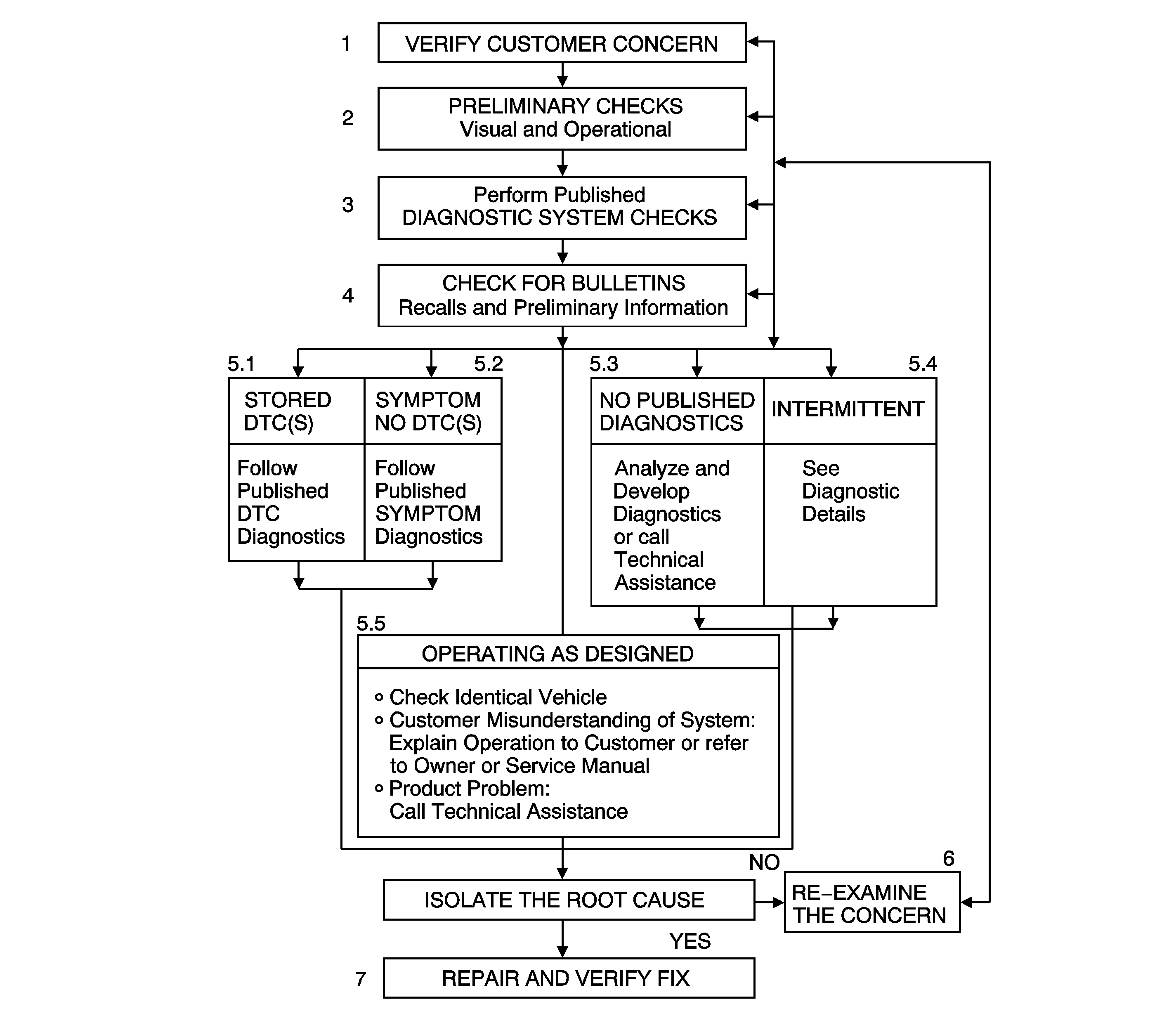
The strategy based diagnostic is a uniform approach to repair all Electrical and Electronic (E/E) systems. Use the diagnostic flow in order to resolve an E/E system problem. When repairs are necessary, the diagnostic flow is also a starting point. The steps below are defined in order to instruct the technician how to proceed with a diagnosis.
- Verify the Customer Concern
- Preliminary Checks
- Perform Published Diagnostic System Checks
- Check Bulletins and Other Service Information
- Diagnostics
- Re-Examine the Concern
- Repair and Verify Fix
In order to verify the customer complaint, the technician should know the normal operation of the system.
Perform the following steps:
| 2.1. | Conduct a thorough visual inspection |
| 2.2. | Review the service history |
| 2.3. | Detect unusual sounds or odors |
| 2.4. | Gather diagnostic trouble code information in order to achieve an effective repair |
One or more DTCs may not support a system. System checks verify the proper operation of the system. This will lead the technician in an organized approach to diagnostics.
Also check the videos, the newsletters, and the Pulsat programs.
Service Diagnostics (Paper and Electronic)
| 5.1. | Stored DTC(s) - Follow the designated DTC Table exactly in order to make an effective repair. |
| 5.2. | Symptom No DTC(s) - Select the symptom from the symptom tables. Follow the diagnostic paths or suggestions in order to complete the repair, or refer to the applicable component/system check. |
| 5.3. | No Published Diagnostics- Analyze the complaint. Develop a plan for the diagnostics. Utilize the wiring diagrams and theory of operation. |
| 5.4. | Intermittents - Conditions that are not always present are intermittents. In order to resolve intermittents, perform the following steps: |
| 5.4.1. | Observe the history DTCs, the DTC modes and, the freeze frame data. |
Check Bulletins for similar cases where repair history may be available. Combine the technician knowledge with efficient use of the available service information.
| 5.4.2. | Evaluate the symptoms and conditions described by the customer. |
| 5.4.3. | Use a check sheet or other method in order to identify the circuit or electrical system component. |
| 5.4.4. | Follow the suggestions for intermittent diagnosis found in the service documentation. |
| 5.4.5. | The Tech 1, Tech 2 and Fluke 87 scan tools have data capturing capabilities that can assist in detection of Intermittents. |
| 5.5. | Vehicle operates as designed |
| • | This condition exists when the vehicle is found to operate normally. |
| • | The condition described by the customer may be normal. Verify against another vehicle that is operating normally. |
| • | The condition may be intermittent. Verify the complaint under the conditions described by the customer before releasing the vehicle. |
If a technician cannot successfully find or isolate the complaint, a reevaluation is necessary. Re-verify the complaint. The complaint could be an intermittent or normal.
After isolating the cause, make the repairs. Then validate for proper operation. Verify that the symptom has been corrected. Verification may involve road testing the vehicle.
