DTC P1133 HO2S Insufficient Switching Bank 1 Sensor 1 w/o RPO OSG
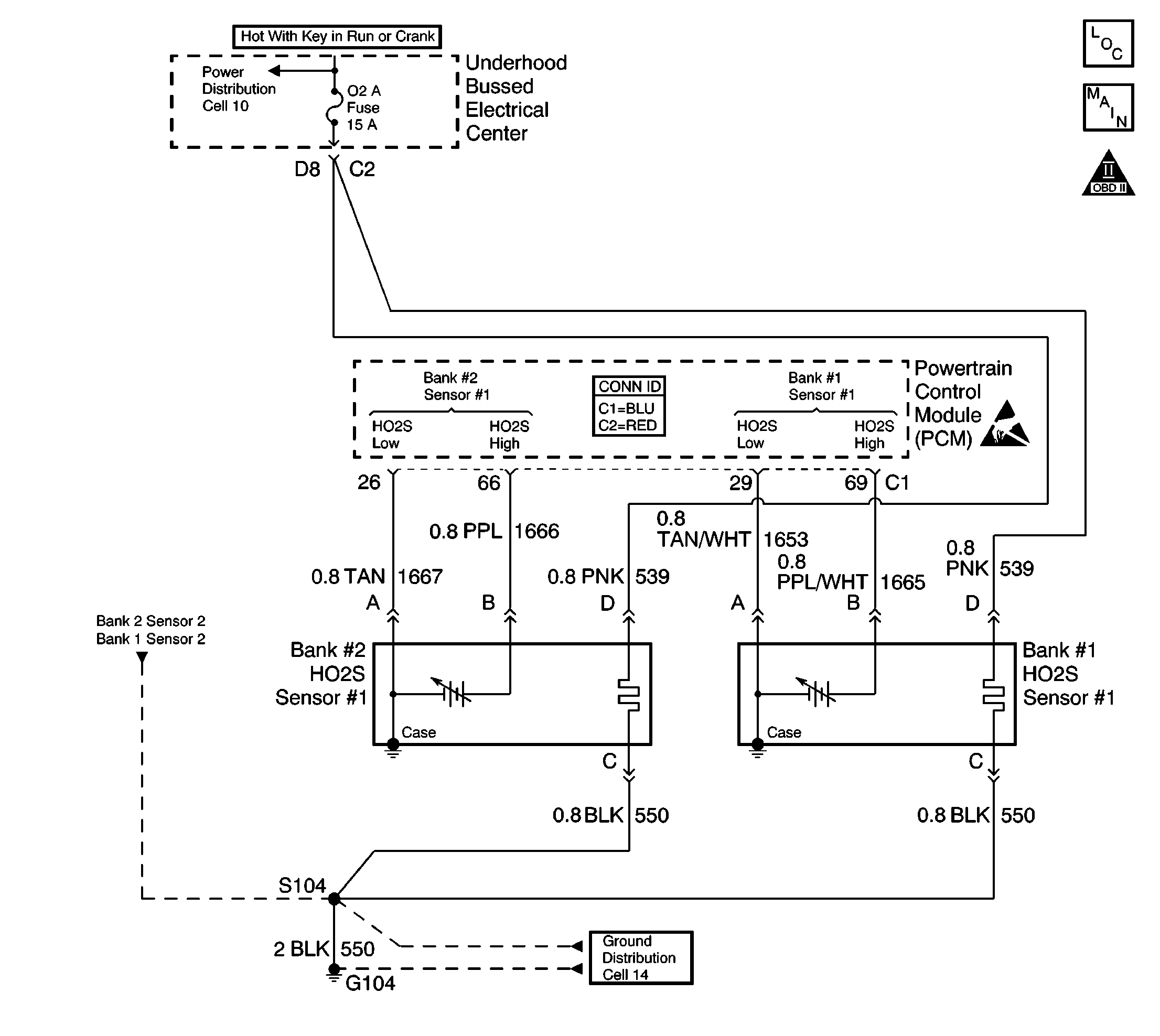
Circuit Description
The powertrain control module (PCM) monitors the heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) activity for 100 seconds. During this monitor period, the PCM counts the number of times that the HO2S switches from rich to lean and lean to rich. A DTC P1133 sets when the PCM determines that the HO2S did not switch enough times.
