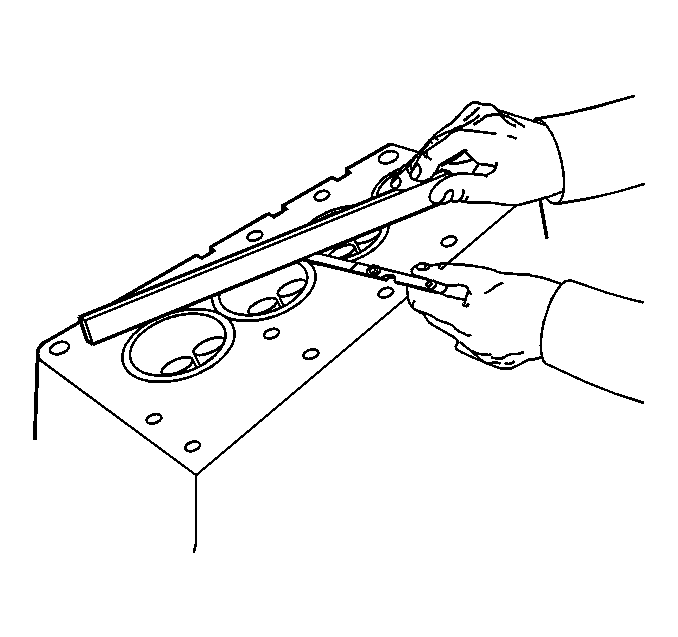
- Measure the cylinder head for warpage with a straight edge and feeler gage.
| • | A cylinder head block deck with warpage in excess of 0.050 mm (0.002 in) within a 150.0 mm (6.0 in) area must be repaired or replaced. |
| • | A cylinder head exhaust manifold deck with an overall warpage in excess of 0.102 mm (0.004 in) must be repaired or replaced. |
| • | A cylinder head intake manifold deck with warpage in excess of 0.080 mm (0.003 in) must be repaired or replaced. |
- A cylinder head block deck can be resurfaced up to 0.305 mm (0.012 in) maximum removal.
Note: Excessive cylinder head resurfacing will affect compression ratio and emission control.
- A cylinder head that requires excessive resurfacing must be replaced.
