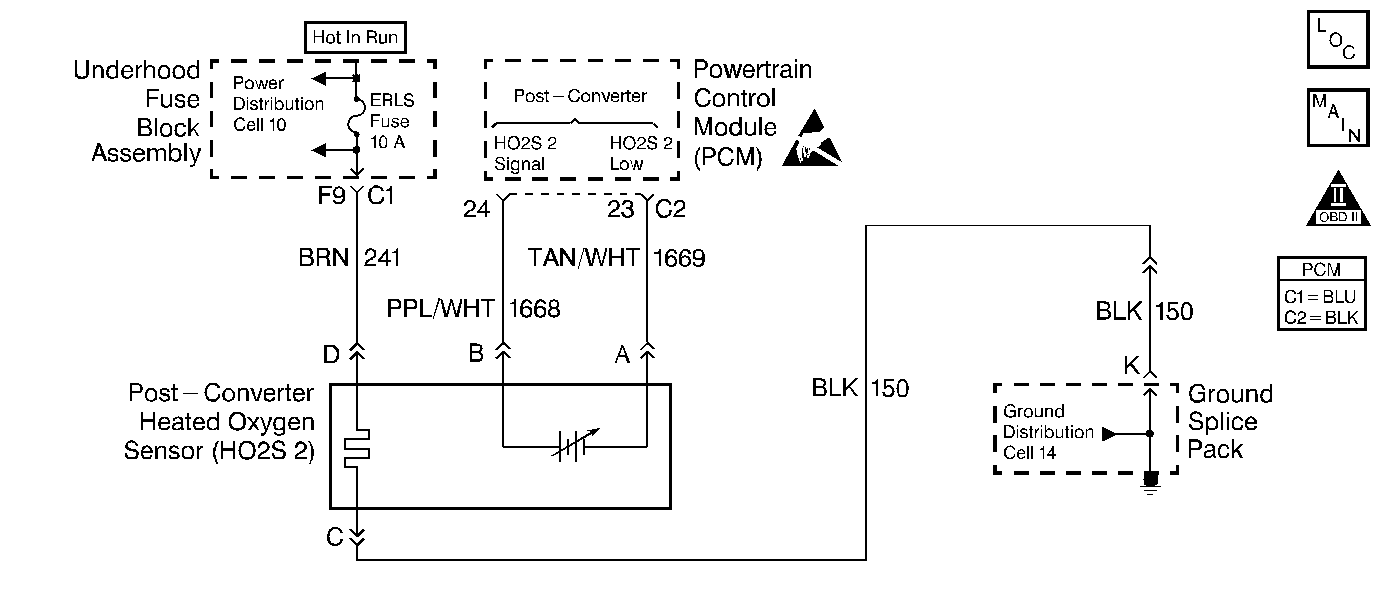
Circuit Description
In order to control emissions, a catalytic converter converts any harmful exhaust emissions into harmless water vapor and carbon dioxide.
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) has the capability to monitor this process by using a rear heated oxygen sensor (HO2S 2). The HO2S 2 , located in the exhaust stream past the catalytic converter, produces an output signal which indicates the storage capacity of the catalyst. This in turn indicates the catalyst's ability to convert the exhaust emissions effectively. If the catalyst is functioning properly, the HO2S 2 signal will be far less active than the signal produced by the front oxygen sensor (O2S 1).
Replace the entire HO2S 2 assembly. Do not attempt to repair the HO2S 2 if the following conditions exist:
| • | Damaged wiring |
| • | Damaged electrical connectors |
| • | Damaged terminals |
Obstruction of the air reference and degraded HO2S 2 performance could result from any attempt to repair the above conditions.