A lean to rich switch is determined when the HO2S voltage changes from less than 300 mV to more than 600 mV. A rich to lean switch is determined when the HO2S voltage changes from more than 600 mV to less than 300 mV.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | No active mass air flow (MAF) DTCs |
| • | No active intake air temperature (IAT) DTCs |
| • | No active engine coolant temperature (ECT) DTCs |
| • | No active throttle position (TP) DTCs |
| • | No active Injector DTCs |
| • | No active crankshaft position (CKP) sensor DTCs |
| • | No active ignition control (IC) DTCs |
| • | The fuel system is operating in Closed Loop. |
| • | The engine run time is more than 120 seconds. |
| • | The engine speed is between 1,200 RPM and 3,000 RPM. |
| • | The ignition voltage is more than 9 volts. |
| • | The ECT is more than 65°C (149°F). |
| • | The MAF is between 23 g/s and 50 g/s. |
| • | The evaporative emission (EVAP) purge duty cycle is more than 0 percent. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The PCM determines that within 100 seconds the HO2S lean to rich switches are less than 10 and rich to lean switches are less then 10.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) on the second consecutive ignition cycle that the diagnostic runs and fails. |
| • | The PCM records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The first time the diagnostic fails, the PCM stores this information in the Failure Records. If the diagnostic reports a failure on the second consecutive ignition cycle, the PCM records the operating conditions at the time of the failure. The PCM writes the conditions to the Freeze Frame and updates the Failure Records. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The PCM turns OFF the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) after 3 consecutive ignition cycles that the diagnostic runs and does not fail. |
| • | A last test failed, or current DTC, clears when the diagnostic runs and does not fail. |
| • | A history DTC clears after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles, if no failures are reported by this or any other emission related diagnostic. |
| • | Use a scan tool in order to clear the MIL and the DTC. |
Diagnostic Aids
Important: Remove any debris from the PCM connector surfaces before servicing the PCM. Inspect the PCM connector gaskets when diagnosing or replacing the PCM. Ensure that the gaskets are installed correctly. The gaskets prevent water intrusion into the PCM.
| • | Inspect the HO2S signal circuit for being shorted to a PCM ground. The HO2S signal circuit shorted to a PCM ground sets a switching DTC. |
| • | A malfunction in the HO2S heater circuits will cause a DTC P1133 to set. Check HO2S heater circuits for intermittent opens or loose connections. |
| • | An oxygen supply inside the HO2S is necessary for proper operation. This supply of oxygen is provided through the HO2S wires. All HO2S wires and connections should be inspected for breaks or contamination. Refer to Heated Oxygen Sensor Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. |
| • | Using the Freeze Frame and Failure Records data may aid in locating an intermittent condition. If the DTC cannot be duplicated, the information included in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records data can be useful in determining how many miles since the DTC set. The Fail Counter and Pass Counter can also be used to determine how many ignition cycles the diagnostic reported a pass or a fail. Operate vehicle within the same Freeze Frame conditions, such as RPM, load, vehicle speed, temperature etc., that you observed. This will isolate when the DTC failed. |
For an intermittent, refer to Symptoms .
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
This step determines if the fault is present. This test may take 5 minutes for the diagnostic to run. For any test that requires probing the PCM or a component harness connector, use the connector test adapter kit . Using this kit prevents damage to the harness connector terminals.
-
When DTCs P1133 and P1153 are set at the same time, this is a good indication that a fuel contamination condition is present.
-
An exhaust leak 6-12 inches away from the HO2S can cause a DTC to set.
-
This step tests the HO2S for being tight and the connectors and circuits are OK.
-
This step tests the integrity of the HO2S low signal circuit to the PCM.
-
This step tests the integrity of the signal circuit to the PCM.
-
Certain room temperature vulcanizing (RTV) silicon gasket materials give off vapors that can contaminate the HO2S. There is also a possibility of silicon contamination caused by silicon in the fuel. If the sensors appear to be contaminated by silicon and all the silicon sealant is a non-silicon base, advise the customer to try a different fuel company. A missing fuel filler restrictor indicates the customer may have used leaded fuel.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||||||||||
|
Important: If any DTCs are set, except P1153, refer to those DTCs before proceeding with this diagnostic table.