Valve Inspection Procedure
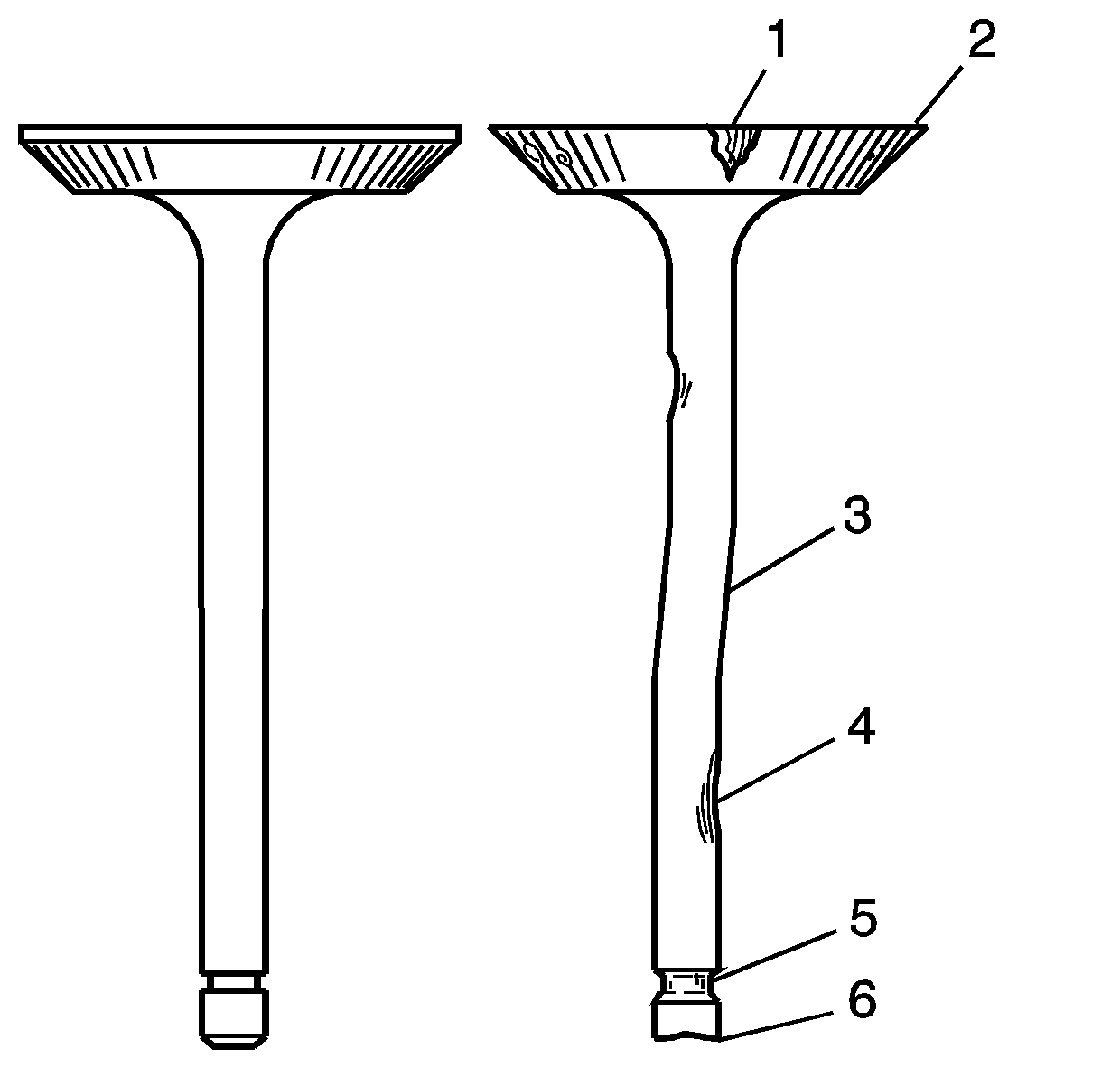
- Inspect the valves for the following conditions:
| • | Burnt or damaged areas (1) |
| • | Undersized valve margin (2) |
| • | Scoring or other damage to the stem (4) |
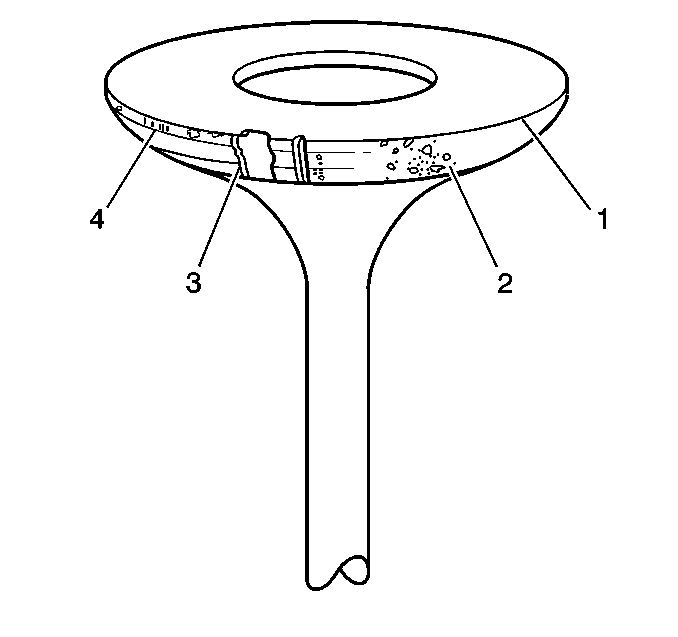
- Inspect the valve contact surface for the following conditions:
| • | Burnt or eroded areas (3) |
| • | Acceptable edge, margin (4) |
Note: Minor imperfections of the valve may be corrected during reconditioning.
- Valves with excessive damage must be replaced.
Valve Spring Inspection and Measurement
- Inspect the valve springs for broken coils or coil ends.
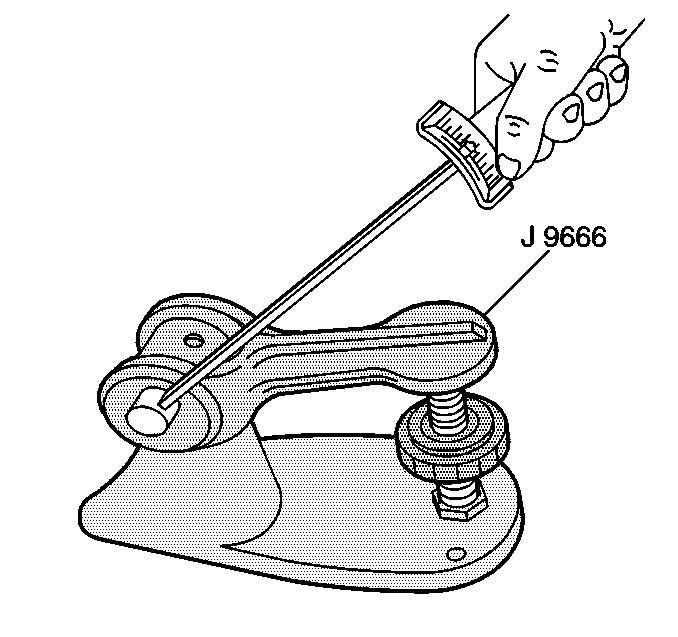
- Use the
J 9666 tester
in order to measure the valve spring force.
