For 1990-2009 cars only
Completely inspect the turbocharger and all other engine components that may cause similar conditions before replacing the turbocharger.
Use the following information to diagnose problems caused by the turbocharger.
The turbocharger is serviced as a complete unit.
- Remove the turbocharger oil return pipe bolts.
- Remove the turbocharger oil return pipe and gasket.
- Clean mating surfaces.
- Inspect for damage to the compressor wheel, compared to a normal compressor wheel.
- Inspect for damage to the compressor wheel, by a soft object.
- Inspect for damage to the compressor wheel, by a hard object.
- Inspect compressor blades for heavy rubbing.
- Check the housing for signs of rubbing.
- Install the turbocharger oil return pipe and new gasket.
- Install the turbocharger oil return pipe bolts and tighten to 21 N·m (15 lb ft).
- Inspect the coolant outlet lines for damage.
- Clean the turbocharger inlet duct.
- Clean the turbocharger inlet duct mating surfaces.
- Inspect the turbocharger inlet duct for cracks.
- Inspect the turbocharger inlet duct mating surfaces for damage.
- Replace the turbocharger inlet duct if any damage is found and tighten the inlet duct clamp to 5 N·m (44 lb in).
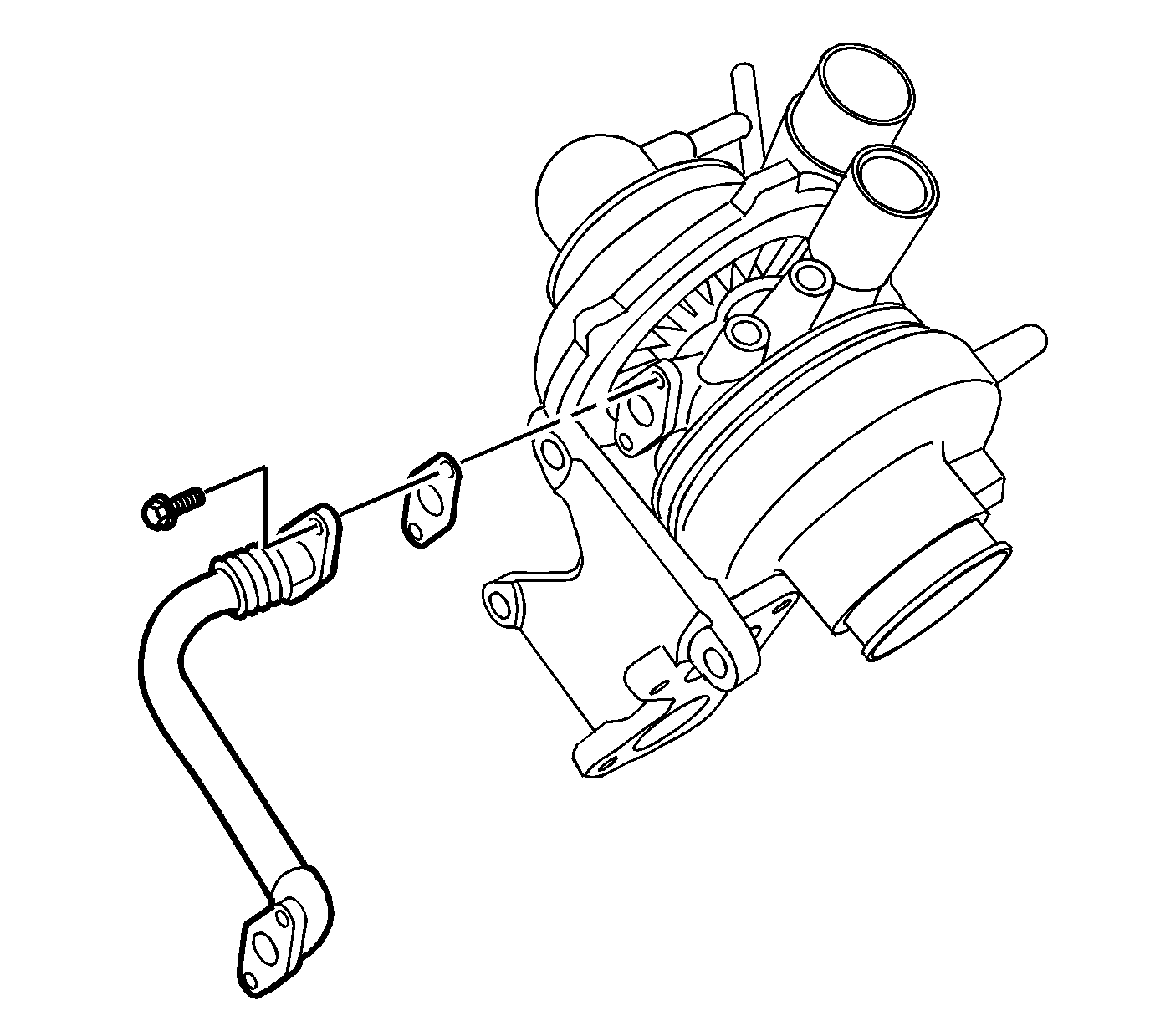
Note: Oil residue on the turbocharger compressor wheel is normal with a closed PCV system.
