DTC C0235 or C035 Rear Wheel Speed Signal Circuit Open 4.3L
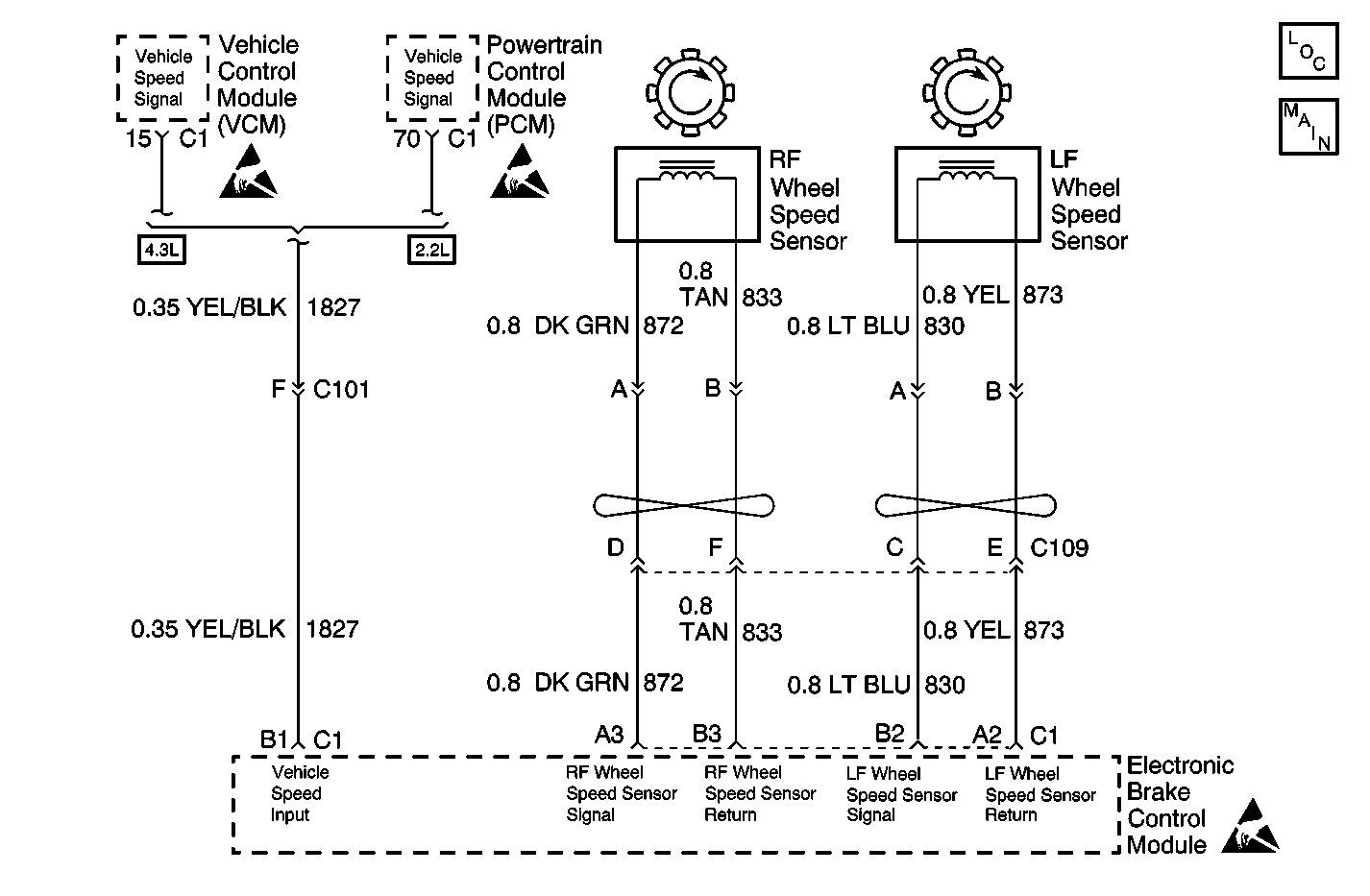
Circuit Description
The EBCM receives the rear wheel speed signal from the vehicle control module (VCM) (4.3L). The rear wheel speed signal originates from the vehicle speed sensor (VSS) which is connected to the VCM. The EBCM can not directly detect an actual vehicle speed sensor problem, so the EBCM checks for the presence of the VCM when the vehicle is not moving. This is accomplished by detecting 12 VDC from the VCM when the vehicle is powered-up and not moving. The EBCM will look for a persistent low signal from the VCM. If this condition is detected and persists for greater than 500 milliseconds, the DTC will set.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | Ignition switch in the RUN position. |
| • | The vehicle is not moving. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The EBCM senses no voltage from the VCM, for 500 milliseconds or greater, when the ignition is turned to RUN.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The ABS indicator lamp turns on |
| • | The ABS disables |
Malfunction responses to DTC C0235 vary, depending on the affected subsystem.
| • | ABS--Condition latched |
| • | DRP--DRP critical |
For a detailed explanation of DTC malfunction responses, refer to Self-Diagnostics
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
| • | Repair the conditions responsible for setting the DTC. |
| • | Use the Clear DTCs function on the Scan Tool |
| • | A Condition Latched DTC may exist momentarily, or constantly. In either case, the DTC will be stored in the EBCM memory until it is repaired, and/or the DTC is cleared. After the DTC is repaired and/or cleared and the ignition is turned to ON, the ABS lamp will remain lit until the EBCM completes a power-up self test. This test concludes when the vehicle has reached a speed of greater than 13 km/h (8 mph) and the wheel speed inputs have been checked by the EBCM. |
Diagnostic Aids
Check for and clear DTCs in the VCM first.
