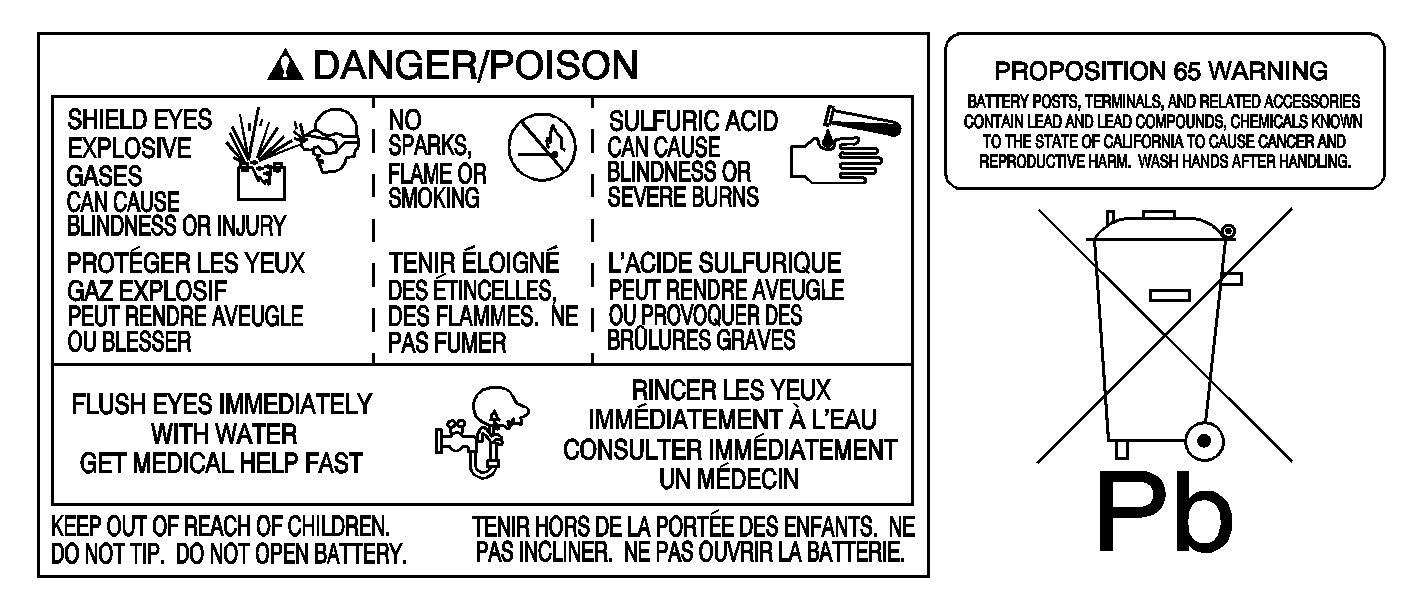
Caution: Batteries produce explosive gases. Batteries contain corrosive acid.
Batteries supply levels of electrical current high enough to cause burns.
Therefore, in order to reduce the risk of personal injury while working
near a battery, observe the following guidelines:
| • | Always shield your eyes. |
| • | Avoid leaning over the battery whenever possible. |
| • | Do not expose the battery to open flames or sparks. |
| • | Do not allow battery acid to contact the eyes or the skin. |
| - | Flush any contacted areas with water immediately and thoroughly. |
Important: Because of the materials used in the manufacture
of automotive lead-acid batteries, dealers and service shops that handle them are
subject to regulations issued by various state or local agencies. Other regulations
may also apply in other locations. Always know and follow these regulations when handling
batteries.
Batteries that are no longer wanted must be disposed of by
an approved battery recycler and must never be thrown in the rubbish or sent to a
land-fill.
Batteries that are not part of the vehicle itself, not the battery under the
hood, must only be transported on public streets for business purposes via approved
hazardous material transportation procedures.
Battery storage, charging and testing facilities in repair shops must meet various
requirements for ventilation, safety equipment, material segregation, etc.
The maintenance-free battery has no vent plugs in the cover. The battery is
completely sealed except for 2 small vent holes in the side. These vent holes allow
the small amount of gas that is produced in the battery to escape.
