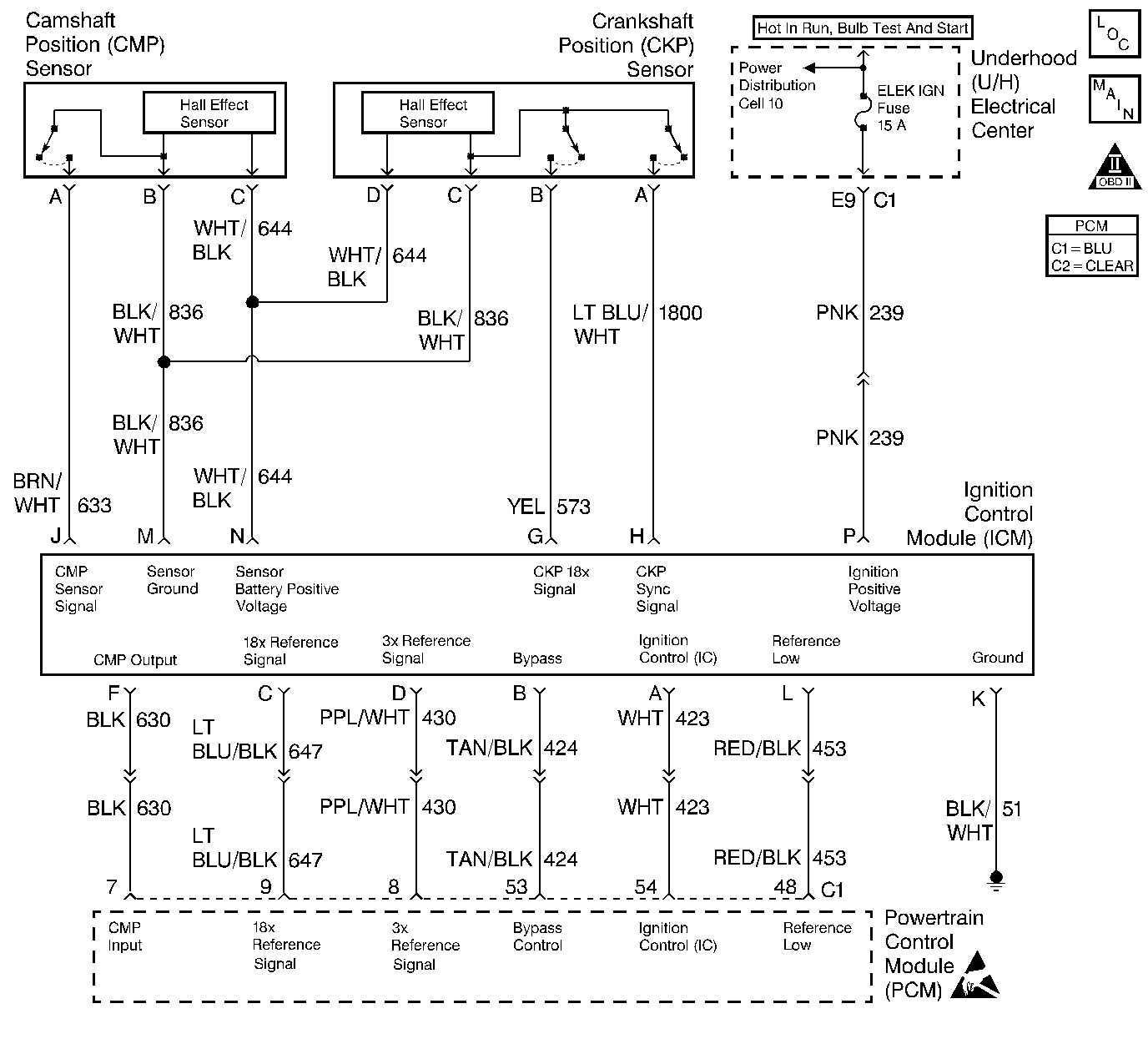
Circuit Description
The camshaft position to powertrain control module (PCM) input is produced by the ignition control module (ICM). The ICM produces the camshaft position input by filtering the camshaft position (CMP) sensor pulses when the engine is running and crankshaft position (CKP) sync pulses are being received. The PCM uses the camshaft position input pulses to initiate sequential fuel injection and to determine the CKP for the misfire diagnostic. The PCM constantly monitors the number of pulses on the camshaft position input circuit and compares the number of CMP input pulses to the number of 18X reference pulses and the number of 3X reference pulses being received. If the PCM receives an incorrect number of pulses on the CMP input circuit, DTC P0341 is set and the PCM initiates the injector sequence without CMP input with a 1 in 6 chance that the injector sequence is correct. The engine continues to start and run normally, although the misfire diagnostic is disabled.
