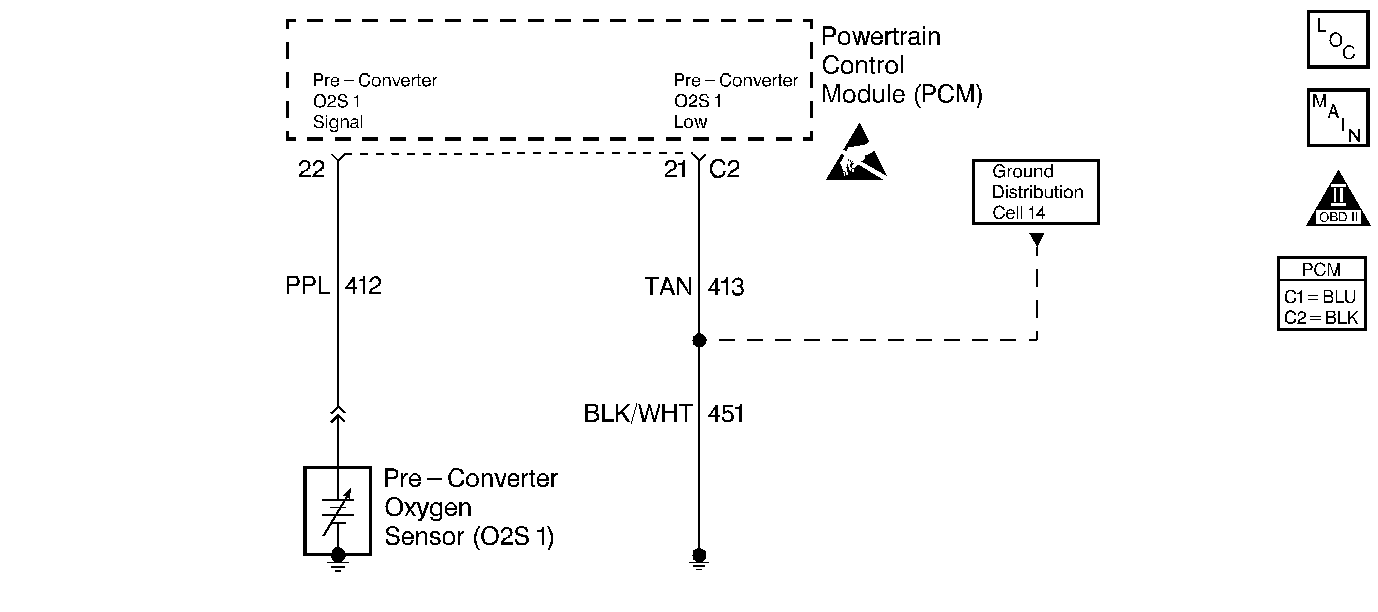
Circuit Description
The powertrain control module (PCM) supplies a voltage of about 0.45 volts to the oxygen sensor 1 (O2S 1). The O2S 1 varies the voltage between a range of about 1 volt if the exhaust is rich, down through about 0.10 volts if the exhaust is lean.
The O2S 1 is like an open circuit and produces no voltage when the O2S 1 temperature is below 315°C (600°F). An open O2S 1 circuit or cold sensor causes an Open Loop operation.
Conditions For Running The DTC
| • | No active MAP DTCs |
| • | No active IAT DTCs |
| • | No active ECT DTCs |
| • | No active TP DTCs |
| • | No active fuel trim DTCs |
| • | No active injector control DTCs |
| • | No active misfire DTCs |
| • | No active CKP DTCs |
| • | No active EVAP DTCs |
| • | No active IAC DTCs |
| • | No active PCM memory DTCs |
| • | Air flow is more than 3 grams per second |
| • | Engine coolant temperature (ECT) is more than 70°C (158°F) |
| • | Engine is operating in Closed Loop |
| • | Throttle position (TP) angle is between 5 percent and 50 percent |
| • | Engine has been in the above conditions for 3.8 seconds |
Conditions For Setting The DTC
O2S 1 voltage is more than 946 mV for 50 seconds.
