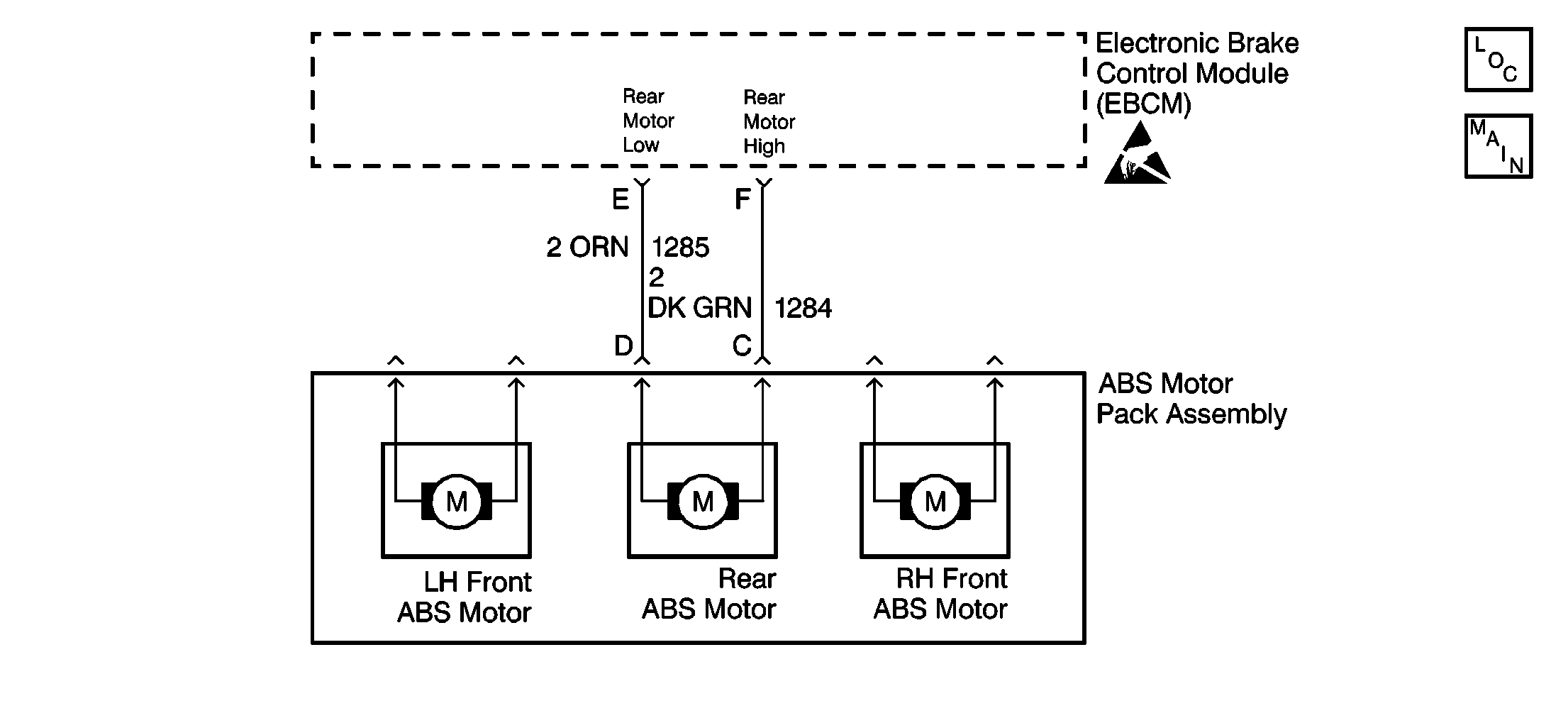
Circuit Description
DTC C1242 detects a slipping rear axle ESB. During initialization and braking, the rear motor is rehomed. If the ESB slips, the motor/piston will move. During the next key to ON initialization, a rehome of the motor verifies the motor/piston remained at the home position. If motor movement is detected, the ESB must be slipping.
