Throttle Body Assembly
The throttle body contains a throttle valve that controls the amount of air entering the engine. The throttle position (TP) sensor and idle air control (IAC) valve are attached to the throttle body. The throttle body has an engine coolant passage that provides warming of the throttle body housing and prevents icing.
The throttle body contains vacuum ports that are located above and below the throttle valve. These vacuum ports provide the vacuum signals used by various components.
Accelerator Controls
The accelerator control system is cable-operated. When the accelerator pedal is depressed the cable pulls the throttle lever open (increasing the throttle plate opening), and when the accelerator pedal is released, the throttle lever spring pressure returns the throttle lever to the idle position (decreasing the throttle plate opening).
Fuel Injector
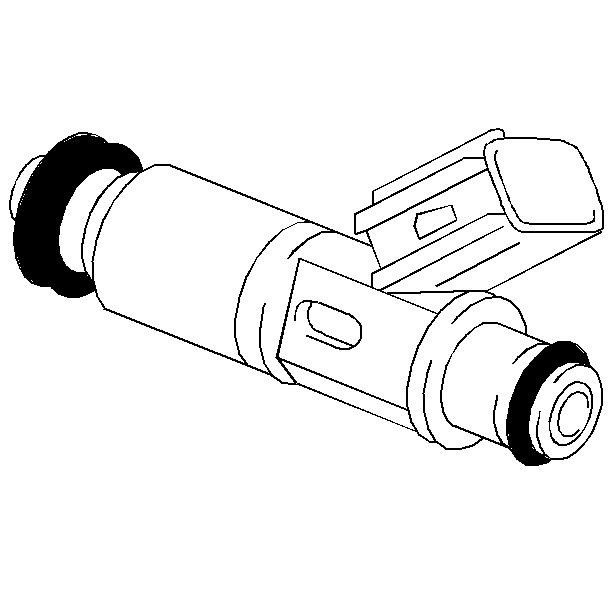
The fuel injector is an electromagnetic (solenoid) type injection nozzle which injects fuel into the intake port of the cylinder head according to the signals from the powertrain control module (PCM). There are four fuel injectors (one for each cylinder) located between the intake manifold and the fuel rail.
The powertrain control module energizes the solenoid coil of the fuel injector, generating an electromagnet field that attracts the solenoid plunger. The needle valve, which is incorporated with the solenoid plunger, is opened by the movement of the solenoid plunger. The opening of the needle valve allows fuel that is under pressure to disperse in a cone shaped (conic) pattern. Because the stroke of the needle valve in the fuel injector is set constant, the amount of fuel injected at one time is determined by the length of time the solenoid coil is energized (pulse width injection time).
Fuel Pressure Regulator
The fuel pressure regulator is installed on the fuel rail. The fuel pressure regulator is a diaphragm-operated pressure relief valve consisting of a diaphragm, a spring and a valve. The fuel pressure applied to the fuel injectors is regulated by the fuel pressure regulator. The fuel pressure regulator keeps the fuel pressure applied to the fuel injectors 264-304 kPa (38-44 psi).