The HO2S 2 must have a clean air reference in order for the HO2S 2 to function properly. This clean air reference is obtained by way of the HO2S 2 wires.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | DTCs P0105, P0107, P0108, P0112, P0113, P0117, P0118, P0122, P0123, P0171, P0200, P0300, P0301, P0302, P0303, P0304, P0335, P0440, P0442, P0446, P0506, P0507, P0601, P0602, or P1441 are not set. |
| • | The air flow is more than 5.5 grams per second. |
| • | The engine coolant temperature (ECT) is more than 40°C (104°F). |
| • | The throttle position (TP) angle is between 5 percent and 50 percent for 4 seconds. |
Conditions For Setting The DTC
HO2S 2 voltage is greater than 1042 mV for 50 to 75 seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) will illuminate after two consecutive ignition cycles in which the diagnostic runs with the malfunction present. |
| • | The PCM will record the operating conditions at the time that the diagnostic fails. This information will store in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records buffers. |
| • | A history DTC stores. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The MIL will turn OFF after three consecutive ignition cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault. |
| • | A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles without a fault. |
| • | The MIL/DTCs can be cleared by using the scan tool. |
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
| • | A rich exhaust--An overly rich exhaust may load the catalyst, causing high HO2S 2 signal voltages. |
| • | Silicone contamination--Silicone contamination of HO2S 2 could cause a false rich condition . A powdery white deposit on the sensor will indicate this condition. |
| • | A malfunctioning HO2S 2--If there is an internal short in the HO2S 2, the HO2S 2 voltage displayed on a scan tool will be more than 1.0 volt. Disconnect the HO2S 2 and connecting a jumper wire between the HO2S 2 low circuit to engine ground. Replace the HO2S 2 if the displayed voltage goes from more than 1000 mV to approximately 450 mV . |
| • | An intermittent test--Observe the HO2S 2 on the scan tool while moving the related electrical connectors and the wiring harness with the ignition switch turned ON. If the malfunction is induced, the HO2S 2 display will change. This should help isolate the location of the malfunction. |
| • | Damaged harness--Inspect PCM harness for a short to voltage in the HO2S 2 signal circuit. |
An intermittent could be the result of the following conditions:
| • | A poor electrical connection |
| • | Rubbed-- through wire insulation |
| • | A broken wire inside of the insulation |
Replace the entire HO2S 2 assembly. Do not attempt to repair the HO2S 2 if the following conditions exist:
| • | Damaged wiring |
| • | Damaged electrical connectors |
| • | Damaged terminals |
Obstruction of the air reference and degraded HO2S 2 performance could result from any attempt to repair the above conditions.
The HO2S 2 must have a clean air reference in order for the HO2S 2 to function properly. This clean air reference is obtained by way of the HO2S 2 wires.
Test Description
The number(s) below refer(s) to the step number(s) on the Diagnostic Table.
-
The Powertrain OBD System Check prompts you to complete some of the basic checks and to store the freeze frame and failure records data on the scan tool if applicable. This creates an electronic copy of the data captured when the malfunction occurred. The scan tool stores this data for later reference.
-
This step determines if DTC P0138 is the result of a hard malfunction or an intermittent condition.
-
Disconnecting the HO2S 2 and connecting a jumper wire between the HO2S 2 signal circuit and the HO2S 2 low circuit to ground, should cause the scan tool to display HO2S 2 voltage below 100 mV (0.1 Volts). If the signal voltage is still high, the this indicates that the PCM is malfunctioning.
-
Reprogram the replacement PCM and perform the crankshaft position system variation learn procedure. Refer to the latest Techline information for PCM programming and Crankshaft Position System Variation Learn for the crankshaft position system variation learn procedure.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | |||||||
Is the HO2S 2 sensor voltage above the specified value? | 1042 mV (1.042 V) | |||||||
3 |
Is the HO2S 2 sensor voltage above the specified value? | 1042 mV (1.042 V) | ||||||
4 |
Caution: Avoid contact with moving parts and hot surfaces while working around a running engine in order to prevent physical injury. Does the DMM indicate a voltage of the specified value? | 0 V (± 0.5) | ||||||
Does the scan tool indicate the HO2S 2 sensor voltage below the specified value? | 100 mV (0.10 V) | |||||||
6 | Repair the short to voltage in the HO2S 2 sensor signal circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||
7 |
Caution: Avoid contact with moving parts and hot surfaces while working around a running engine in order to prevent physical injury. Replace the HO2S 2 sensor. Refer to the Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S) Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||
Is the action complete? | -- | -- | ||||||
9 |
Does the scan tool indicate that this diagnostic ran and passed? | -- | ||||||
10 | Check to see if any additional DTCs are set. Does the scan tool display any DTCs that you have not diagnosed? | -- | Go to applicable DTC table | System OK |