If an ESB cannot hold a piston in the home position, the piston may be driven back when the brake pedal is applied. Then the brake pedal will drop.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DTC C1242 can set during initialization at the following speeds:
| • | 0 km (0 mph) when the brake is OFF |
| • | 5 km (3 mph) when the brake is ON |
A malfunction exists if the EBCM detects that the ESB could not hold the piston in the home position.
DTC C1286 always sets with DTC C1242.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | A malfunction DTC stores. |
| • | The ABS disables. |
| • | The ABS warning indicator turns ON. |
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
| • | The condition responsible for setting the DTC no longer exists and the Scan Tool Clear DTCs function is used. |
| • | 100 drive cycles pass with no DTC(s) detected. A drive cycle consists of starting the vehicle, driving the vehicle over 16 km/h (10 mph), stopping and then turning the ignition OFF. |
Diagnostic Aids
The following conditions may cause an intermittent malfunction if the conditions exist in a mechanical part of the system:
| • | Sticking |
| • | Binding |
| • | Slipping |
Use the enhanced diagnostic function of the Scan Tool in order to measure the frequency of the malfunction.
Use the hydraulic control modulator test function of the Scan Tool in order to locate an intermittent malfunction associated with the ESB.
Clear the DTCs after completing the diagnosis. Test drive the vehicle for three drive cycles in order to verify that the DTC does not reset. Use the following procedure in order to complete one drive cycle:
- Start the vehicle.
- Drive the vehicle over 16 km/h (10 mph).
- Stop the vehicle.
- Turn the ignition switch to the OFF position.
Test Description
-
This test ensures that the motor circuits are in the proper connector cavities.
-
This test checks the operation of the rear ESB.
-
This test checks for high resistance in the rear motor high circuit.
-
This test checks for high resistance in the rear motor low circuit.
-
This test checks for excessive resistance in the rear motor.
-
This test determines if the malfunction is caused by the EBCM.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Important: Zero the J 39200 test leads before making any resistance measurements. Refer to the J 39200 user's manual. | ||||||||||||||||
1 | Was the ABS Diagnostic System Check performed? | -- | Go to Step 2 | |||||||||||||
Inspect the following connectors for the correct wire color/connector cavity combinations:
Are the correct wires located in the correct connector cavities? | -- | Go to Step 3 | Go to Step 10 | |||||||||||||
Do not start the engine. Could the assistant spin the rear wheels? | -- | Go to Step 9 | Go to Step 4 | |||||||||||||
Is the resistance within the specified range? | 0-2 ohms | Go to Step 5 | Go to Step 11 | |||||||||||||
Use the J 39200 in order to measure the resistance between the ABS brake motor pack harness connector terminal D and the EBCM harness connector terminal E. Is the resistance within the specified range? | 0-2 ohms | Go to Step 6 | Go to Step 12 | |||||||||||||
Use the J 39200 in order to measure the resistance between the ABS brake motor pack connector terminal C and the ABS brake motor pack connector terminal D. Is the resistance within the specified range? | 0.2-1.5 ohms | Go to Step 7 | Go to Step 9 | |||||||||||||
7 |
Are there signs of poor terminal contact or corrosion? | -- | Go to Step 13 | Go to Step 8 | ||||||||||||
Does the DTC C1242 set during the last three ignition cycles? | -- | Go to Step 14 | Go to Step 15 | |||||||||||||
9 | Replace the ABS brake motor pack. Refer to ABS Motor Pack Replacement . is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||||
10 | Place the correct wires into the connector cavities. Refer to Antilock Brake System Connector End Views . Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||||
11 | Repair the open or high resistance in CKT 1284. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||||
12 | Repair the open or high resistance in CKT 1285. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||||
13 | Replace the terminals that exhibit signs of poor terminal contact or corrosion. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||||
14 | Replace the EBCM. Refer to Electronic Brake Control Module Replacement . Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||||
15 | The malfunction is intermittent or is not present at this time. Refer to Diagnostic Aids for more information. Is the action complete? | -- | System OK | -- | ||||||||||||