This DTC can be set by a faulty EBCM or a fault in CKT 1827.
If the voltage readings are low or varying, the battery or charging system could be the cause. Check these areas before replacing any components. In addition, any of the following conditions may cause an intermittent malfunction:
| • | A poor connection |
| • | Wire insulation that is rubbed through |
| • | A wire breaks inside the insulation |
Thoroughly check any circuitry that is suspected of causing the intermittent complaint for the following conditions:
| • | Backed out terminals |
| • | Improper mating |
| • | Broken locks |
| • | Improperly formed or damaged terminals |
| • | Poor terminal to wiring connections |
| • | Physical damage to the wiring harness |
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the steps in the diagnostic table:
-
This step uses the voltage output from the VCM to check the CKT 1827.
-
This step attempts to determine if there the VCM can process the VSS input and deliver a VSS output on CKT 1827.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the ABS Diagnostic System Check? | -- | Go to Step 2 | Go to Diagnostic System Check |
2 | Using the scan tool, check for any powertrain DTCs Does the scan tool indicate any powertrain DTCs? | -- | Go to Step 3 | |
Does the voltage measure greater than the specified value? | 10 volts | Go to Step 4 | Go to Step 5 | |
Does the voltage measure greater than the specified value? | 100 mv | Go to Step 7 | Go to Step 6 | |
5 | Test the vehicle speed sensor circuit for an open or short to ground. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 9 | Go to Step 8 |
6 | Test the vehicle speed sensor circuit for a short to voltage. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 9 | Go to Step 8 |
7 | Replace the EBCM. Refer to Electronic Brake Control Module Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | Go to Step 9 | -- |
8 | Replace the VCM. Refer to VCM Replacement/Programming . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | Go to Step 9 | -- |
9 | Operate the vehicle under the conditions for running the DTC as specified in the supporting text. Does the DTC set? | -- | Go to Step 2 | System OK |
DTC C0235 or C035 Rear Wheel Speed Signal Circuit Open 2.2L

Circuit Description
The EBCM receives the rear wheel speed signal from the powertrain control module (PCM) (2.2L). The rear wheel speed signal originates from the vehicle speed sensor (VSS) which is connected to the PCM. The EBCM can not directly detect an actual vehicle speed sensor problem, so the EBCM checks for the presence of the PCM when the vehicle is not moving. This is accomplished by detecting 12 VDC from the PCM when the vehicle is powered-up and not moving. The EBCM will look for a persistent low signal from the PCM. If this condition is detected and persists for greater than 500 milliseconds, the DTC will set.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | Ignition switch in the RUN position. |
| • | The vehicle is not moving. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The EBCM senses no voltage from the PCM, for 500 milliseconds or greater, when the ignition is turned to RUN.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The ABS indicator lamp turns on |
| • | The ABS disables |
Malfunction responses to DTC C0235 vary, depending on the affected subsystem.
| • | ABS--Condition latched |
| • | DRP--DRP critical |
For a detailed explanation of DTC malfunction responses, refer to Self-Diagnostics
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
| • | Repair the conditions responsible for setting the DTC. |
| • | Use the Clear DTCs function on the Scan Tool |
| • | A Condition Latched DTC may exist momentarily, or constantly. In either case, the DTC will be stored in the EBCM memory until it is repaired, and/or the DTC is cleared. After the DTC is repaired and/or cleared and the ignition is turned to ON, the ABS lamp will remain lit until the EBCM completes a power-up self test. This test concludes when the vehicle has reached a speed of greater than 13 km/h (8 mph) and the wheel speed inputs have been checked by the EBCM. |
Diagnostic Aids
Check for and clear DTCs in the PCM first.
This DTC can be set by a faulty EBCM or a fault in CKT 1827.
If the voltage readings are low or varying, the battery or charging system could be the cause. Check these areas before replacing any components. In addition, any of the following conditions may cause an intermittent malfunction.
| • | A poor connection |
| • | Wire insulation that is rubbed through |
| • | A wire breaks inside the insulation |
Thoroughly check any circuitry that is suspected of causing the intermittent complaint for the following conditions:
| • | Backed out terminals |
| • | Improper mating |
| • | Broken locks |
| • | Improperly formed or damaged terminals |
| • | Poor terminal to wiring connections |
| • | Physical damage to the wiring harness |
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the steps in the diagnostic table:
-
This step uses the voltage output from the PCM to check the CKT 1827.
-
This step attempts to determine if there the PCM can process the VSS input and deliver a VSS output on CKT 1827.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the ABS Diagnostic System Check? | -- | Go to Step 2 | Go to Diagnostic System Check |
2 | Using the scan tool, check for any powertrain DTCs Does the scan tool indicate any powertrain DTCs? | -- | Go to Step 3 | |
Does the voltage measure greater than the specified value? | 10 volts | Go to Step 4 | Go to Step 5 | |
Does the voltage measure greater than the specified value? | 100 mv | Go to Step 7 | Go to Step 6 | |
5 | Test the vehicle speed sensor circuit for an open or short to ground. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 9 | Go to Step 8 |
6 | Test the vehicle speed sensor circuit for a short to voltage. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 9 | Go to Step 8 |
7 | Replace the EBCM. Refer to Electronic Brake Control Module Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | Go to Step 9 | -- |
8 | Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement/Programming . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | Go to Step 9 | -- |
9 | Operate the vehicle under the conditions for running the DTC as specified in the supporting text. Does the DTC set? | -- | Go to Step 2 | System OK |
