For 1990-2009 cars only
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Valve Inspection
Caution: If the EGR valve is hot, wear gloves in order to prevent personal injury.
Important: The PCM must see VSS input for operation of the EGR solenoid vacuum valve.
- Start the engine.
- Run the engine to normal operating temperature.
- Raise and suitably support the vehicle's drive axles.
- Place the transfercase in 2H and the transmission in Neutral.
- Check for vehicle speed with a scan tool.
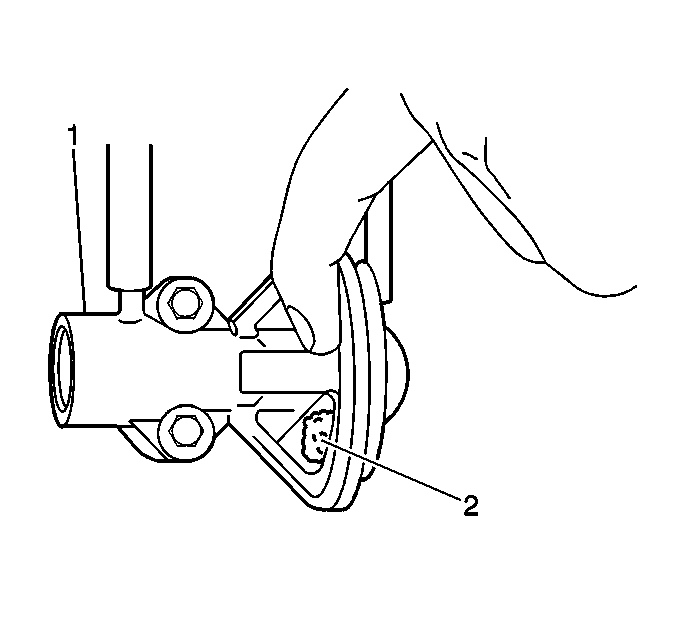
- Place one finger on the exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) valve diaphragm (2) and accelerate the engine. The diaphragm should move.
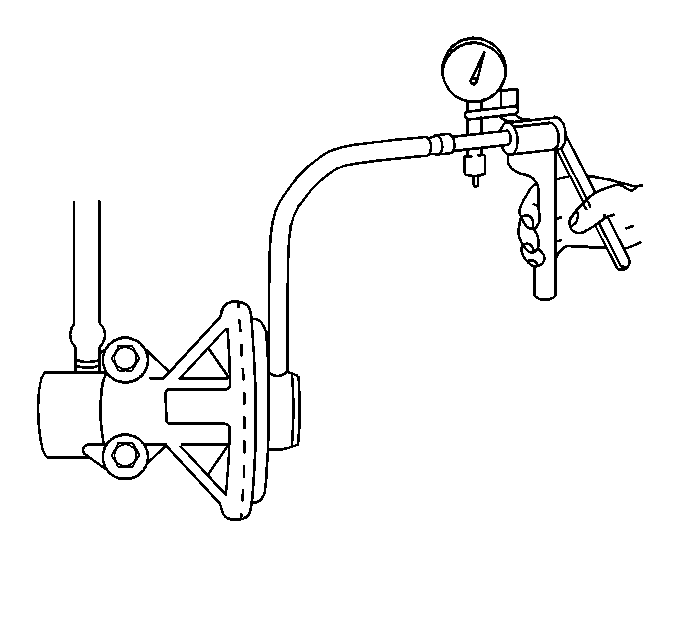
- Disconnect the vacuum hose to the EGR valve.
- Connect a hand vacuum pump to the EGR valve.
- Apply 27 kPa (8 in. Hg) of vacuum pressure while checking for movement of the EGR valve diaphragm with one finger. The diaphragm should move and the engine should stall.
