Circuit Description
The digital steering wheel position sensor (SWPS) inputs to the electronic suspension control (ESC) module consists of 3 digital input circuits, phase A, phase B, and index marker pulse. The SWPS is supplied battery positive voltage and ground. The information that the ESC module receives from the SWPS is used to calculate steering angle, steering velocity, and lateral acceleration. These values are used in the control of the suspension dampers.
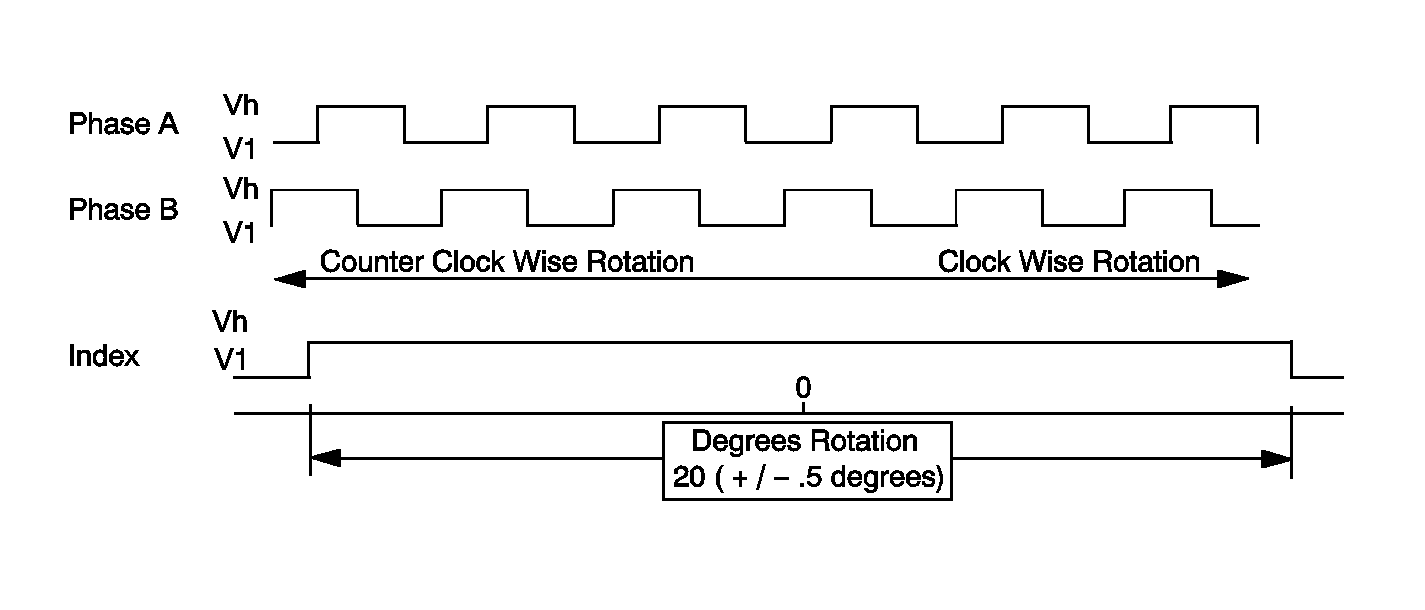
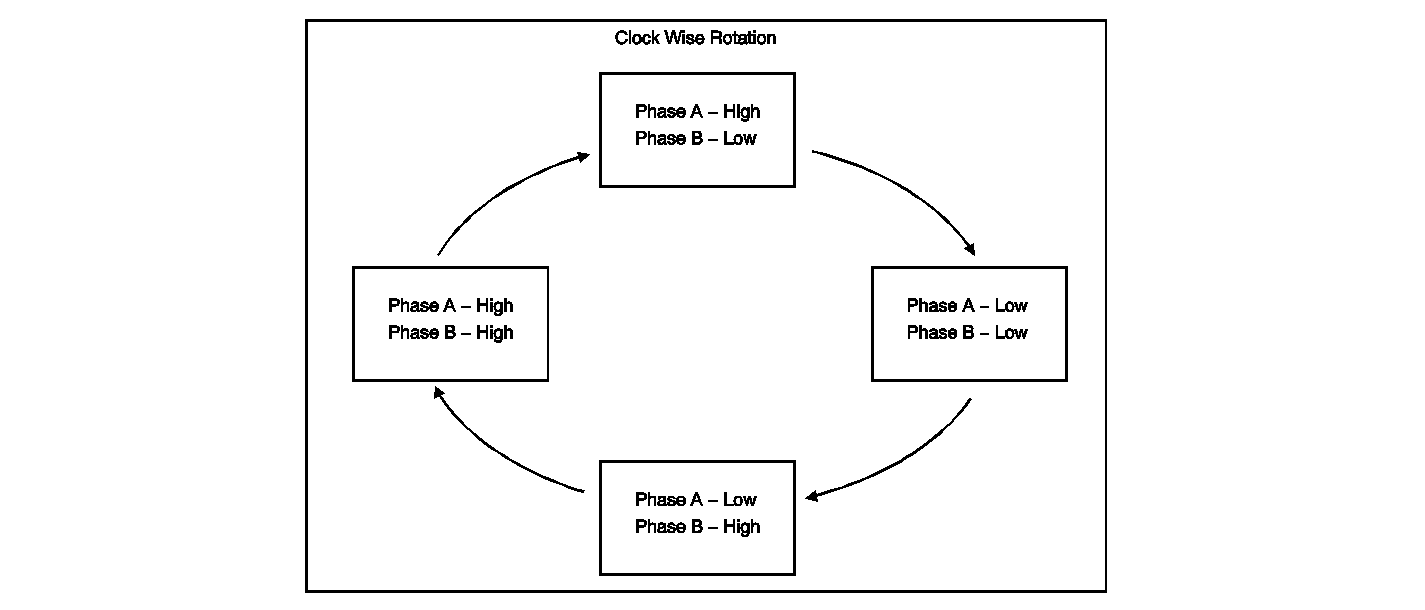
The digital SWPS phase A and phase B circuits are digital pulse signals whose output represents one degree of steering wheel rotation. When observing the Phase A data and the Phase B data parameters on the scan tool, the parameters will not have the same value at the same time. When the steering wheel is rotated, the Phase A data and the Phase B data parameters will be shown as high or low on the scan tool.
