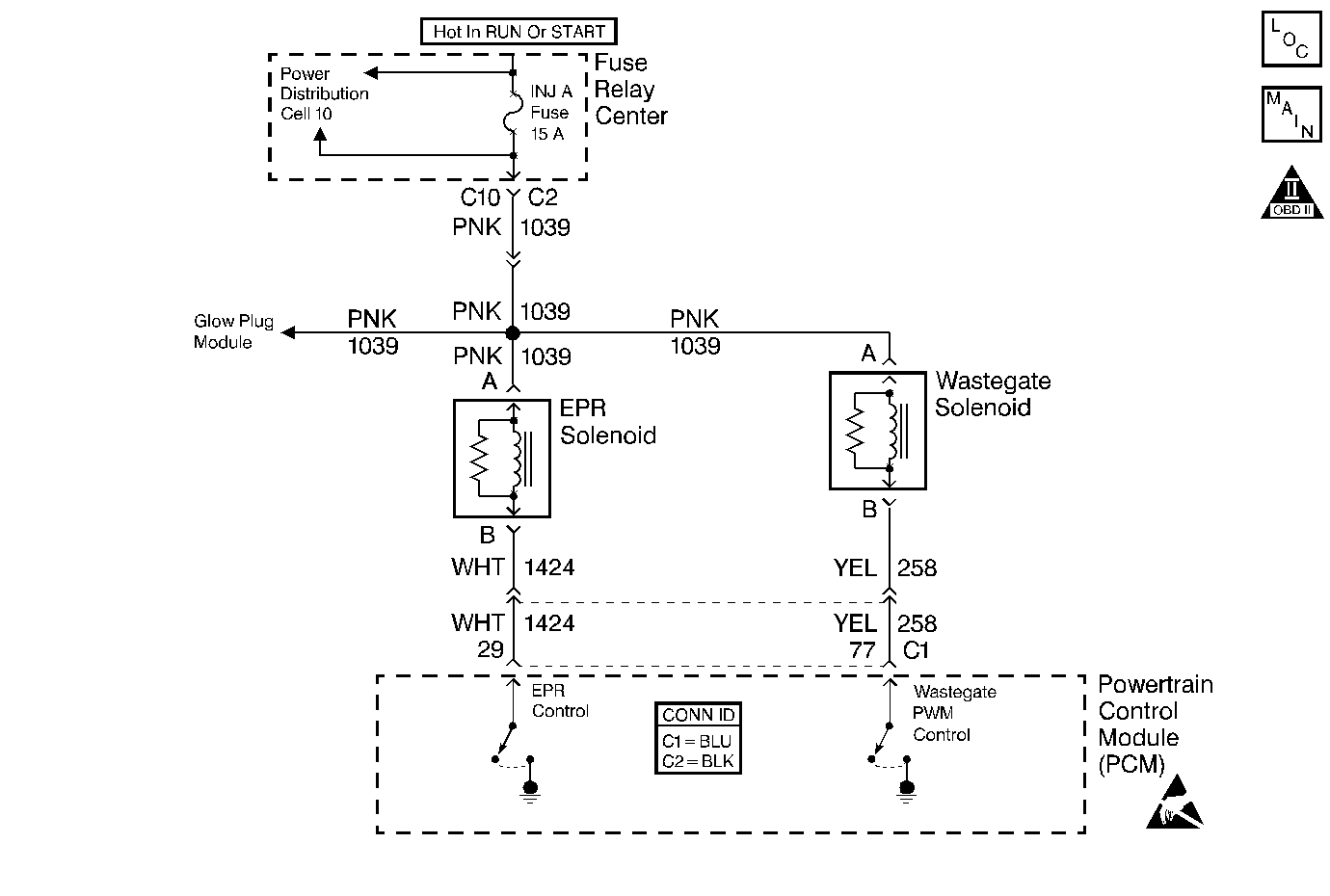
Circuit Description
The EPR flow is controlled by the vacuum actuated EPR valve. The PCM operates the EPR solenoid by turning it on and off. The EPR vacuum solenoid is normally open. By providing a ground path, the PCM energizes the solenoid which then allows vacuum to pass to the EPR vacuum actuator. When the PCM is commanding the EPR solenoid ON, the voltage at the PCM will be low (near 0 volts). When the PCM is commanding the EPR solenoid OFF, the voltage at the PCM will be high (near battery volts). The primary function of the PCM in this circuit is to supply the ground for the EPR solenoid. The EPR system primarily functions when the vehicle is cold, or in warmer climates for a minimum of six seconds to exercise EPR components (prevent freezing up of butterfly valve). This DTC will only diagnosis the functionality of the EPR solenoid an not the mechanical components of the system.