- Review the results of the checks in step 6 and step 9 for the following conditions:
| • | If the EGR valve diaphragm did not move in either check, replace the EGR valve. Refer to Exhaust Gas Recirculation Valve Replacement . |
| • | If the EGR valve diaphragm did not move in step 6, inspect for a vacuum signal from the EGR solenoid vacuum valve. |
| • | If the engine did not stall in step 9, check for carbon deposits or restrictions in the EGR valve and passages. The restriction may be small enough that engine performance is normal, yet large enough to cause a DTC to set. Refer to Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) System Cleaning . |
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Back Pressure Transducer Inspection
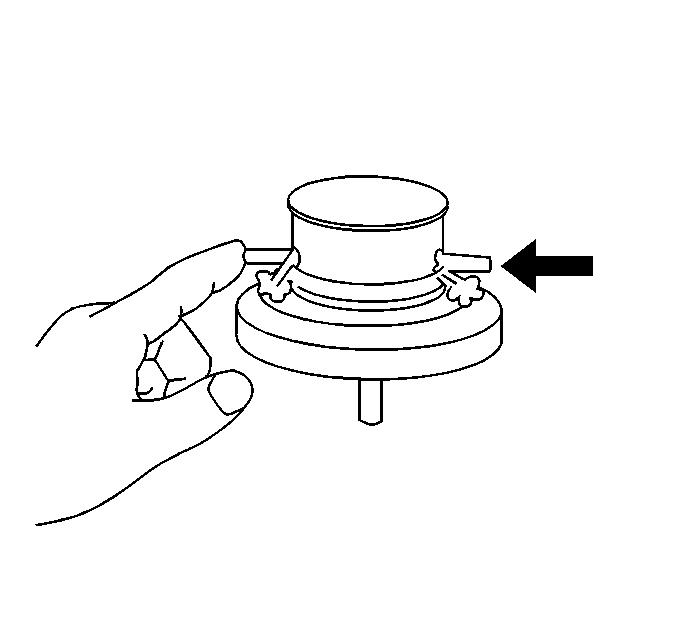
- Check the filter (1) for any contamination and damage. Use compressed air to clean filter.
- Remove the three vacuum hoses from the exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) back pressure transducer.
- Place one finger over the EGR back pressure transducer tube.
- Blow air into the opposite tube. Air should pass through the filter part of the pressure transducer.
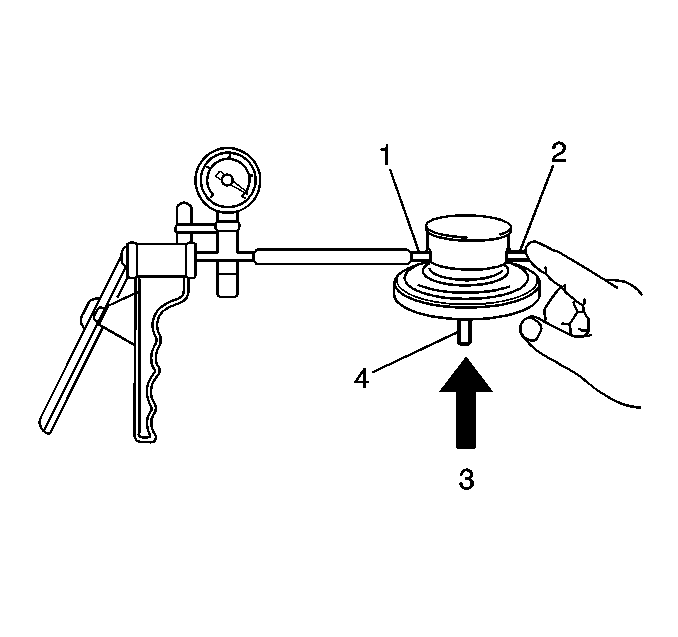
- Connect a vacuum pump to tube P (1) and plug tube Q (2) with your finger.
- Blow air (3) into tube A (4) while applying vacuum to tube P at the same time. You should be able to obtain vacuum on the vacuum pump gauge.
- Stop blowing air into tube A. The vacuum pump gauge should read zero.
- Replace the EGR back pressure transducer if the transducer fails either test. Refer to Exhaust Gas Recirculation Back Pressure Sensor Replacement .
