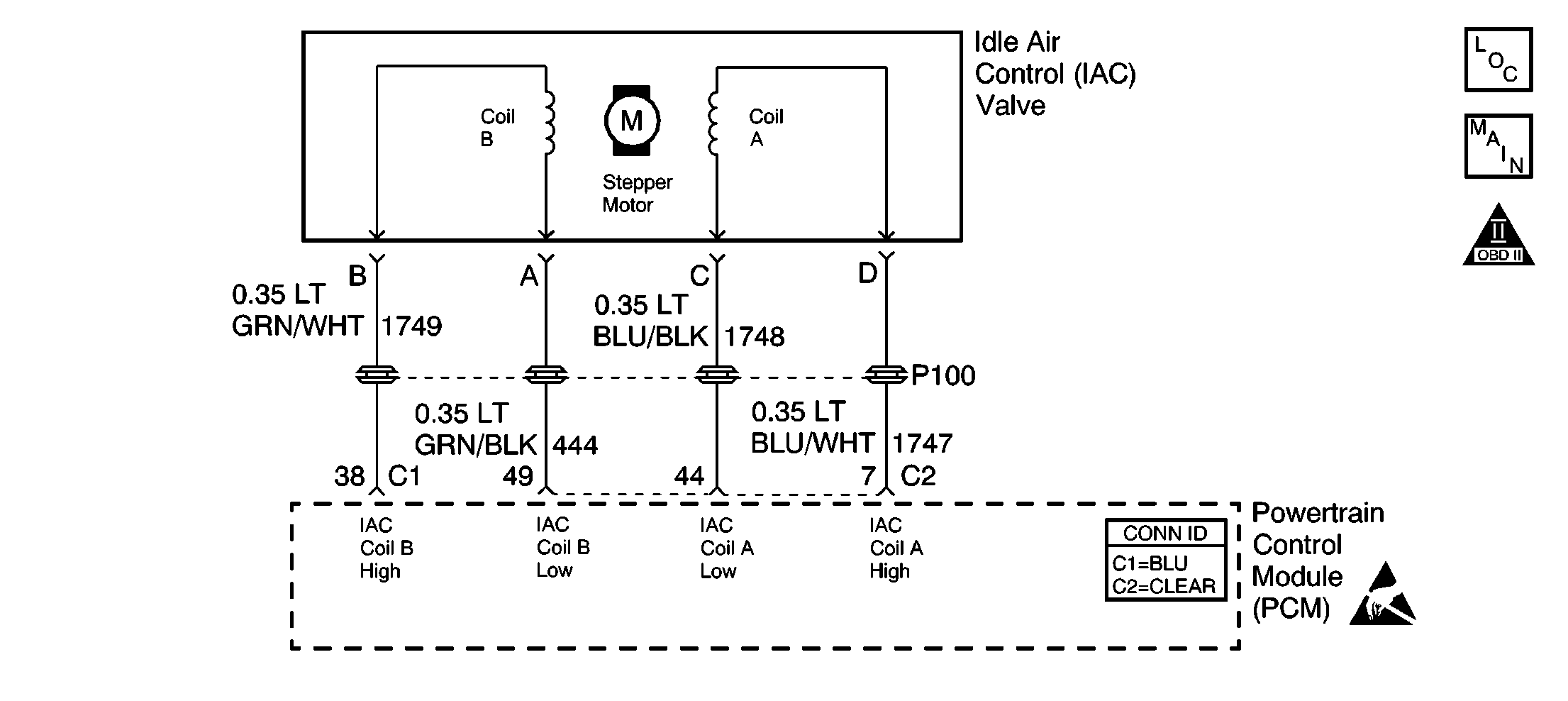
Circuit Description
The powertrain control module (PCM) controls engine idle speed by adjusting the position of the idle air control (IAC) motor pintle. The IAC is a bi-directional motor driven by two coils. The PCM pulses current to the IAC coils in steps to extend the IAC pintle into a passage in the throttle body to decrease air flow. The PCM reverses the current pulses to retract the pintle, increasing air flow. This method allows highly accurate control of idle speed and quick response to changes in engine load.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
| • | Poor connection at PCM or IAC motor -- Inspect harness connectors for the following conditions: |
| - | Backed out terminals |
| - | Improper mating |
| - | Broken locks |
| - | Improperly formed or damaged terminals |
| - | Faulty terminal to wire connection--Use a corresponding mating terminal to test for proper tension. Refer to Wiring Repairs Wiring Systems for diagnosis and repair. |
| • | Restricted air intake system -- Inspect for the following conditions: |
| - | Collapsed air intake duct |
| - | Restricted air filter element |
| - | Foreign objects blocking the air intake system |
| • | Throttle body -- Inspect for objects blocking the IAC passage or throttle bore, excessive deposits in the IAC passage and on the IAC pintle, and excessive deposits in the throttle bore and on the throttle plate. |
| • | Inspect for a sticking throttle plate -- Also inspect the IAC passage for deposits or objects which will not allow the IAC pintle to fully extend. |
| • | Vacuum leak -- Inspect for a condition that causes a vacuum leak, such as disconnected or damaged hoses, leaks at EGR valve and EGR pipe to intake manifold, leaks at throttle body, faulty or incorrectly installed PCV valve, leaks at intake manifold brake booster hose disconnected, etc. |
Many situations may lead to an intermittent condition. Perform each inspection or test as directed.
Important: : Remove any debris from the connector surfaces before servicing a component. Inspect the connector gaskets when diagnosing or replacing a component. Ensure that the gaskets are installed correctly. The gaskets prevent contaminate intrusion.
| • | Loose terminal connection |
| - | Use a corresponding mating terminal to test for proper tension. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections , and to Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems for diagnosis and repair. |
| - | Inspect the harness connectors for backed out terminals, improper mating, broken locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and faulty terminal to wire connection. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections , and to Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems for diagnosis and repair. |
| • | Damaged harness--Inspect the wiring harness for damage. If the harness inspection does not reveal a problem, observe the display on the scan tool while moving connectors and wiring harnesses related to the sensor. A change in the scan tool display may indicate the location of the fault. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems for diagnosis and repair. |
| • | Inspect the powertrain control module (PCM) and the engine grounds for clean and secure connections. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems for diagnosis and repair. |
If the condition is determined to be intermittent, reviewing the Snapshot or Freeze Frame/Failure Records may be useful in determining when the DTC or condition was identified.
Test Description
The number below refers to the step number on the diagnostic table:
Step | Action | Values | Yes | No | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||||||||||
2 |
Does Engine Speed remain within the specified value of Desired Idle for each RPM command? | approx. 50 RPM | System OK | |||||||||
3 |
Does each node illuminate cycle red and green, never OFF? | -- | ||||||||||
4 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||||
5 | Was a low idle symptom or rich condition noticed? | -- | ||||||||||
6 | Visually and physically inspect for the following conditions:
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||||
7 | Visually and physically inspect for the following conditions:
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||||
8 | Inspect for a poor connection at the IAC harness connector. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||||
9 | Replace the IAC valve. Refer to Idle Air Control Valve Replacement . Did you complete the repair? | -- | -- | |||||||||
10 | Inspect for a poor connection at the PCM harness connector. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||||
|
Important: The replacement PCM must be programmed. Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement/Programming . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | -- | ||||||||||
12 |
Does engine speed remain within the specified value of desired idle for each RPM command? | approximately 50 RPM | System OK |