Did DTC P1133 fail this ignition? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | ||||||||||
Did DTC P1153 also fail this ignition? | -- | |||||||||||
Did you isolate an exhaust leak? | -- | |||||||||||
Visually and physically inspect the following items:
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | |||||||||||
Does the scan tool indicate a voltage within the specified range? | 350-550 mV | |||||||||||
Does the scan tool indicate a voltage below the specified value? | 200 mV | |||||||||||
|
Important: Determine and correct the cause of the contamination before replacing
a sensor. Inspect for the following conditions:
Replace the affected heated oxygen sensor (H20S). Refer to Heated Oxygen Sensor Replacement - Bank 1 or Heated Oxygen Sensor Replacement - Bank 2 . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | ||||||||||
9 |
Does the DMM indicate a voltage near the specified value? | 5 V | ||||||||||
10 | Repair the high signal circuit for a short to ground or a short to voltage. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||
11 | Repair the open HO2S low circuit, or repair the faulty PCM connections. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||
12 | Repair the HO2S high signal circuit for an open, or repair the faulty PCM connections. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||
13 | Replace the HO2S. Refer to Heated Oxygen Sensor Replacement - Bank 1 . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||
14 |
Does the scan tool indicate that this test ran and passed? | -- | ||||||||||
15 | Select the Capture Info option and the Review Info option using the scan tool. Does the scan tool display any DTCs that you have not diagnosed? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | System OK |
DTC P1133 HO2S Insufficient Switching Bank 1 Sensor 1 w/ RPO OSG
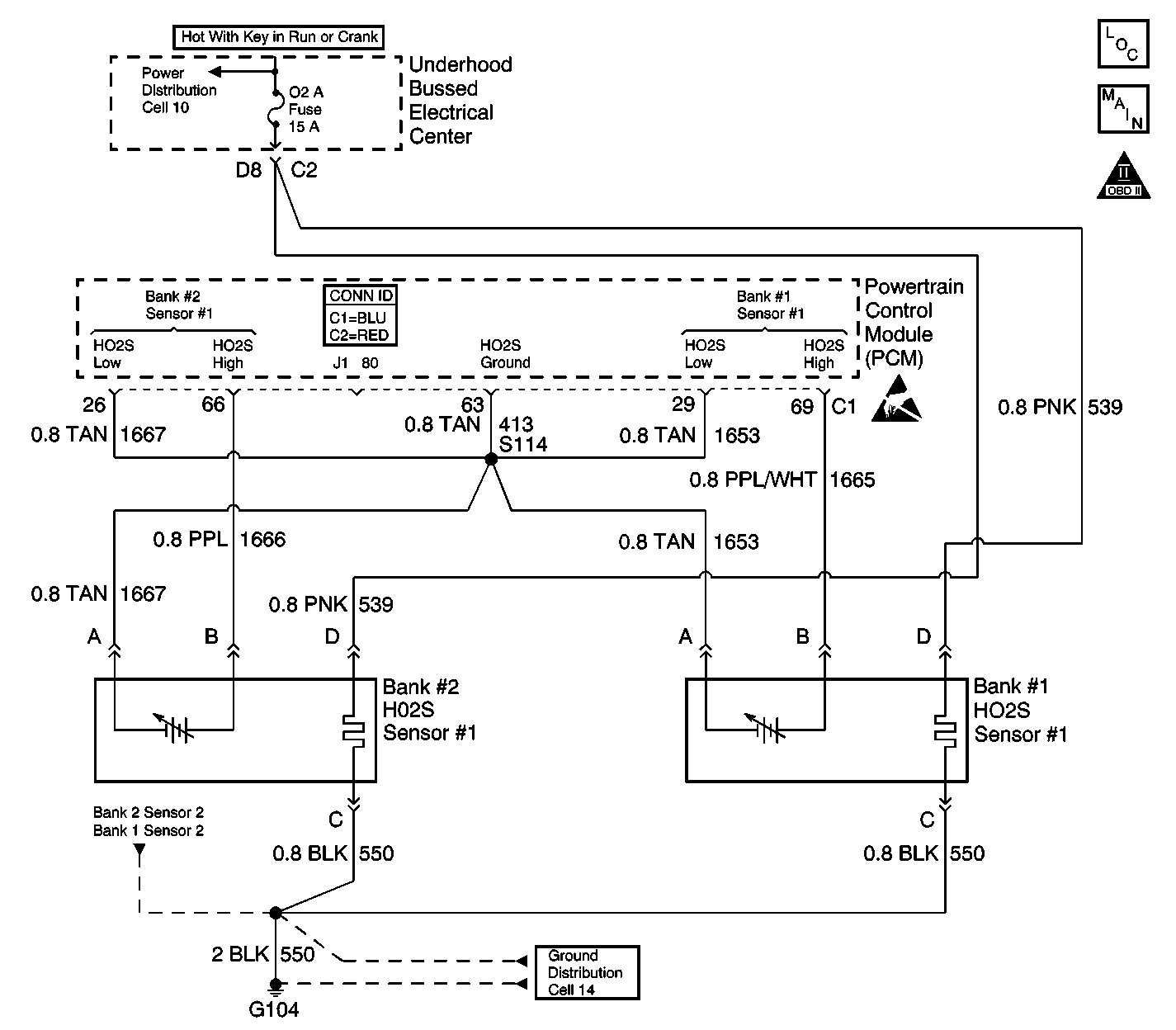
Circuit Description
The heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) is a sensor designed to create a voltage relative to the oxygen content in the engine exhaust stream. The control module supplies the HO2S with signal high and low circuits. Ignition voltage and ground are supplied to the HO2S heater by independent circuits. The oxygen content of the exhaust indicates when the engine is operating lean or rich. When the HO2S detects that the engine is operating rich, the signal voltage is high, and decreases the signal voltage as the engine runs leaner. This oscillation above and below the bias voltage, sometimes referred to as activity or switching, can be monitored with the HO2S signal voltage.
The HO2S contains a heater that is necessary in order to quickly warm the sensor to operating temperature. The heater also maintains the operating temperature during extended idle conditions. The HO2S needs to be at a high temperature in order to produce a voltage. When the HO2S reaches operating temperature, the control module monitors the HO2S bias, or reference, voltage. It also monitors the HO2S signal voltage for Closed Loop fuel control. During normal Closed Loop fuel control operation, the control module will add fuel, or enrich the mixture, when the HO2S detects a lean exhaust content. The control module will subtract fuel, or "lean-out" the mixture, when the HO2S detects a rich exhaust condition.
