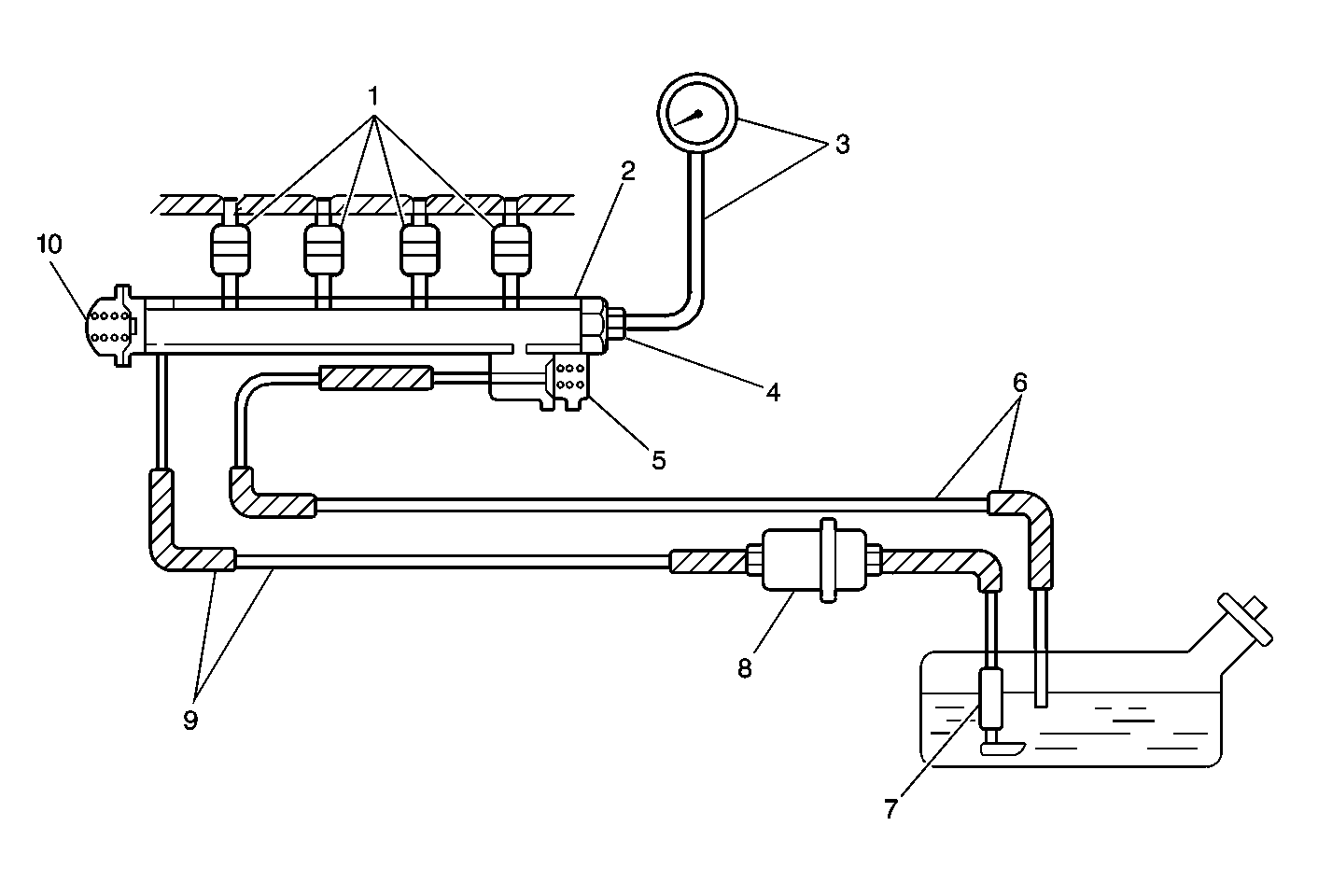
The powertrain control module (PCM) will energize the fuel pump relay
for 3 seconds when the ignition switch is turned to the ON position. The fuel
pump will operate and pressurize the fuel system when the fuel pump relay
is energized. The PCM receives ignition system reference pulses when the engine
is being cranked or when the engine is running. The PCM will continue to energize
the fuel pump relay as long as the PCM receives ignition system reference
pulses. The PCM will de-energize the fuel pump relay when ignition system
reference pulses are no longer detected.
The fuel supply system delivers fuel to the fuel injectors at a controlled
pressure. The controlled fuel pressure is 250-300 kPa (36-43 psi)
when the fuel pump is energized and the engine not running. The controlled
fuel pressure is 210-260 kPa (30-37 psi) when the
engine is idling at normal operating temperatures. The fuel pressure regulator
maintains the correct fuel pressure at all times by returning excess fuel
to the fuel tank.
One minute after the fuel pump stops, fuel pressure should hold at approximately
180 kPa (25 psi) or higher.
An intermittent malfunction may be caused by a problem in the fuel pump
electrical circuit. Inspect the wiring harness and components for any of the
following conditions:
The numbers below refer to the step numbers in the Diagnostic Table.