Conditions for Running the DTC
PCM requested EPR solenoid ON (test 1).
or
PCM requested EPR solenoid OFF (test 2).
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | Voltage on EGR solenoid control circuit high (near battery volts) (test 1). |
| • | Conditions met for 2 seconds. |
or
| • | Voltage on EGR solenoid control circuit low (near 0 volts) (test 2). |
| • | Conditions met for 2 seconds. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM illuminates the Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) on the second consecutive drive trip the diagnostic runs and fails. |
| • | The PCM records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The first time the diagnostic fails, the Failure Records store this information. If the diagnostic reports a failure on the second consecutive drive trip, the Freeze Frame records the operating conditions at the time of failure and updates the Failure Records. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The PCM will turn the MIL off after three consecutive trips without a fault condition. |
| • | A History DTC clears after forty consecutive warm-up cycles, if this or any other emission related diagnostic does not report any failures. |
| • | The use of a scan tool. |
Diagnostic Aids
The EPR vacuum actuator can be replaced separately from the turbocharger assembly, although the turbocharger is sold with a new actuator. The butterfly valve is not serviceable. When the EPR is commanded on, the actuator rod should move to a closed position, the actuator rod will move up into the vacuum actuator. Assure vacuum arrives to the vacuum actuator. Visually inspect the action of the vacuum actuator linkage, their should be a fast response of the mechanism, not a sluggish response. For removal of the EPR actuator, refer to EPR Solenoid Replacement. If the EPR butterfly valve is stuck open, it is probable that no symptoms will be seen. Although, it is possible that a slight increase in white smoke on start up only and longer cab warm up times may be noticed. If the EPR butterfly valve is stuck closed, then symptoms include loss of power, black smoke, and stumble, especially over 1500 rpm. Other associated concerns with unwanted excessive back pressure (Butterfly valve stuck closed) over 1200 rpm includes possible valve train damage and exhaust manifold gasket leakage. It is possible that exhaust leaks from the bushing area of the butterfly valve may create a whistling noise, this is normal. Possible causes of failure in the system include frozen butterfly valve, vacuum leaks, binding or sticking linkage, plugged EPR solenoid vent, misrouted vacuum lines, wiring, vacuum actuator not holding vacuum, plugged catalytic converter.
An intermittent may be caused by the following:
| • | Poor connections. |
| • | Rubbed through wire insulation. |
| • | Broken wire inside the insulation. |
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the Diagnostic Table.
-
The scan tool data list will display status of a EPR Solenoid Test (Pass, Open/Grounded or Shorted to B+) and what the desired state of the EPR Solenoid (On or Off) is.
-
The ECT is disconnected in this step to energize the EPR solenoid continuously.
-
This check can detect a partially shorted coil which would cause excessive current flow. Leaving the circuit energized for 2 minutes allows the coil to warm up. When warm, the coil may open (amps drop to zero), or short (amp draw greater than 0.75A).
-
This check can detect an open in the EPR control circuit. If the PCM responds to the test (Pass), the circuit is OK.
-
When the PCM is replaced, the correct programing procedures need to be per formed.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Important: Before clearing any DTCs, use the scan tool Capture Info to save freeze frame and failure records for reference, as the Scan tool loses data when using the Clear Info function. Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||
Does the scan tool display Open/Grounded? | -- | |||
Important: The ECT sensor must be reconnected after this test has been completed. Does the scan tool display Short to B+? | ||||
Is the current draw less than the specified value, but not zero? | 0.75 A | |||
5 |
Does the scan tool display Open/Grounded? | -- | ||
6 |
Is the test light ON? | -- | ||
Does the EPR Solenoid Test on the scan tool display Pass? | -- | |||
8 | The DTC is intermittent. If no additional DTCs are stored, refer to Diagnostic Aids. If additional DTCs were stored refer to the applicable DTC table(s) first. Are any additional DTCs stored? | -- | Go to the Applicable DTC Table | Go to Diagnostic Aids |
9 | locate an repair the short to B+ in the EPR solenoid control circuit. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
10 |
Did you find a problem? | -- | ||
11 |
Did any terminals require replacement? | -- | ||
12 | Check for a proper connection at the PCM EPR solenoid control circuit. Did you find a problem? | -- | ||
13 | Repair the open in the ignition feed circuit. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
14 | Replace the EPR solenoid. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
Replace the PCM. Important: The new PCM must be programmed. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | ||
16 |
Does the Scan Tool indicate the diagnostic Passed? | -- | ||
17 | Does the Scan tool display any additional undiagnosed DTCs? | -- | Go to the Applicable DTC Table | System OK |