The index marker pulse is a digital pulse that is displayed as high on the scan tool for 20 degrees only when the steering wheel angle is between -10 and +10 degrees.
DTC Descriptor
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTC:
DTC C0455 Front Steering Position Sensor Circuit
Conditions for Running the DTC
Turn ON the ignition, with engine ON.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | The Index Marker Pulse data parameter is high for less than 20 degrees of the steering wheel angle. |
| • | The Index Marker Pulse data parameter is high for greater than 20 degrees of the steering wheel angle. |
| • | The Index Marker Pulse data parameter is high when the steering wheel angle parameter is greater than 90 degrees . |
| • | The Index Marker Pulse data parameter is high when the Steering Wheel Angle parameter is less than -90 degrees. |
| • | The SWPS phase A circuit is shorted to ground, open, or shorted to voltage. |
| • | The SWPS phase B circuit is shorted to ground, open, or shorted to voltage. |
| • | The index marker pulse is shorted to ground, open, or shorted to voltage. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The code is displayed on the scan tool as DTC C0455. |
| • | The suspension control defaults to firm. |
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
| • | Conditions for DTC are not currently present. |
| • | The module receives a clear code command from the scan tool. |
| • | The DTC clears after 100 malfunction-free ignition cycles. |
Diagnostic Aids
The following conditions are possible causes:
| • | A malfunctioning SWPS is present. |
| • | A SWPS circuit is open. |
| • | A SWPS circuit was shorted. |
Perform an inspection of the wiring and of the connectors. Failure to carefully inspect the wiring and the connectors may result in misdiagnosis. Misdiagnosis causes part replacement with reappearance of the malfunction.
Steering Wheel Position Sensor - Digital Signal
| • | 3 outputs used--Phase A, Phase B, Index Marker Pulse |
| • | Phase A & Phase B--Offset pulse width modulation (PWM) wave forms created when turning the wheel |
| • | Index marker pulse--The signal is present only when the steering wheel is within 10 degrees either side of center. |
Output is used to determine Direction of Rotation and Rate of Rotation.
Steering Wheel Position Sensor--Digital Signal
Steering Wheel Position Sensor--A and B Phase
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
Test for the proper operation of the phase A circuit.
-
Test for the proper operation of the phase B circuit.
-
Test for the proper operation of the index marker pulse circuit.
Step | Action | Values | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Schematic Reference: Suspension Controls Schematics Connector End View Reference: Suspension Controls Connector End Views | ||||
1 | Did you perform the Diagnostic System Check - Vehicle? | -- | Go to Step 2 | |
2 |
Do all of the parameters change? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | Go to Step 3 |
With a scan tool, observe the phase A parameter while turning the steering wheel. Does the Phase A data parameter change state? | high/low | Go to Step 5 | Go to Step 4 | |
4 | Does the scan tool indicate that the Phase A data parameter is high? | -- | Go to Step 10 | Go to Step 9 |
With a scan tool, observe the Phase B parameter while turning the steering wheel. Does the phase B data parameter change state? | high/low | Go to Step 7 | Go to Step 6 | |
6 | Does the scan tool indicate that the Phase B data parameter is high? | -- | Go to Step 10 | Go to Step 9 |
With a scan tool, observe the Index Marker Pulse data parameter while turning the steering wheel. Does the index marker pulse data parameter change state? | high/low | Go to Step 15 | Go to Step 8 | |
8 | Does the scan tool indicate that the index marker pulse data parameter is high? | -- | Go to Step 10 | Go to Step 9 |
9 | Test the steering wheel position sensor phase A, phase B, or index marker pulse circuit for a short to ground. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs . Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 15 | Go to Step 11 |
10 | Test the steering wheel position sensor phase A, phase B, or index marker pulse circuit for an open or short to voltage. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs . Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 15 | Go to Step 11 |
11 | Inspect for poor connections at the harness connector of the digital steering wheel position sensor connector. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections and Connector Repairs . Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 15 | Go to Step 13 |
12 | Inspect for poor connections at the harness connector of the electronic suspension control (ESC) module. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections and Connector Repairs .
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 15 | Go to Step 14 |
13 | Replace the digital steering wheel position sensor. Refer to Steering Wheel Position Sensor or Steering Shaft Lower Bearing Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | Go to Step 15 | -- |
14 | Replace the ESC module. Refer to Control Module References for replacement, setup, and programming. Did you complete the replacement? | -- | Go to Step 15 | -- |
15 |
Does the DTC reset? | -- | Go to Step 2 | System OK |