Refer to
Engine Mechanical Specifications.
Note: Add a maximum of 1 shim, up to 0.726 mm (0.030 in) thick, to increase tension.
- If the valve spring tension is low, use a shim to increase tension.
- Inspect the valve spring tension again. A valve spring that does not meet specification must be replaced.
Valve Guide Measurement Procedure
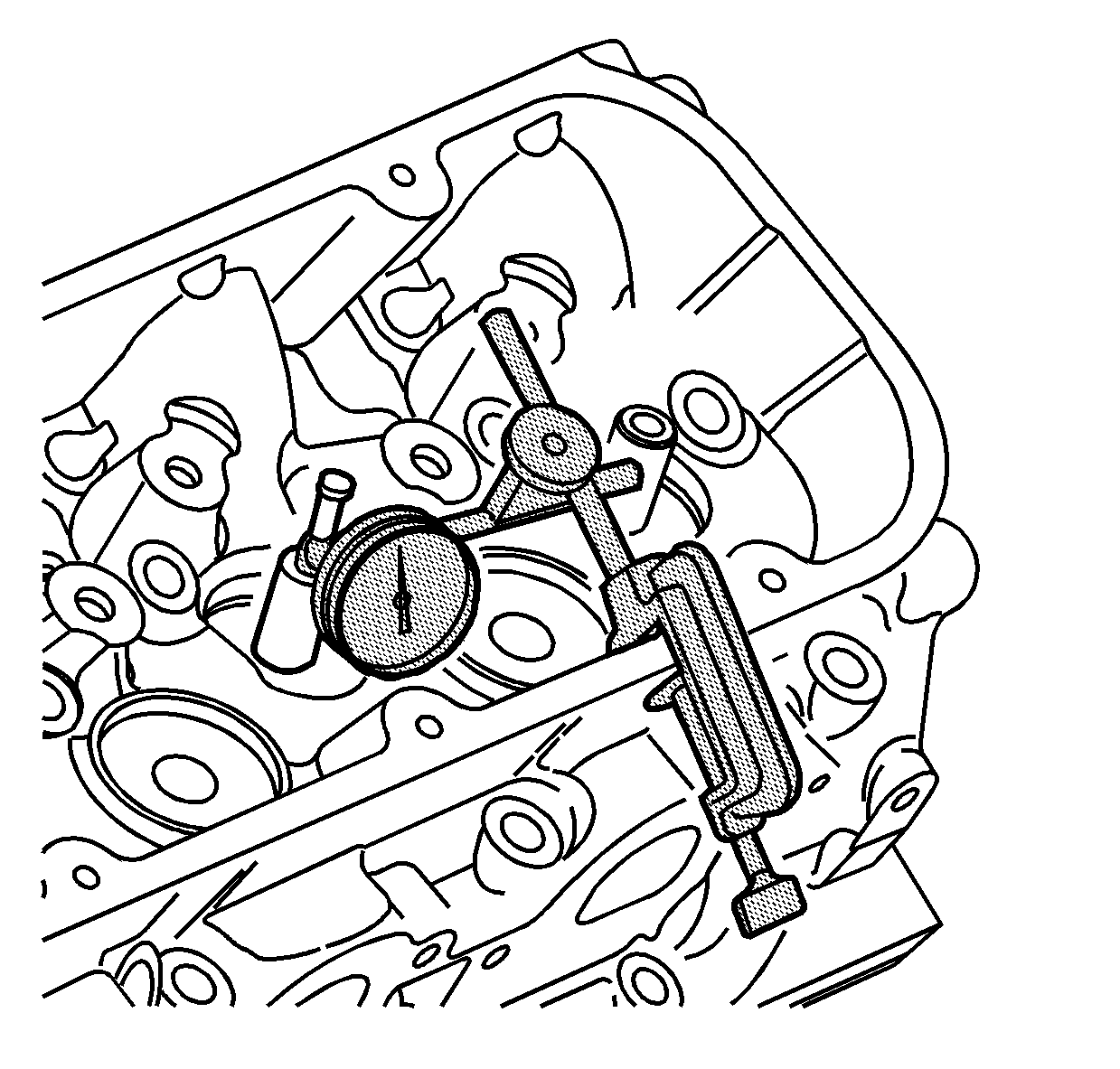
Note: Excessive valve stem-to-guide clearance may cause an excessive oil consumption and may also cause a valve to break. Insufficient clearance results in noisy and sticky functioning of the valve and disturbs the engine assembly smoothness.