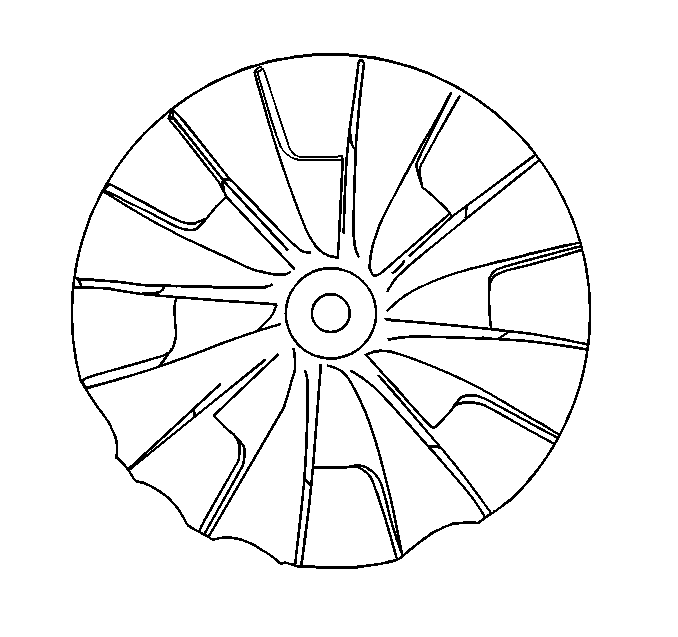
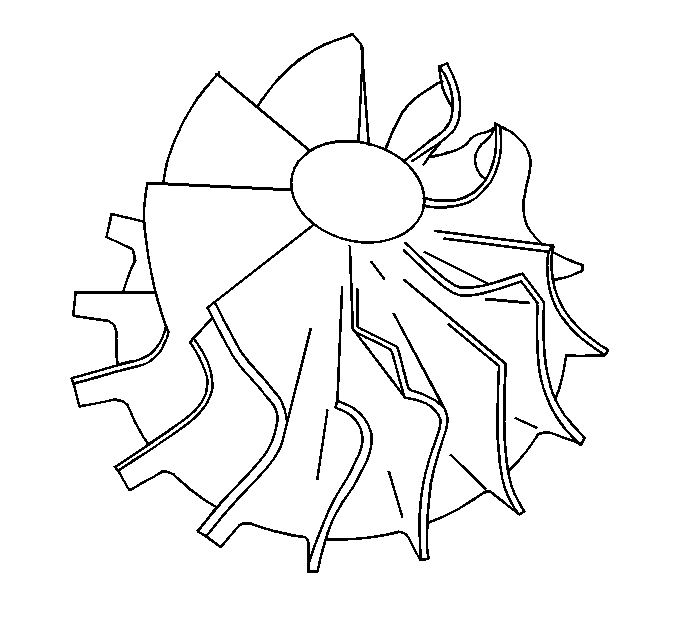
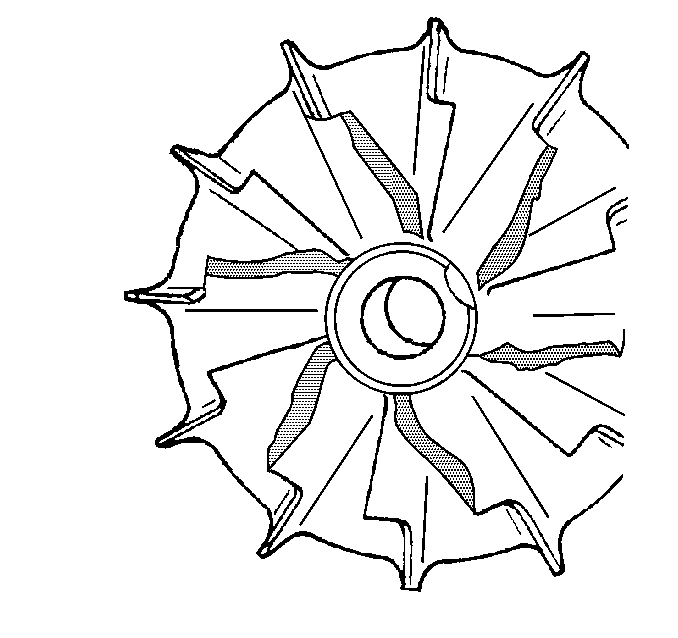
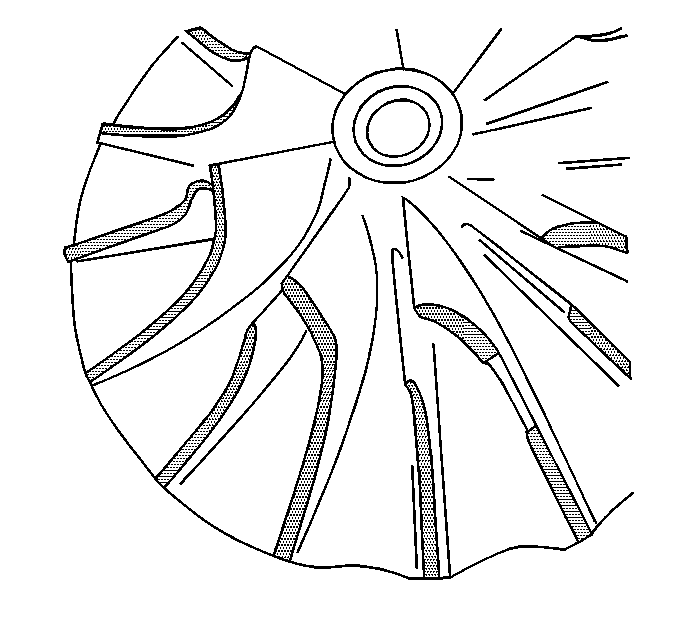
Ensure that the following conditions do not exist on the compressor wheel blades:
| • | Cracks |
| • | Bends |
| • | Erosion of the blades |
| • | Broken blades |

Caution: Refer to Fastener Caution in the Preface section.
