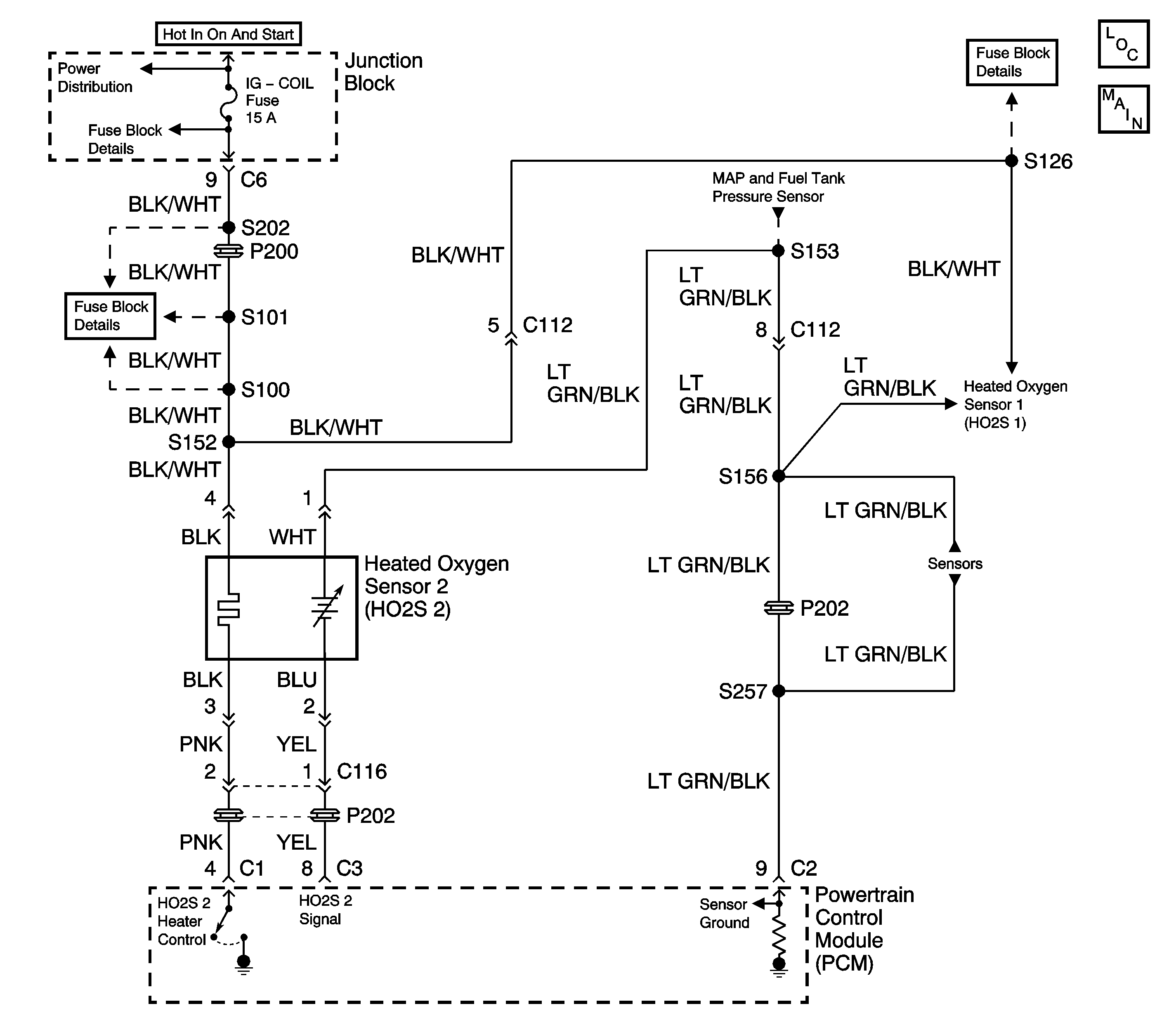
Circuit Description
In order to control emissions of Hydrocarbons (HC), Carbon Monoxide (CO), and Oxides of Nitrogen (NOx), a three-way catalytic (TWC) converter is used. The catalyst within the converter promotes a chemical reaction that oxidizes the HC and CO present in the exhaust gases. The oxidation process converts the HC and CO into harmless water vapor and carbon dioxide. The catalyst also reduces NOx by converting NOx to nitrogen. The powertrain control module has the ability to monitor this process using the HO2S 1 and the HO2S 2. The HO2S 1 produces an output signal which indicates the amount of oxygen present in the exhaust gases entering the TWC converter. The HO2S 2 produces an output signal that indicates the oxygen storage capacity of the catalyst in the TWC converter. The oxygen storage capacity of the catalyst is an indicator of the converter's ability to convert exhaust gases efficiently. The HO2S 1 output signal is more active than the HO2S 2 output signal when the catalyst is operating efficiently.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | Engine speed is greater than 1,500 RPM. |
| • | Vehicle speed is 32 to 80 km/h (20 to 50 mph). |
| • | Engine coolant temperature is greater than or equal to 80°C (176°F). |
| • | Intake air temperature is between -10°C and 70°C (14°F to 158°F). |
| • | Barometric pressure is greater than 75 kPa. |
| • | Fuel tank level is greater than 25%. |
| • | Engine is running in closed loop mode. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
Maximum HO2S 2 voltage is less than 600 mV for at least 8 minutes.