Certain vehicle models utilize an oxygen sensor behind the catalytic converter in order to monitor catalyst efficiency.
This diagnostic trouble code (DTC) determines if the HO2S is functioning properly. It checks for an adequate number of HO2S voltage transitions above and below the bias range of 300-600 mV. This DTC sets when the vehicle control module (VCM) fails to detect a minimum number of voltage transitions above and below the bias range during the test period. Possible causes of this DTC are:
| • | An open or a short to voltage on either the HO2S signal or HO2S low circuits |
| • | A malfunctioning HO2S |
| • | A problem in the HO2S heater or its circuit |
| • | A faulty HO2S ground |
This DTC is designed to detect an HO2S that produces too few lean to rich and rich to lean signal transitions within a calibrated time window.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | No active throttle position (TP) sensor DTCs. |
| • | No active evaporative emission (EVAP) system DTCs. |
| • | No active intake air temperature (IAT) sensor DTCs. |
| • | No active manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor DTCs. |
| • | No active engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor DTCs. |
| • | No active mass air flow (MAF) sensor DTCs. |
| • | No active misfire DTCs. |
| • | No intrusive tests are in progress. |
| • | The system voltage is between 11.7-18 volts. |
| • | DTCs P0131, P0132, P0134, and P0135 not active. |
| • | The system is in a Closed Loop. |
| • | The ECT is more than 57°C (135°F). |
| • | The engine has been running for more than 75 seconds. |
| • | The MAF is between 15-55 g/s. |
| • | The engine speed is between 1,100-3,000 RPM. |
| • | The EVAP canister purge is active. |
| • | The above conditions are present for more than 2 seconds. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The number of lean-to-rich and rich-to-lean transitions within a 100 second sample period were less than a calibrated number.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The control module illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) if a failure is detected during 2 consecutive key cycles. |
| • | The control module sets the DTC and records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic failed. The failure information is stored in the scan tool Freeze Frame/Failure Records. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL or DTC
| • | The control module turns OFF the MIL after 3 consecutive drive trips when the test has run and passed. |
| • | A history DTC will clear if no fault conditions have been detected for 40 warm-up cycles. A warm-up cycle occurs when the coolant temperature has risen 22°C (40°F) from the startup coolant temperature and the engine coolant reaches a temperature that is more than 70°C (158°F) during the same ignition cycle. |
| • | Use a scan tool in order to clear the DTCs. |
Diagnostic Aids
Important: Never solder the HO2S wires. For proper wire and connector repairs, refer to Wiring Repairs or Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems.