Step
| Action
| Value(s)
| Yes
| No
|
1
| Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic System Check?
| --
|
Go to Step 2
| Go to
Powertrain On Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check
|
2
|
- Turn OFF the ignition.
- Install the
J 34730-1A
fuel pressure
gauge or an equivalent. Refer to
Fuel Pressure Gage Installation and Removal
.
- Check that the vehicle has an adequate supply of fuel.
- Turn ON the ignition, leaving the engine OFF (the fuel pump should
run for approximately 2 seconds).
Was there any fuel pressure indicated?
| --
|
Go
to Step 3
|
Go to Step 13
|
3
|
- Turn OFF the ignition.
Important: In order to obtain maximum fuel pressure it may be necessary to cycle
the ignition ON to OFF to ON more than once.
- Turn ON the ignition, leaving the engine OFF (the fuel pump should run
for approximately 2 seconds).
- Observe the fuel pressure while the fuel pump is running.
Is the fuel pressure indicated within the specified values?
| 250 to 300 kPa
(36 to 43 psi)
|
Go to Step 4
|
Go to Step 11
|
4
|
- Turn OFF the ignition.
- Observe the fuel pressure gauge for one minute after the fuel
pump stops.
Does the fuel pressure hold at or above the specified value?
| 180 kPa
(25 psi)
|
Go to Step 5
|
Go to Step 7
|
5
| Start the engine.
Does the vehicle start and run?
| --
|
Go to Step 6
|
Fuel Injector Circuit Diagnosis
|
6
| Run the engine to normal operating temperature.
Is the fuel pressure indicated within the specified values?
| 210 to 260 kPa
(30 to 37 psi)
| System OK
|
Go to Step 9
|
7
|
- Check the fuel injectors and the fuel feed pipes and hoses for
leaks.
- Repair as necessary.
Was a repair necessary?
| --
|
Go to Step 19
|
Go to Step 8
|
8
|
- Turn ON the ignition, leaving the engine OFF (the fuel pump should
run for approximately 2 seconds).
- Observe the fuel pressure while blocking (pinching) the fuel feed
hose between the fuel pressure gauge and the fuel pump, immediately after
the fuel pump stops.
Does the fuel pressure hold at or above the specified value?
| 180 kPa
(25 psi)
|
Go to Step 18
|
Go to Step 9
|
9
|
- Turn ON the ignition, leaving the engine OFF (the fuel pump should
run for approximately 2 seconds).
- Observe the fuel pressure while blocking (pinching) the fuel return
hose.
Does the fuel pressure remain at or above the specified value?
| 180 kPa
25 psi)
|
Go to Step 17
|
Go to Step 10
|
10
|
- Check for any of the following:
| • | A leaking fuel pressure regulator. |
- Repair or replace as necessary.
Is the action complete?
| --
|
Go to Step 19
| --
|
11
| Is the fuel pressure below the specified value?
| 250 kPa (36 psi)
|
Go to Step 12
|
Go to Step 15
|
12
|
Important: In order to obtain maximum fuel pressure it may be necessary to cycle
the ignition ON to OFF to ON more than once.
- Turn ON the ignition, leaving the engine OFF (the fuel pump should
run for approximately 2 seconds).
- Check the fuel pressure while blocking (pinching) the fuel return
hose.
Is the fuel pressure at the specified value or higher?
| 400 kPa (57 psi)
|
Go to Step 17
|
Go to Step 13
|
13
| Was the fuel pump relay diagnostic procedure/table performed?
| --
|
Go to Step 14
| Go to
Fuel Pump Electrical Circuit Diagnosis
|
14
|
- Check for any of the following conditions:
| • | Check for a restricted fuel feed pipe, hose, or fuel filter. |
| • | Check for restrictions or leaks in fuel feed pipes, hoses, or
connections inside the fuel tank. |
| • | Inspect entire fuel pump circuit. Verify B+ voltage at fuel pump
connector and less than 5.0 ohms of resistance to ground. |
- Repair as necessary.
Was a repair necessary?
| --
|
Go to Step 19
|
Go to Step 18
|
15
|
- Turn OFF the ignition.
- Relieve fuel system pressure. Refer to
Fuel Pressure Relief
.
- Disconnect the fuel return hose from the fuel pressure regulator.
- Connect a new fuel hose to the fuel pressure regulator.
- Insert the other end of the new fuel hose into an approved gasoline
container.
- Turn ON the ignition, leaving the engine OFF.
Is the fuel pressure within the specified value?
| 250 to 300 kPa (36
to 43 psi)
|
Go to Step 16
|
Go to Step 17
|
16
| Repair/replace the restricted
fuel return pipe or hose.
Is the action complete?
| --
|
Go to Step 19
| --
|
17
| Replace the fuel pressure regulator. Refer to
Fuel Pressure Regulator Replacement
.
Is the action complete?
| --
|
Go to Step 19
| --
|
18
| Replace the fuel pump. Refer to
Fuel Pump Replacement
.
Is the action complete?
| --
|
Go to Step 19
| --
|
19
| Operate the vehicle within the conditions under which the original symptom
was noted.
Does the system now operate properly?
| --
| System OK
| Go to Diagnostic Aids
|