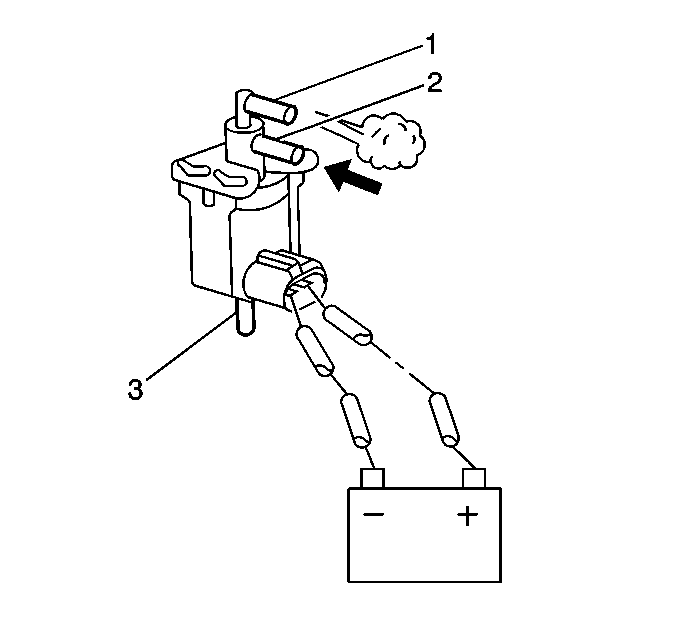
Exhaust Gas Recirculation Solenoid Vacuum Valve Inspection
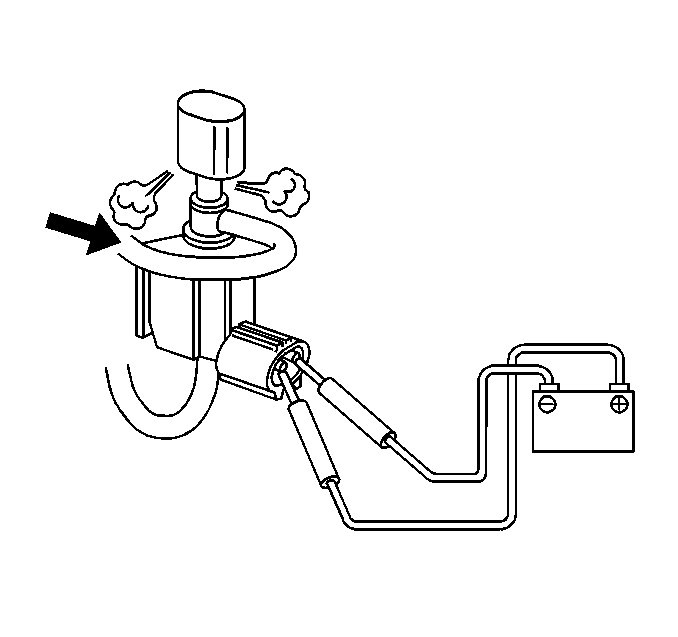
- Disconnect the two vacuum hoses from the EGR solenoid vacuum valve.
- Disconnect the EGR solenoid vacuum valve electrical connector.
- Connect the battery voltage to the EGR solenoid vacuum valve.
- Blow air into tube A (side port). The air should exhaust from the filter and not from tube B (bottom port).
- Replace the EGR solenoid vacuum valve if the valve does not pass both checks. Refer to Exhaust Gas Recirculation Solenoid Vacuum Valve Replacement .
- Connect the EGR solenoid vacuum valve electrical connector.
- Connect the two vacuum hoses to the EGR solenoid vacuum valve.
