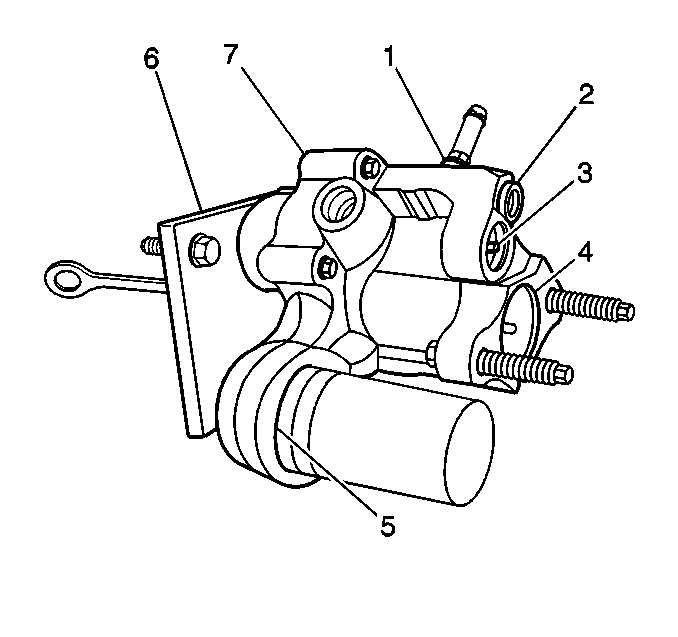
Input Rod Seal
A fluid leak from the inside of the driver's compartment at the power brake booster vent hole indicates a damaged input rod seal (6). Replace the hydraulic brake booster. Refer to Power Brake Booster Replacement .
Power Piston Seal
Fluid leaking between the brake master cylinder and the power brake booster indicates damage of the power piston seal (4). This can possibly reduce the power assist. Replace the hydraulic brake booster. Refer to Power Brake Booster Replacement .
Housing Seal
A fluid leak between the two housings indicates a damaged housing seal (7). Replace the hydraulic brake booster. Refer to Power Brake Booster Replacement .
Relief Valve
Damage to the relief valve seal (2) causes fluid to leak past the relief valve. Replace the hydraulic brake booster. Refer to Power Brake Booster Replacement .
Spool Valve Plug Seal
Damage to the spool valve plug seal (3) causes fluid to leak past the spool valve. Replace the hydraulic brake booster. Refer to Power Brake Booster Replacement .
Accumulator Seal
Damage to the accumulator seal (5) causes fluid to leak past the accumulator cap. Replace the accumulator seal (5) with the power brake booster on the vehicle. Refer to Hydraulic Brake Booster Accumulator Replacement .
Return Port Fitting
Notice: Use the correct fastener in the correct location. Replacement fasteners must be the correct part number for that application. Fasteners requiring replacement or fasteners requiring the use of thread locking compound or sealant are identified in the service procedure. Do not use paints, lubricants, or corrosion inhibitors on fasteners or fastener joint surfaces unless specified. These coatings affect fastener torque and joint clamping force and may damage the fastener. Use the correct tightening sequence and specifications when installing fasteners in order to avoid damage to parts and systems.
Tighten the return port fitting (1) to 10 N·m (88 lb in). If the leak continues, replace the seal ring under the return port fitting.
