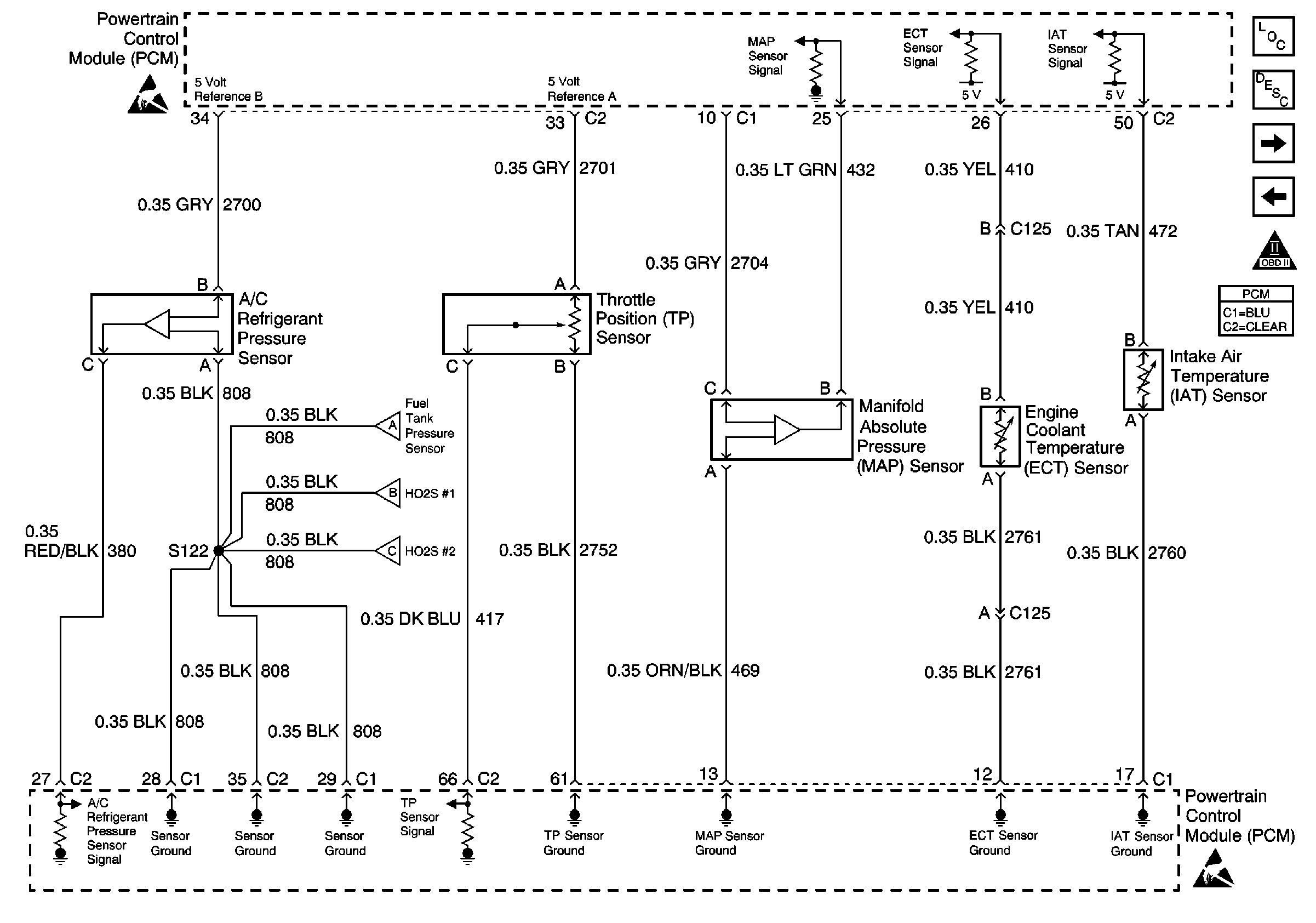
Refer to Engine Controls Schematics
A/C Pressure Switch, TPS, MAP, ECT and IAT
.
Circuit Description
The intake air temperature (IAT) sensor contains a semiconductor device which changes resistance based on temperature. The IAT sensor is located in the air intake passage of the engine air induction system. The IAT sensor has a signal circuit and a ground circuit. The powertrain control module (PCM) applies about 5 volts on the signal circuit to the sensor. The PCM monitors changes in this voltage caused by changes in the resistance of the sensor to determine intake air temperature.
When the intake air is cold, the sensor resistance is high, and the PCM signal voltage is only pulled down a small amount through the sensor to ground. Therefore, the PCM will sense a high signal voltage or a low temperature. When the intake air is warm, the sensor resistance is low, and the signal voltage is pulled down a greater amount. This causes the PCM to sense a low signal voltage or a high temperature.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | No engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor, mass air flow (MAF) sensor, or vehicle speed sensor (VSS) diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) are present. |
| • | The engine has been running for over 10 seconds. |
| • | The vehicle speed is more than 25 mph. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
IAT signal voltage intermittently indicates an intake air temperature more than 134°C (274°F).
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The powertrain control module (PCM) stores the DTC information into memory when the diagnostic runs and fails. |
| • | The malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) will not illuminate. |
| • | The PCM records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The PCM stores this information in the Failure Records. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | A History DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles, if no failures are reported by this or any other non-emission related diagnostic. |
| • | The current DTC will clear when the diagnostic runs and does not fail. |
| • | Use a scan tool in order to clear the MIL diagnostic trouble code. |
| • | Interrupting the PCM battery voltage may or may not clear DTCs. This practice is not recommended. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Description , Clearing Diagnostic Trouble Codes. |
Diagnostic Aids
Notice: Use the connector test adapter kit J 35616-A for any test that
requires probing the following items:
• The PCM harness connectors • The electrical center fuse/relay cavities • The component terminals • The component harness connector
Check for the following conditions:
| • | A faulty connection at the PCM -- Inspect harness connectors for backed out terminals, improper mating, broken locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and poor terminal to wire connection. |
| • | A damaged harness -- Inspect the wiring harness for damage. If the harness appears to be OK, observe the IAT display on the scan tool while moving connectors and wiring harnesses related to the IAT sensor. A change in the IAT display will indicate the location of the malfunction. |
| • | A skewed or incorrectly calibrated IAT sensor -- Refer to the Temperature Versus Resistance table . |
Reviewing the Failure Records vehicle mileage since the diagnostic test last failed may help determine how often the condition that caused the DTC to be set occurs. This may assist in diagnosing the condition.
If the problem is intermittent, refer to Intermittent Conditions .
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
This step verifies that the malfunction is present.
-
If DTC P1112 can be repeated only by duplicating the Failure Records conditions, refer to the Temperature vs Resistance. The table may be used to test the IAT sensor at various temperatures to evaluate the possibility of a shifted sensor that may be shorted above or below a certain temperature. If this is the case, replace the IAT sensor.
Step | Action | Values | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||
Using the scan tool, select DTC Info, Last Test Fail and note any other DTCs that are set. Is DTC P0112 also set? | -- | Go to DTC P0112 Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor Circuit Low Voltage | ||
Was a problem found and corrected? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | ||
4 |
Does the scan tool indicate that this test ran and passed? | -- | ||
5 | Review Captured Info using the scan tool. Are there any DTCs that have not been diagnosed? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | System OK |