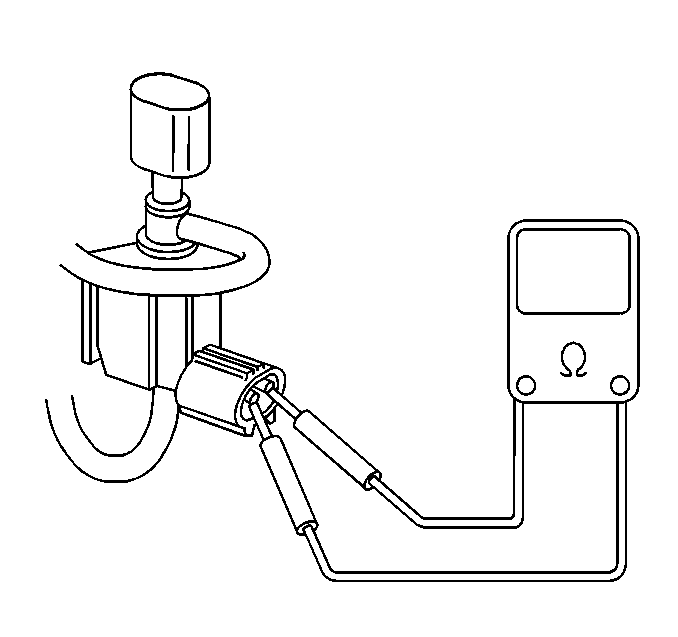
Measure
| • | Measure the resistance of the EGR solenoid vacuum valve terminals (valve side). The resistance should be 28-36 ohms at 20°C (68°F). |
| • | Replace the EGR solenoid vacuum valve If the resistance is not within the correct specification. |
| • | Blow air into tube A (side port). The air should exhaust from tube B (bottom port). |
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Bypass Valve Inspection
- Disconnect the three vacuum hoses from the exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) bypass valve (2).
- Disconnect the EGR bypass valve electrical connector.
- Connect battery voltage to the EGR bypass valve.
- Blow air into the inlet tube (2). Air should exhaust from bypass tube (1) and not from the outlet tube (3).
- Replace the EGR bypass valve if the valve does not perform satisfactorily. Refer to Exhaust Gas Recirculation Bypass Valve Replacement .
- Connect the EGR bypass valve electrical connector.
- Connect the three vacuum hoses to the EGR bypass valve.
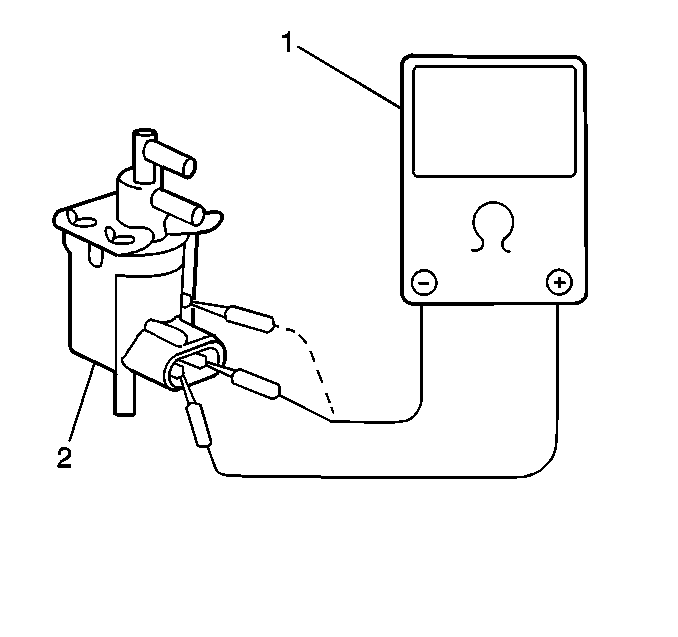
Measure
| • | Measure the resistance of the EGR bypass valve terminals (valve side). The resistance should be 37-44 ohms at 20°C (68°F). |
| • | Measure the resistance between the terminal (valve side) and the body. The DMM should read 1M ohm or higher. |
| • | If the resistance is not within the correct specification in either check, replace the EGR bypass valve. Refer to Exhaust Gas Recirculation Bypass Valve Replacement . |