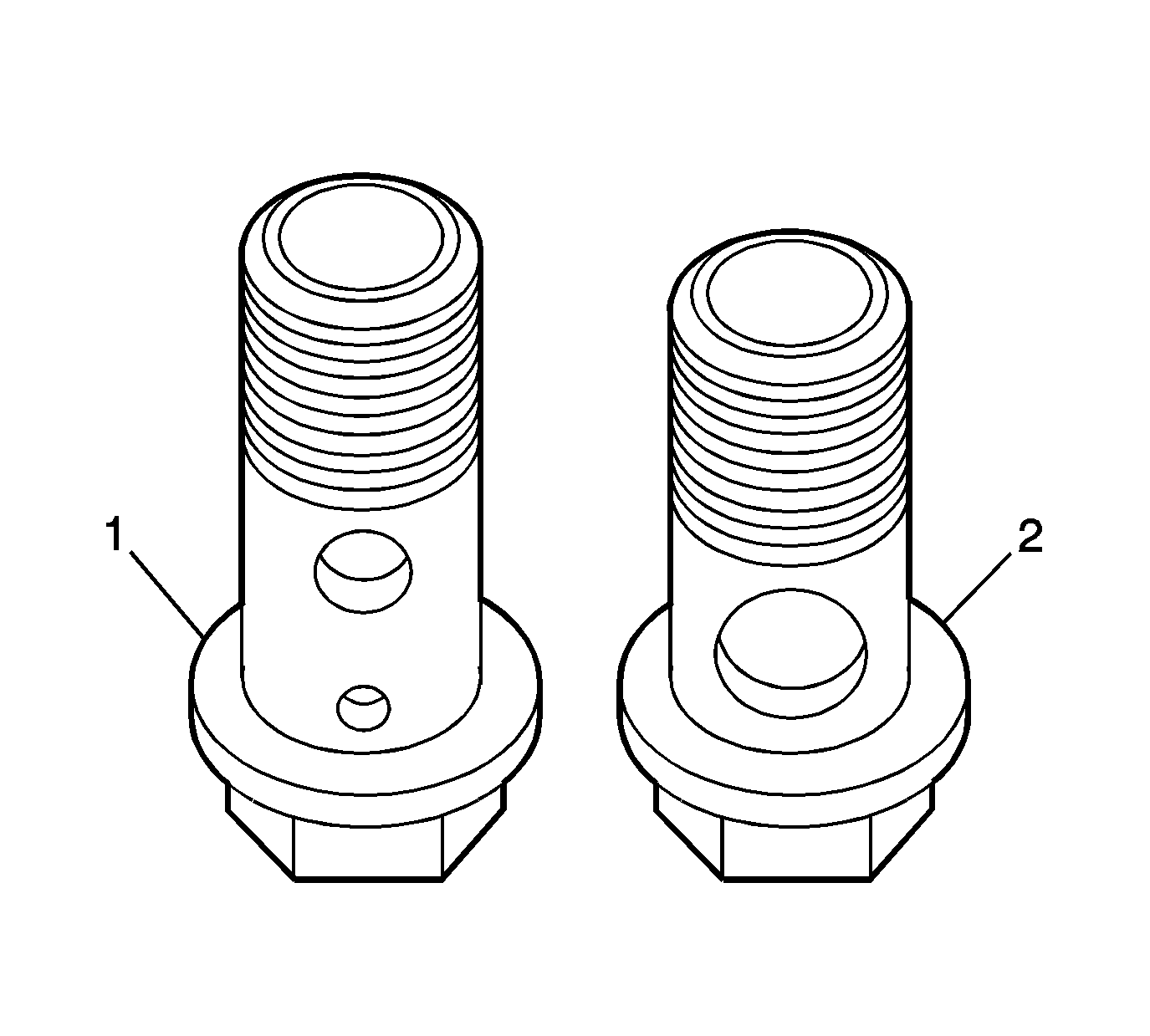
Note: If the cooling outlet hose eye bolts were removed, install the longer bolt (1) with two holes, in the top location. Install the shorter bolt (2) in the lower location.