Check for the following conditions:
| • | An improperly installed air cleaner outlet duct |
| • | The air cleaner outlet duct for a collapsed duct, restrictions, or a missing or plugged air filter |
| • | Throttle body and intake manifold vacuum leaks |
| • | A damaged or blocked throttle body inlet |
| • | Exhaust system for corrosion, leaks, or loose or missing hardware--Refer to Exhaust System Inspection in Engine Exhaust. |
| • | The HO2S is installed securely and the pigtail harness is not contacting the exhaust manifold or wires |
| • | HO2S contamination |
| • | The vacuum hoses for splits, kinks, and proper connections |
| • | Excessive water, alcohol, or other contaminants in the fuel--Refer to Alcohol/Contaminants-in-Fuel Diagnosis . |
| • | PCM sensor grounds that are clean, tight, and properly positioned |
An intermittent may be caused by any of the following conditions:
| • | A poor connection |
| • | Rubbed through wire insulation |
| • | A broken wire inside the insulation |
Thoroughly inspect any circuitry that is suspected of causing the intermittent complaint. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections in Wiring Systems.
If a repair is necessary, refer to Wiring Repairs or Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
HO2S contamination is indicated if multiple Response, Switching or Time Ratio HO2S DTCs are set.
-
The use of leaded fuel may be indicated by the removal or tampering of the fuel filler restrictor.
An HO2S contaminated by silicon will have a white, powdery deposit on the portion of the HO2S that is exposed to the exhaust stream. The usual cause of silica contamination is the use of unapproved silicon room temperature vulcanizing (RTV) engine gasket material or the use of silicon based sprays or fluids within the engine.
If the cause of this contamination is not corrected, the replacement HO2S will also get contaminated.
-
Even small exhaust leaks can cause slow response from the HO2S.
-
An HO2S contaminated by silicon will have a white, powdery deposit on the portion of the HO2S that is exposed to the exhaust stream. The usual cause of silica contamination is the use of unapproved silicon RTV engine gasket material or the use of silicon based sprays or fluids within the engine. If the cause of this contamination is not corrected, the replacement HO2S will also get contaminated.
-
If the voltage observed in step 8 is less than the range specified, a short between the HIGH and LOW circuits or a short between the HIGH circuit and ground is indicated. With the HO2S and the PCM disconnected, the resistance between the HIGH and LOW circuits and the resistance between the HIGH circuit and ground should measure infinite.
If the voltage observed in step 8 is more than the range specified a short between the HIGH circuit and an ignition voltage source is indicated.
-
If the voltage observed in step 9 is not below the voltage specified, a high resistance, or open, HIGH or LOW circuit is indicated.
Good circuit continuity measures less than 5 ohms with the PCM and sensor disconnected. Measure between the PCM connector and the HO2S connector. Ensure PCM terminal contact is good.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Important: Before clearing the DTCs, use the scan tool in order to record the Freeze Frame and the Failure Records for reference. This data will be lost when the Clear DTC Information function is used. Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
In addition to this DTC, check for the following HO2S DTCs:
Are any of the above listed HO2S DTCs set? | -- | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
3 | Are any powertrain component DTCs set? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Important: The contamination source must be removed prior to operating the engine with the replacement sensors.
Has the contamination source been removed and the affected sensors replaced? | -- | -- | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
5 |
Did this DTC run and fail this ignition? | -- | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
6 | The condition that set this DTC is not present. This DTC may have been set by one of the following conditions:
Repair any of the above or similar engine conditions as necessary. Did you find a problem? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Did you find and repair a problem? | -- | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
8 |
Is the HO2S voltage within the value range specified? | 351-551 mV | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
9 |
Is the HO2S voltage less than the value specified? | 20 mV | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
10 |
Does the test lamp illuminate? | -- | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
11 | Connect the test lamp between the HO2S heater ignition feed circuit terminal and the HO2S heater ground circuit terminal, both on engine harness side. Does the test lamp illuminate? | -- | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Is the action complete? | -- | -- | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Is the action complete? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Is the action complete? | -- | -- | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
15 | Repair the HO2S heater ignition feed circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
16 | Repair the HO2S heater ground circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
17 | Replace the HO2S. Refer to Heated Oxygen Sensor Replacement - Bank 1 . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
18 |
Did this DTC run and pass this ignition? | -- | System OK |
