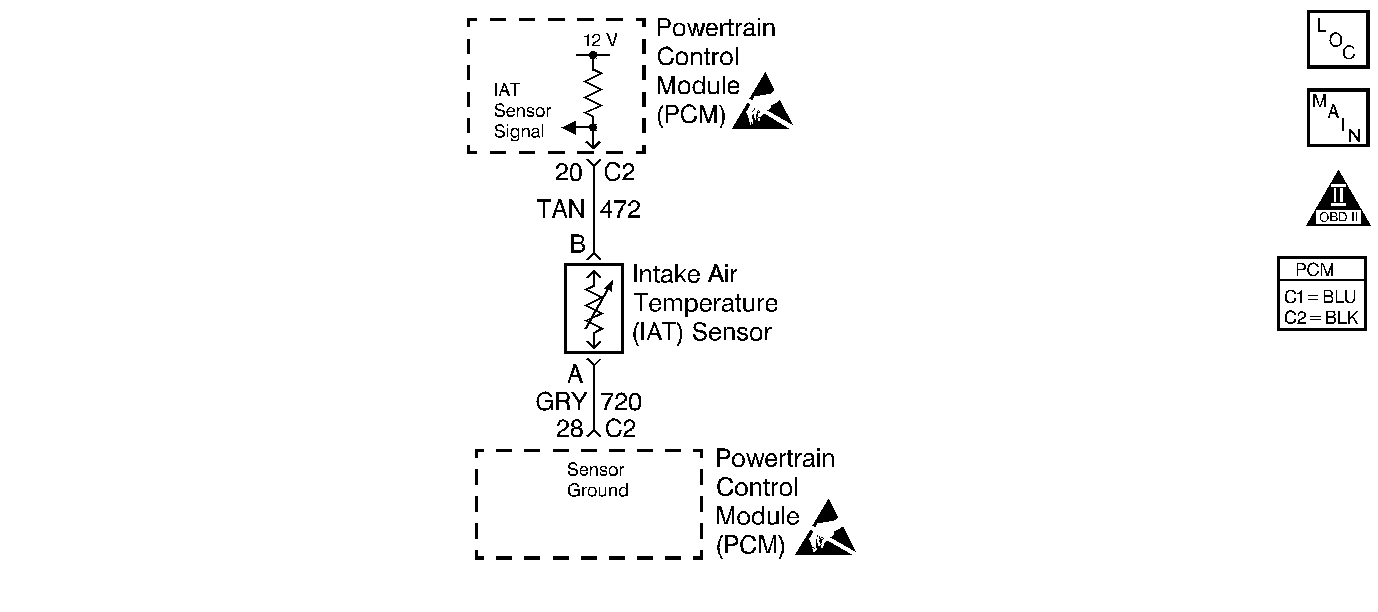
Circuit Description
The intake air temperature (IAT) sensor uses a thermistor to control the signal voltage to the Powertrain Control Module (PCM). The PCM supplies a 5 volt reference and a ground to the sensor. When the air is cold the resistance is high, therefore the IAT signal voltage will be high. If the intake air is warm, resistance is low, therefore the IAT signal voltage will be low.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | The engine run time is greater than 320 seconds. |
| • | The engine coolant temperature (ECT) is greater than -40°C. |
| • | The vehicle speed sensor indicates that vehicle speed is less than 15 mph (24 km/h). |
| • | The IAT sensor signal voltage indicates that the intake air temperature is less than -40°C for 3.125 seconds. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illuminate. |
| • | The PCM will record operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. This information will be stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records buffers. |
| • | A history DTC is stored. |
| • | Coolant fan turns ON. |
| • | The PCM will default to 60°C (140°F) for intake air temperature. The scan tool will not the show the defaulted value. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The MIL will turn OFF after three consecutive ignition cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault. |
| • | A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles without a fault. |
| • | The MIL/DTCs can be cleared by using the scan tool. |
Diagnostic Aids
| • | If the vehicle is at ambient temperature compare the IAT sensor to the ECT sensor. The IAT sensor and the ECT sensor should be relatively close to each other. |
| • | Use the Temperature vs. Resistance Values table, refer to Temperature vs Resistance to evaluate the possibility of a skewed sensor. |
Test Description
The number(s) below refer(s) to the step number(s) on the Diagnostic Table.
-
The Powertrain OBD System Check prompts you to complete some of the basic checks and to store the freeze frame and failure records data on the scan tool if applicable. This creates an electronic copy of the data captured when the malfunction occurred. The scan tool stores this data for later reference.
-
This step simulates a DTC P0112. If the PCM senses the change, the PCM and wiring are OK.
-
This step will determine if the reason that the PCM did not sense the change was due to the following condition(s):
-
Reprogram the replacement PCM and perform the crankshaft position system variation learn procedure. Refer to the latest Techline information for PCM programming and the Crankshaft Position System Variation Learn for the crankshaft position system variation learn procedure.
| • | Open ground circuit |
| • | Short to voltage in the signal circuit |
| • | Malfunctioning PCM |
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | |||||||
2 |
Is the IAT sensor value less than the specified value? | -30°C (-22°F) | ||||||
3 |
Is the IAT sensor value less than the specified value? | -30°C (-22°F) | Go to Diagnostic Aids | |||||
Is the IAT sensor value greater than the specified value? | 130°C (266°F) | |||||||
Connect a fused jumper wire to the IAT sensor signal circuit terminal to a known good ground. Is the IAT sensor value greater than the specified value? | 130°C (266°F) | |||||||
6 |
Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||||||
7 |
Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||||||
8 |
Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||||||
9 |
Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||||||
10 | Replace the IAT sensor. Refer to the Intake Air Temperature Sensor Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||
Replace the PCM. Refer to the Powertrain Control Module Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | ||||||
12 |
Does the scan tool indicate that this diagnostic has ran and passed? | -- | ||||||
13 | Check to see if any additional DTCs are set. Does the scan tool display any DTCs that you have not diagnosed? | -- | Go to applicable DTC table | System OK |