- Measure the valve stem-to-guide clearance.
| 1.1. | Clamp the
J 8001 set
on the exhaust port side of the cylinder head. |
| | Note: The indicator stem must contact the side of the valve stem just above the valve guide.
|
| 1.2. | Locate the indicator so that the movement of the valve stem from side to side, crosswise to the cylinder head, causes a direct movement of the indicator stem. |
| 1.3. | Drop the valve head approximately 1.6 mm (0.064 in) off the valve seat. |
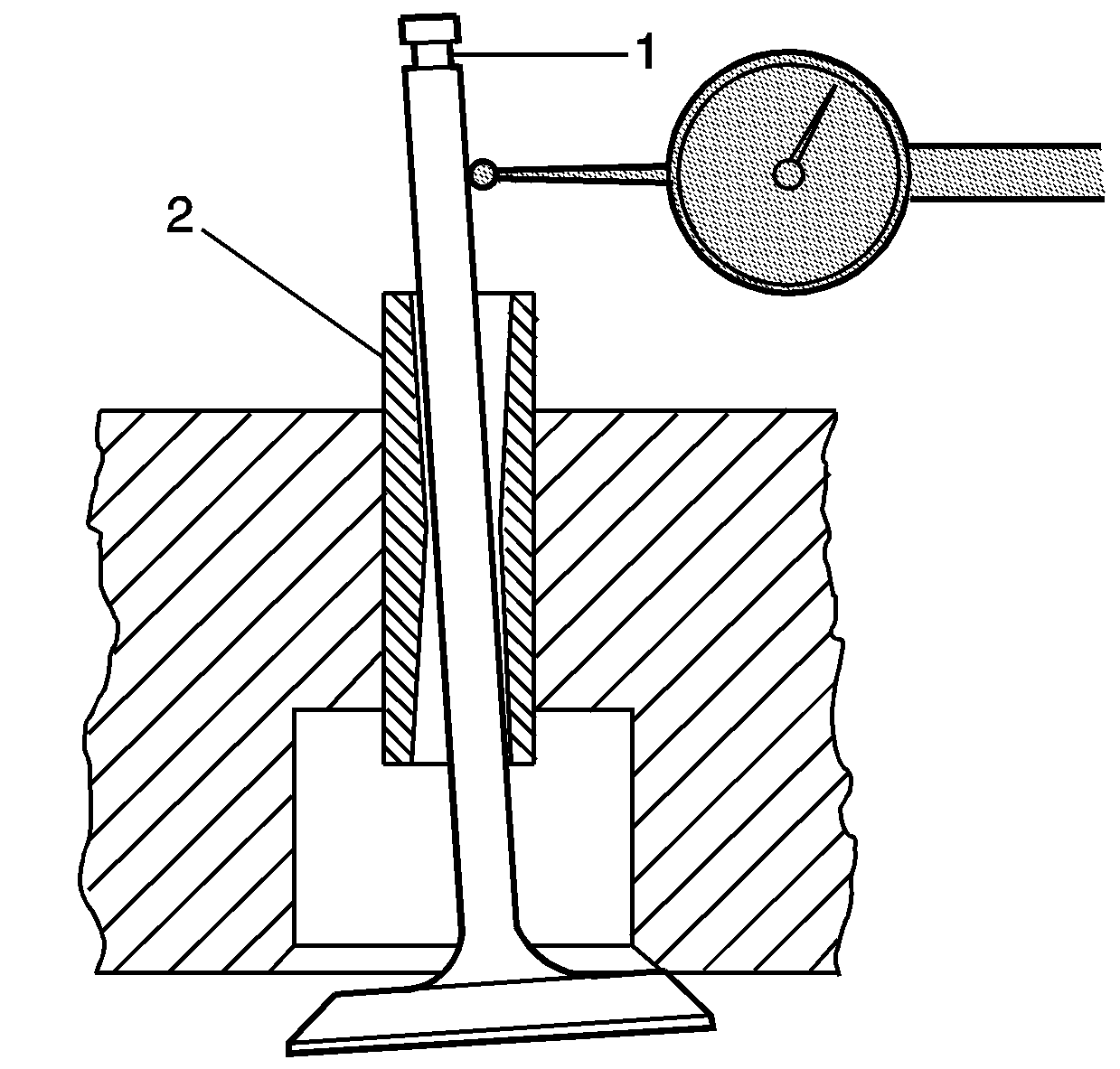
- Valve guide (2) with excessive clearance must be repaired. Refer to
Valve Guide Reaming, and Valve and Seat Grinding.
- Replace the cylinder head if the valve guide cannot be repaired or reamed to accept an oversize valve stem.








