Refer to
Cell 22: G103, Fuel Pump
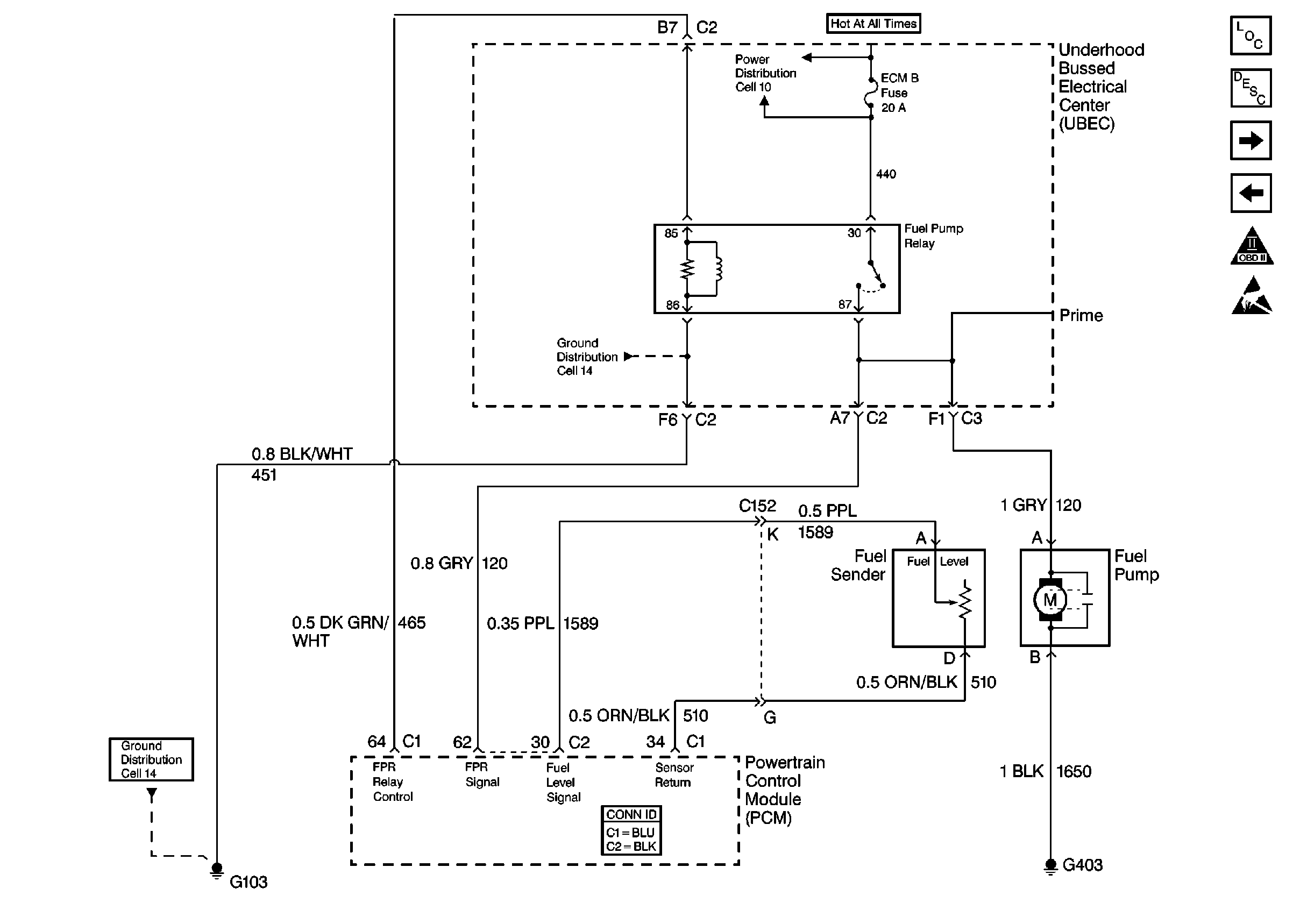
Circuit Description
The fuel level sensor changes resistance based on fuel level. The fuel level sensor has a signal circuit and a ground circuit. The PCM applies a voltage (about 5.0 volts) on the signal circuit to the sensor. The PCM monitors changes in this voltage caused by changes in the resistance of the sensor to determine fuel level.
When the fuel tank is full, the sensor resistance is high, and the PCM's signal voltage is only pulled down a small amount through the sensor to ground. Therefore, the PCM will sense a high signal voltage (fuel tank full). When the fuel tank is empty, the sensor resistance is low, and the signal voltage is pulled down a greater amount. This causes the PCM to sense a low signal voltage (fuel tank empty).
The PCM uses inputs from the fuel level sensor to calculate the total fuel remaining in the fuel tank. This information is then sent to the fuel gauge.
This DTC sets when the PCM senses a signal voltage lower than the normal operating range of the sensor.
Conditions for Running the DTC
The ignition switch is in the On position.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | The fuel level sender voltage is below 0.25 volts. |
| • | All conditions present for 10 seconds. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) on the second consecutive drive trip that the diagnostic runs and fails. |
| • | The PCM records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The first time the diagnostic fails, the Failure Records will store this information. If the diagnostic reports a failure on the second consecutive drive trip, the Freeze Frame records the operating conditions at the time of failure and updates the Failure Records. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The PCM will not turn the MIL on. |
| • | A History DTC clears after forty consecutive warm-up cycles, if this or any other emission related diagnostic does not report any failures. |
| • | The use of a scan tool |
Diagnostic Aids
Important: Remove any debris from the PCM module connector surfaces before servicing the PCM module. Inspect the PCM module connector gaskets when diagnosing/replacing the module. Ensure that the gaskets are installed correctly. The gaskets prevent contaminate intrusion into the PCM module.
The vehicle fuel gauge displays empty with this DTC set:
Using Freeze Frame and/or Failure Records data may aid in locating an intermittent condition. If you cannot duplicate the DTC, the information included in the Freeze Frame and/or Failure Records data can aid in determining how many miles since the DTC set. The Fail Counter and Pass Counter can also aid determining how many ignition cycles the diagnostic reported a pass and/or a fail. Operate the vehicle within the same freeze frame conditions (RPM, load, vehicle speed, temperature etc.) that you observed. This will isolate when the DTC failed.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the Diagnostic Table.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Important: Before clearing any DTCs, use the scan tool Capture Info to save Freeze Frame and Failure Records for reference. The control module's data is deleted once the Clear Info function is used. Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||
Does the scant indicate that this diagnostic failed this ignition? | -- | |||
3 | The DTC is intermittent. If no additional DTCs are stored, refer to Diagnostic Aids If any additional DTCs were stored, refer to those table(s). Are there any additional DTCs stored? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | Go to Diagnostic Aids |
4 |
Is the voltage greater than the specified value? | 4.70 V | ||
5 |
Is the test light on? | -- | ||
6 |
Did you perform a repair? | -- | ||
7 | Replace the Fuel Level sender. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
8 |
Did you perform a repair? | -- | ||
9 | Replace the PCM. Important: The new PCM must be programmed. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
10 |
| -- | ||
11 | Does the scan tool display any additional undiagnosed DTCs? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC | System OK |
