Description
The Engine Cranks but Does Not Run diagnostic table assumes that the battery condition and the engine cranking speed are OK. If the battery condition and the cranking speed are not OK, refer to Diagnostic System Check - Engine Electrical in Engine Electrical for diagnosis. Make sure that there is adequate fuel in the fuel tanks.
Diagnostic Aids
| • | Check the duct work between the mass air flow (MAF) sensor and the throttle body for air leaks. |
| • | A malfunctioning MAF sensor may cause a no start or a stall after start. If you suspect this, disconnect the MAF sensor. The powertrain control module (PCM) will default to the speed density in order to calculate the load and the air flow. If this corrects the condition and the connections are OK, replace the MAF sensor. |
If the steps above check OK, refer to Symptoms .
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
It may be necessary to connect a battery charger to the battery for this step. If the battery state of charge is low, the scan tool may reset during the cranking test.
-
This step tests the ignition relay for proper operation. The ignition relay supplies voltage to the injectors and the ignition coils. When the ignition relay is not operating properly, a no start condition occurs. If the test lamp does not illuminate, this indicates the ignition relay is not suppling a voltage to the fuses.
-
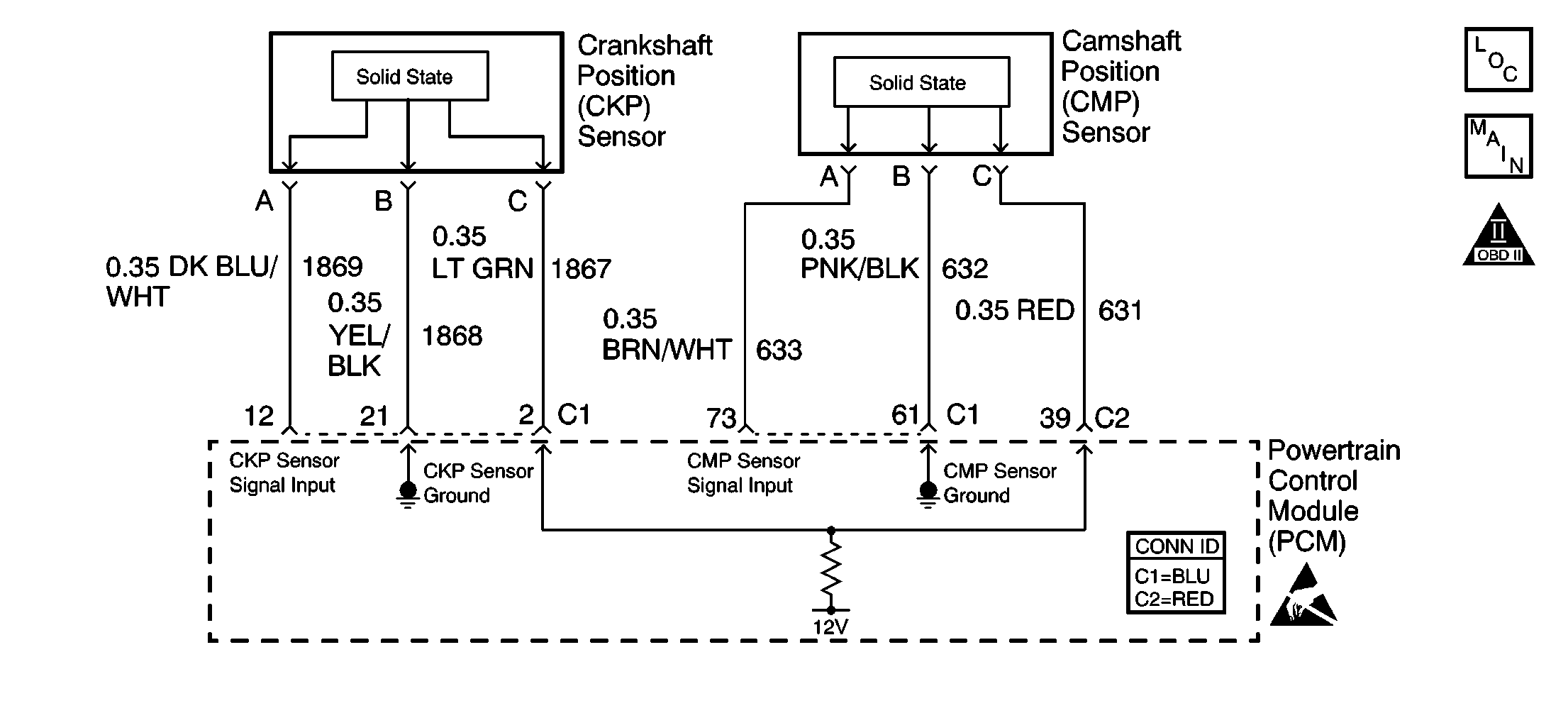
The crankshaft position (CKP) sensor is located above the starter.
-
The camshaft position (CMP) sensor is located at the rear of the engine behind the intake manifold.
-
The ignition feed circuit for the CMP and CKP sensors is internally connected within the PCM. A short to ground on either circuit will cause a no start condition.
-
The fuel cap may need to be removed in order to hear if the fuel pump is operating.
-
At this point the engine should start. Refer to Hard Start for further diagnosis.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||||||||||||||
2 |
Important: Refer to the applicable DTC table if any of the following DTCs are set: P0230, P0335, P0336, P0601, P0602, P0604, P1626, P1631, or any communication codes (U type). Crank the engine for the specified amount of time. Does the scan tool display any DTCs that failed this ignition? | 15 Seconds | Go to the applicable DTC table | |||||||||||||
3 | Check the body control module (BCM) for DTCs related to the vehicle theft deterrent (VTD) system. Does the scan tool display any BCM VTD DTCs? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check - Theft Deterrent in Theft Deterrent | |||||||||||||
Monitor the engine speed while cranking the engine. Is engine RPM indicated on the scan tool? | -- | |||||||||||||||
Does the test lamp illuminate on both sides of the fuses? | -- | Go to Ignition Relay Diagnosis | ||||||||||||||
Does the DMM display near the specified value? | B+ | |||||||||||||||
Does the DMM display near the specified value? | B+ | |||||||||||||||
Inspect the camshaft and crankshaft position sensor ignition positive voltage circuits for a short to ground. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | |||||||||||||||
9 | Monitor the engine coolant temperature (ECT) using the scan tool. Is the ECT on the scan tool close to the actual engine temperature? | -- | Go to DTC P0118 Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor Circuit High Voltage | |||||||||||||
Enable the fuel pump using the scan tool. Does the fuel pump operate? | -- | |||||||||||||||
11 |
Important: The fuel pump operates for about 2 seconds when the ignition is turned ON. The fuel pressure must be observed when the fuel pump is operating. Is the fuel pressure within the specified range? | 379-427 kPa (55-62 psi) | Go to Fuel System Diagnosis | |||||||||||||
Perform the following additional inspections:
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Hard Start for diagnosis | ||||||||||||||
13 | Replace the CKP sensor. Refer to Crankshaft Position Sensor Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||||
14 | Replace the CMP sensor. Refer to Camshaft Position Sensor Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||||
15 |
Important:: The replacement PCM must be programmed. Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||||
16 |
Does the engine start and continue to run? | -- | ||||||||||||||
17 |
Are any DTCs displayed? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | |||||||||||||
18 | Select the Capture Info option and the Review Info option using the scan tool. Are any DTCs displayed that you have not diagnosed? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | System OK |
