Circuit Description
The EBTCM Diagnostic System Check is an organized approach to identify problems associated with the EBTCM. This check must be the starting point for any EBTCM complaint, and will direct you to the next logical step in diagnosing the complaint. The EBTCM is a very reliable component and is not likely the cause of the malfunction. Most system complaints are linked to faulty wiring, connectors, and occasionally to components. Understanding the ABS/ETS (Antilock Brake System/Enhanced Traction Control System which is standard for this vehicle) system and using the tables correctly will reduce diagnostic time and prevent unnecessary parts replacement.
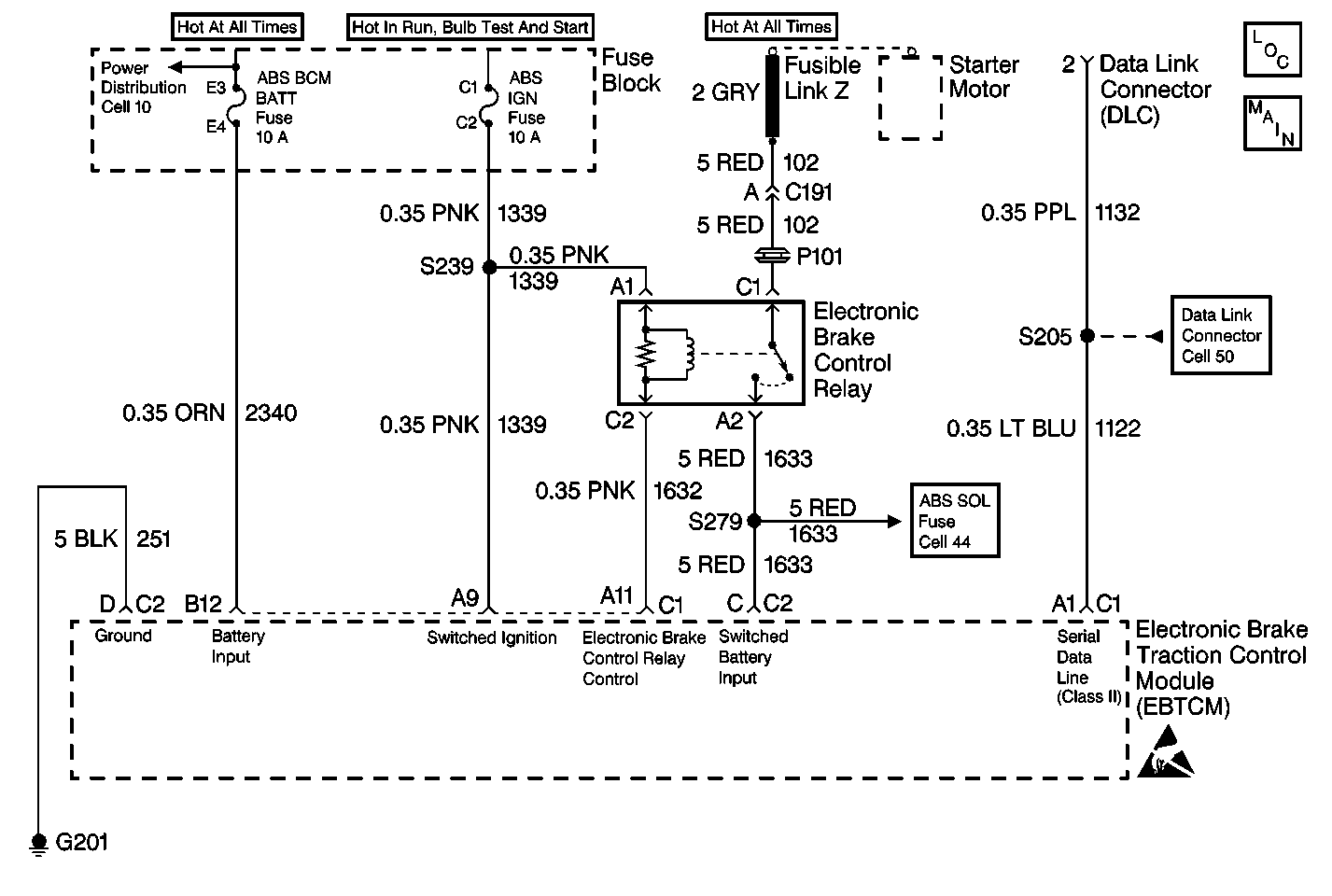
The Diagnostic system check directs the service technician to the next logical step in diagnosing the complaint. The following connectors/terminals will give you a better understanding on what each terminal performs.
| • | Connector C1 terminal A1 exchanges serial data to and from the EBTCM. |
| • | Connector C1 terminal A9 supplies the switched ignition voltage to the EBTCM. |
| • | Connector C1 terminal B12 supplies the battery voltage to the EBTCM. |
| • | Connector C2 terminal C supplies the switched battery voltage to the EBTCM. |
| • | Connector C2 terminal D provides the ground for the EBTCM. |
Diagnostic Aids
| • | An intermittent failure in the electronic system may be very difficult to detect and to accurately diagnose. The EBTCM tests for different malfunctions under different vehicle conditions. For this reason, a thorough test drive is often needed in order to repeat a malfunction. If the system malfunction is not repeated during the test drive, a good description of the complaint may be very useful in locating an intermittent malfunction. Faulty electrical connections or wiring causes most intermitting problems. When an intermittent condition is suspected, check the suspected circuits for the following conditions: |
| - | Poor mating of connector halves or backed out terminals |
| - | Improperly formed or damaged terminals |
| - | Wiring damage, especially at vehicle attachment points |
| - | Poor wire to terminal connections |
| - | Dirty or corroded terminals |
| - | Damage to connector bodies |
| • | If the DTC is a history DTC, the problem may be intermittent. Perform the tests shown while moving related wiring and connectors. This can often cause the malfunction to occur. Perform a thorough inspection of all related wiring and connectors pertaining to the history DTC stored. |
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Does the scan tool communicate with the EBTCM? | -- | ||
2 | Does the scan tool communicate with other modules on the Class 2 serial data line, such as the PCM? | -- | ||
3 |
Is the resistance measured within the specified range? | 0-2 ohms | Go to Wiring Repairs | |
4 |
Are there any current Diagnostic Trouble Codes? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) List for the Applicable DTC | |
5 |
Does the ABS Indicator turn on then turn off after several seconds? | -- | ||
6 | Turn the ignition switch from the OFF to ON position, engine off. Does the ETS/TRAC Off Indicator turn on then turn off after several seconds? | -- | ||
7 | Does the ABS Indicator stay on? | -- | Go to ABS Indicator Always On | |
8 | Does the ETS/TRAC Off Indicator stay on? | -- | ||
9 | Are there any history DTCs? | -- | System OK | |
10 |
Did the history DTC set as a current DTC while the vehicle was being driven? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) List for the Applicable DTC | System OK |