The battery has 3 functions as a major source of energy:
| • | Alternate source of energy with alternator overload |
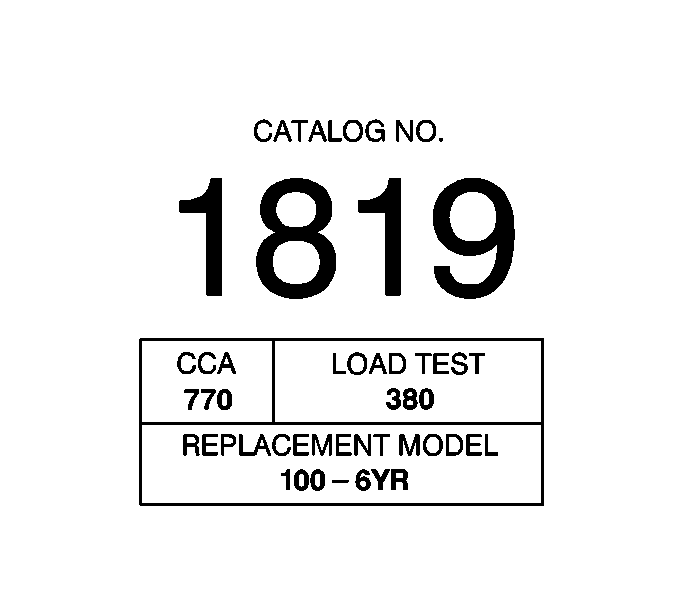
The battery specification label, example below, contains information about the
following:
| • | The original equipment catalogue number |
| • | The recommended replacement model number |
Battery Ratings
A battery may have 3 ratings:
| • | Cold Cranking Amperage (CCA) |
When a battery is replaced, use a battery with the same ratings. Refer to the
battery specification label on the original battery or refer to
Battery Usage
.
Amp Hour (AH)
The amp hour rating of a battery is the amount of time it takes a fully charged
battery, being discharged at a constant rate of 1 amperes and a constant temperature
of 27°C (80°F), to reach a terminal voltage of 10.5 volts. Refer to
Battery Usage
for the amp hour rating of the
original equipment battery.
Reserve Capacity (RC)
Reserve capacity is the amount of time in minutes it takes a fully charged battery,
being discharged at a constant rate of 25 amperes and a constant temperature
of 27°C (80°F), to reach a terminal voltage of 10.5 volts. Refer to
Battery Usage
for the reserve capacity rating
of the original equipment battery.
Cold Cranking Amperage (CCA)
The cold cranking amperage is an indication of the ability of the battery to
crank the engine at cold temperatures. The cold cranking amperage rating is the minimum
amperage the battery must maintain for 30 seconds at -18°C (0°F)
while maintaining at least 7.2 volts. Refer to
Battery Usage
for the cold cranking amperage rating for this vehicle.
Police Package Special Equipment Battery Options
Important: GM cannot be held responsible for any changes
made to the vehicle. All electrical and body modifications must be preformed by experience
and qualified technicians.
| • | Be sure that any modified or added wiring will not impact the function
of the vehicles factory wiring system. |
| • | See that all wiring is correctly protected by fuses, and not causing a
overload to connectors and components. |
| • | Do not route wiring in areas of the vehicle where temperatures can be
high or where wiring may be cut, pinched or rubbed. |
| • | See that all wiring is of the same or smaller gauge to that of the wire
it is being attached to for correct fuse protection. |
| • | Be sure that all holes drilled in the body are correctly sealed and corrosion
protected. See that the vehicles wiring harnesses, piping, and other components have
not been displaced or damaged during customer installation of equipment and wiring. |
| • | See that the vehicles wiring harnesses, piping, and other components have
not been displaced or damaged during customer installation of equipment and wiring. |
Electrical Connections
Overloading the vehicles electrical system may damage the vehicles accessories.
Do not overload the vehicles system by having unnecessary accessories at the same
time.
Auxiliary Battery
The auxiliary battery is located in the rear compartment in the right hand side
quarter panel cavity. The auxiliary battery has a secondary fuse box attached to the
right hand side of the battery tray. The function of the auxiliary battery is to supply
power to all of the after market components fitted to the vehicle:
| • | Flashing lights (Front, rear and roof). |
Battery Isolator
The electrical system has a battery isolator located in the rear compartment
mounted on the left hand side quarter panel, the isolator should be mounted as close
as possible to the Start Battery with the coil terminal facing up or horizontal. The
battery isolator is designed to protect the Start Battery from excessive discharge
whist allowing the auxiliary battery to supply non-essential loads. The battery isolator
detects the Start Battery voltage when it drops below 12.7 Volts on a 12V system (25.4
volts on a 24V system) the solenoid will open, separating the Start Battery from the
auxiliary battery. Once the engine has been started the battery isolator monitors
the Start Battery and the charging system. When the charging system reaches 13.6V
(27.2 Volts on a 24V system) indicating a fully charge Start Battery, the battery
isolator will close the solenoid connecting the auxiliary battery to the Start Battery
and the charging system.