Or
O2S 1 voltage is more than 1,042 mV for 2.5 seconds while in deceleration Fuel Cut-Off Mode.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The control module illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) if a failure is detected during 2 consecutive key cycles. |
| • | The control module sets the DTC and records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic failed. The failure information is stored in the scan tools Freeze Frame and Failure Records. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The control module turns OFF the MIL after 3 consecutive drive trips when the test has Run and Passed |
| • | A history DTC will clear if no fault conditions have been detected for 40 warm-up cycles. A warm up cycle occurs when the coolant temperature has risen 22°C (40°F) from the startup coolant temperature and the engine coolant reaches a temperature that is more than 70°C (158°F) during the same ignition cycle. |
| • | Use a scan tool to clear the DTCs. |
Diagnostic Aids
The DTC P0132 or rich exhaust is most likely caused by one of the following conditions:
| • | The fuel pressure -- The system will go rich if the fuel pressure is too high. The PCM can compensate for some increase. However, if the fuel pressure gets too high, a DTC P0132 will set, DTC P0133 and Po172 may also set. Refer to Fuel System Diagnosis . |
| • | A leaking injector -- A leaking or faulty fuel injector can cause the system to go rich causing a DTC P0132. Refer to Fuel Injector Solenoid Coil Test - Engine Coolant Temperature Between 10-35 Degrees C (50-95 Degrees F) and Fuel Injector Solenoid Coil Test - Engine Coolant Temperature Outside 10-35 Degrees C (50-95 Degrees F) . |
| • | The electronic ignition (EI) shielding -- An open ground circuit may result in EMI or induced electrical noise. The PCM looks at this noise as crankshaft position (CKP) sensor pulses. The additional pulses result in a higher than actual engine speed signal. The PCM then delivers too much fuel causing the system to go rich. The engine tachometer will also show higher than actual engine speed which can help in diagnosing this problem. |
| • | The manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor -- An output that causes the PCM to sense a higher than normal manifold pressure, or low vacuum, can cause the system to go rich. Disconnecting the MAP sensor will allow the PCM to set a fixed value for the MAP sensor. Substitute a different MAP sensor if the rich condition is gone while the sensor is disconnected. |
| • | The throttle position (TP) sensor -- An intermittent TP sensor output will cause the system to go rich due to a false indication of the engine accelerating. |
| • | An O2S 1 contamination -- Inspect the O2S 1 for a silicone contamination from fuel or use of improper RTV sealant. The O2S 1 may have a white powdery coating and result in a high but false voltage signal (rich exhaust indication). The PCM will then reduce the amount of fuel delivered to the engine causing a severe surge or driveability problem. |
| • | Whenever the oxygen sensor pigtail wiring, the connector, or the terminal are damaged, replace the entire oxygen sensor assembly. Do not attempt to repair the wiring, the connectors, or the terminals. In order for the sensor to function properly, the O2S 1 must have a clean air reference. The oxygen sensor wires obtains this clean air reference. Any attempt to repair the wires, the connectors, or the terminals may result in the obstruction of the clean air reference. Any attempt to repair the wires, the connectors, or the terminals may degrade the oxygen sensors performance. |
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table:
-
This DTC failing during deceleration fuel mode operation, with the vehicle speed more than 25 mph, and the throttle position (TP) angle less than 3 percent, may indicate a condition described in Diagnostic Aids. If this DTC test passes while the Failure Records conditions are being duplicated, an intermittent condition is indicated. Review the Failure Records vehicle mileage since the diagnostic test last failed. This may help determine how often the condition that caused the DTC to be set occurs.
-
The replacement PCM must be reprogrammed and the Crankshaft Position System Variation Learn procedure must be preformed.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||
2 |
Is the O2S 1 voltage fixed more than the specified value? | 946 mV | ||
Operate vehicle in the Decel fuel mode, with the vehicle speed more than 25 mph and the TP angle less than 3 percent, while observing the O2S 1 voltage on the scan tool. Does the O2S 1 voltage read more than the specified value? | 1042 mV | |||
4 | Operate the vehicle within the Failure Records conditions. Does the DTC reset? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | |
5 |
Does the O2S 1 voltage read more than the specified value? | 500 mV | ||
6 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||
7 | Replace the O2S 1. Refer to Oxygen Sensor Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | -- | |
|
Important:: The replacement PCM must be programmed. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement/Programming . Replace the PCM. Did you complete the replacement? | -- | -- | ||
9 |
Does the DTC reset? | -- | System OK |
