Operation
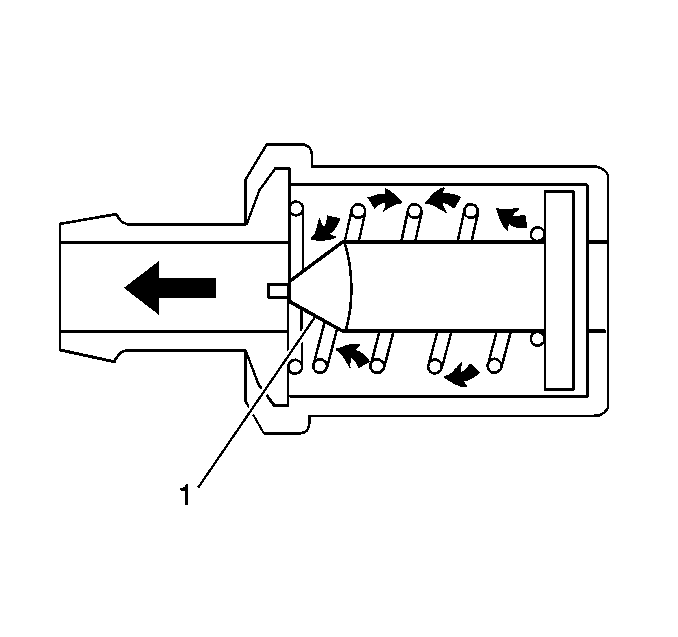
The
primary control is through the crankcase ventilation valve which meters the
flow at a rate depending on inlet vacuum. To maintain idle quality, the crankcase
ventilation valve restricts the flow when inlet vacuum is high. If abnormal
operating conditions arise, the system is designed to allow excessive amounts
of blow-by gases to back flow through the crankcase vent into the throttle
body to be consumed by normal combustion.
Results of Incorrect Operation
A plugged valve may cause the following conditions:
| • | Stalling or slow idle speed. |
A leaking valve would cause:
Functional Check of Crankcase Ventilation Valve
If an engine is idling rough, check for a clogged crankcase ventilation
valve. Replace if required. Use the following procedure:
- Remove crankcase ventilation valve from intake manifold.
- Shake valve and listen for the rattle of needle inside the valve.
- If valve does not rattle, replace valve.
With this system, any blow-by in excess of the system capacity (from
a badly worn engine, sustained heavy load, etc.) is exhausted into the intake
manifold and is drawn into the engine.
Proper operation of the crankcase ventilation system is dependent upon
a sealed engine. If oil sludging or dilution is noted, and the crankcase ventilation
system is functioning properly, check engine for possible cause and correct
to ensure that system will function as intended.