Conditions for Running the DTC
The engine is running and 3X reference pulses are being received.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | The ratio of 3X reference pulses to CMP pulses received by the PCM does not equal 6. |
| • | The ratio of 3X reference pulses to 18X reference pulses received by the PCM equals 6. |
| • | The above conditions are present for 290 occurrences. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) during the second consecutive trip cycle in which the diagnostic test has run and failed. |
| • | The PCM initiates the injector sequence without the CMP signal with a 1 in 6 chance that the injector sequence is correct. |
| • | If equipped with traction control, the PCM commands the EBCM, via Class 2 serial data, to set an ABS/TCS DTC. The EBCM turns the traction control and illuminates the TRACTION OFF lamp. |
| • | The PCM stores the conditions which were present when the DTC set as Freeze Frame and Fail Records data. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The PCM turns the MIL off during the third consecutive trip in which the diagnostic has run and passed. |
| • | The history DTC clears after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles have occurred without a malfunction. |
| • | The DTC may be cleared by using the scan tool Clear Info function or by disconnecting the PCM battery feed. |
Diagnostic Aids
An intermittent may be caused by a faulty connection, rubbed through wire insulation, or a wire broken inside the insulation. Inspect for the following conditions:
| • | A faulty connection. Inspect the PCM harness and connectors for improper mating, broken locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and faulty terminal to wire connection. |
| • | A damaged harness. Inspect the wiring harness for damage. If the harness appears to be OK, disconnect the PCM, turn the ignition on and observe a voltmeter connected to the 18X reference circuit at the PCM harness connector while moving the connectors and wiring harnesses related to the ICM. A change in voltage indicates the location of the malfunction. |
| • | A misrouted wiring harness. Inspect the ICM harness to ensure that it is not routed near secondary ignition components. |
| • | A malfunctioning ignition coil. Remove the ignition coils and inspect the ignition control module and the coils for cracks, carbon tracking, or other signs that indicate that the coil secondary circuit is arcing to the ICM or the ICM wiring harness. |
| • | Any secondary ignition wires arcing to wiring harness. Inspect the secondary ignition wires for carbon tracking or other signs of damage. |
Reviewing the Fail Records vehicle mileage since the diagnostic test last failed may help determine how often the condition that caused the DTC to be set occurs. This may assist in diagnosing the condition.
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the Diagnostic Table.
-
Ensures that the malfunction is present.
-
Determines whether the malfunction is being caused by a missing camshaft magnet or a malfunctioning PCM. The voltage measured in this step should read around 4 volts, toggling to near 0 volts when the CMP sensor interfaces with the camshaft magnet.
-
This vehicle is equipped with a powertrain control module (PCM) which utilizes an electrically erasable programmable read-only memory (EEPROM). When the PCM is replaced, the new PCM must be programmed.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Important:: If the engine cranks but will not run, refer to Engine Cranks but Does Not Run . Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | Go to Step 2 | |||||||
Does the scan tool indicate DTC P0341 Failed This Ign? | -- | Go to Step 3 | Go to Diagnostic Aids | |||||||
3 |
Is the voltage near the specified value? | 5 V | Go to Step 4 | Go to Step 5 | ||||||
4 |
Is the voltage near the specified value? | 0 V | Go to Step 16 | Go to Step 8 | ||||||
5 | Does the voltage on the CMP input signal circuit measure more than the specified value? | 5 V | Go to Step 7 | Go to Step 6 | ||||||
6 |
Was a problem found? | -- | Go to Step 23 | Go to Step 13 | ||||||
7 |
Was a problem found? | -- | Go to Step 23 | Go to Step 18 | ||||||
8 |
Is the voltage near the specified value? | B+ | Go to Step 9 | Go to Step 12 | ||||||
9 | Measure the voltage between the CMP sensor signal circuit and the sensor ground circuit at the CMP sensor harness connector. Is the voltage within the specified range? | 5-7 V | Go to Step 10 | Go to Step 11 | ||||||
10 |
Does the voltage switch from 5 volts to 0 volts whenever the test lamp is touched to the CMP sensor signal circuit? | -- | Go to Step 15 | Go to Step 14 | ||||||
11 |
Was a problem found? | -- | Go to Step 23 | Go to Step 14 | ||||||
12 |
Was a problem found? | -- | Go to Step 23 | Go to Step 14 | ||||||
13 |
Was a problem found? | -- | Go to Step 23 | Go to Step 14 | ||||||
14 |
Was a problem found? | -- | Go to Step 23 | Go to Step 17 | ||||||
15 |
Was a problem found? | -- | Go to Step 23 | Go to Step 19 | ||||||
16 |
Was a problem found? | -- | Go to Step 23 | Go to Step 20 | ||||||
17 |
Was a problem found? | -- | Go to Step 23 | Go to Step 18 | ||||||
18 | Replace the ignition control module. Refer to Ignition Control Module Replacement . Did you complete the repair? | -- | Go to Step 23 | -- | ||||||
19 | Replace the camshaft position sensor. Refer to Camshaft Position Sensor Replacement . Did you complete the repair? | -- | Go to Step 23 | -- | ||||||
20 |
Does voltage switch between the specified values? | 4 V 0 V | Go to Step 21 | Go to Step 22 | ||||||
|
Important:: The replacement PCM must be programmed. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement/Programming . Replace the PCM. Did you complete the repair? | -- | Go to Step 23 | -- | |||||||
22 | Replace the malfunctioning or missing CMP sensor magnet. Refer to Camshaft Position Sensor Replacement . Did you complete the repair? | -- | Go to Step 23 | -- | ||||||
23 |
Does the scan tool indicate DTC P0341 Failed This Ign? | -- | Go to Step 2 | System OK |