OR
| • | Minimum HO2S 2 voltage is greater than or equal to 300 mV, after a maximum voltage check during fuel shut-off mode. |
| • | The above condition is present for 5 seconds. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) after two consecutive ignition cycles in which the diagnostic runs with the fault active. |
| • | The PCM records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. This information is stored in the Freeze Frame buffer. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The MIL turns OFF after three consecutively passing trips without a fault present. |
| • | A History DTC clears after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles without a fault. |
| • | Use the scan tool Clear DTC Information function or disconnect the PCM battery feed in order to clear the DTC. |
Diagnostic Aids
Check for any of the following conditions:
| • | Inspect the exhaust system for leaks. Check the exhaust system between the three way catalytic converter and the flange for leaks, for corrosion, or for loose or missing hardware. Repair as necessary. |
| • | Misrouted heated oxygen sensor wiring. The sensor pigtail may be misrouted and contacting the exhaust system causing a fault in the sensor circuitry. |
| • | Inspect the HO2S 2 carefully for physical damage. Road hazards are more likely to damage the HO2S 2 because of the sensor's location under the vehicle chassis. |
| • | A shorted heated oxygen sensor (HO2S). An HO2S 2 that is shorted to ground or voltage can set a DTC P0136. Water contamination of the HO2S 2 can cause a short to occur in the sensor circuitry. A DTC P0136 that occurs more frequently when driving through standing water or when operating the vehicle in wet driving conditions can indicate a water intrusion. Replace the HO2S 2 if it is adversely affected by moisture. |
| • | A faulty HO2S 2 electrical connection to the PCM. |
An intermittent malfunction may be caused by a fault in the HO2S 2 sensor electrical circuit. Inspect the wiring harness and components for any of the following conditions:
| • | Backed out terminals. |
| • | Improper mating of terminals. |
| • | Broken electrical connector locks. |
| • | Improperly formed or damaged terminals. |
| • | Faulty terminal to wiring connections. |
| • | Physical damage to the wiring harness. |
| • | A broken wire inside the insulation. |
| • | Corrosion of electrical connections, splices, or terminals. |
If a DTC P0136 cannot be duplicated, the information included in the Freeze Frame data can be useful in determining vehicle operating conditions when the DTC was first set.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers in the Diagnostic Table.
-
The Powertrain OBD System Check prompts the technician to complete some basic checks and store the freeze frame data on the scan tool if applicable. This creates an electronic copy of the data taken when the fault occurred. The information is then stored in the scan tool for later reference.
-
A cold HO2S 2 will read 1 275 mV on a scan tool. The engine must be at normal operating temperature in order to continue diagnosis.
-
Review the Freeze Frame data in order to determine when the DTC set. Always record this information.
-
Normal voltage on the HO2S 2 signal circuit with the sensor disconnected is 4 to 5 volts. When the temperature of the HO2S 2 rises the voltage will decrease and fluctuate between 100 mV and 900 mV.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic System Check? | -- | |||
Did the HO2S 2 voltage start at the specified value and then drop to less than the specified value as the engine warmed? | 1 275 mV | |||
Is a DTC P0136 set? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | ||
Is the HO2S 2 signal circuit voltage within the specified value? | 4 to 5 volts | |||
5 |
Does the scan tool indicate HO2S 2 voltage below the specified value? | 100 mV | ||
6 |
Does the test lamp illuminate? | -- | ||
7 | Replace the HO2S 2. Refer to Heated Oxygen Sensor Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
8 |
Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||
9 |
Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||
10 |
Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||
11 | Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
12 |
Are any DTCs displayed on the scan tool? | -- | Go to the Applicable DTC Table | System OK |
