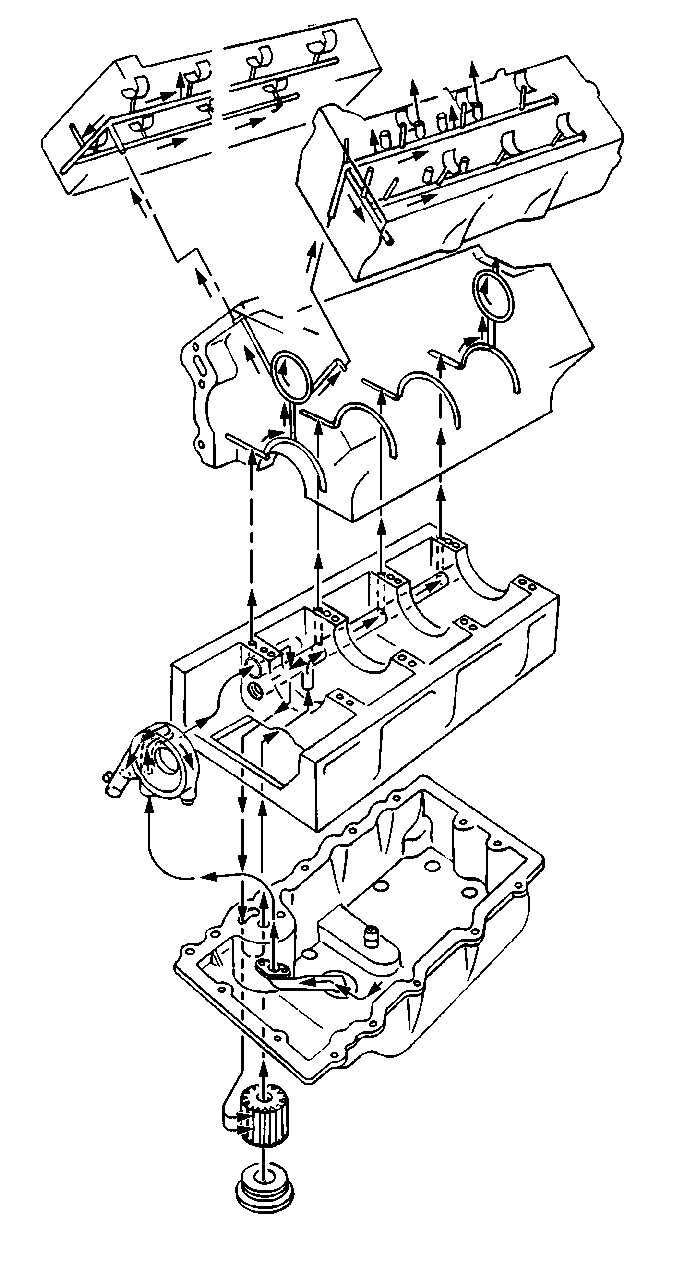
The cast aluminum oil pan is used as a structural member of the powertrain by providing mounting bosses for both the transaxle case and mounting brace located at the extension housing of the transaxle. The oil pan incorporates riveted internal oil baffle plates and seals to the lower crankcase with a silicone gasket. The oil pan also provides mounting for an oil level sensor.
The oil sump pickup is fastened to the oil pump by a bolt and nut to one stud-headed main bearing bolt. A silicone o-ring seals this joint on the suction side of the oil system. The engine oil pump is a gerotor design mounted to the lower crankcase behind the engine front cover. The inner gerotor element is driven by splines on the crankshaft timing chain sprocket which, in turn, is driven by a pin in the crankshaft. As the pump rotates, oil is drawn from the sump through the sump pickup to the pump inlet. Oil compressed by the pump enters the lower crankcase and is routed to the oil filter inlet passage in the oil pan.
The oil filter bypass valve is located in the lower crankcase and is not serviceable. The valve will route oil directly from the filter inlet to the filter outlet should the filter become plugged.
After passing through the filter, the oil is directed to the main longitudinal gallery in the lower crankcase. Each of the four crankshaft bearing feeds from the main gallery through passages in the lower crankcase which intersect passages in the upper crankcase half of the crankshaft bearing saddle. Drilled passages in the crankshaft between the crankshaft bearing journals and the connecting rod journals providing lubrication for them and ultimately provide splash lubrication for the cylinder walls. The number one and four crankshaft bearing oil feed also provides lubrication to the respective balance shaft bearings. Oil leaking past the front balance shaft bearing lubricates the primary timing chain via oil splash. The primary timing chain tensioner is fed through an oil transfer tube.
From the front balance shaft bearing, oil is fed through passages in each bank of the crankcase and into each cylinder head where longitudinal passages supply each hydraulic lash adjuster and the camshaft journals. Oil returns to the sump either through the cam chain area or by way of cast passages on the outside walls of the cylinder heads, cylinder block and oil pan.
