Refer to Engine Controls Schematics
Heated O2 Sensors
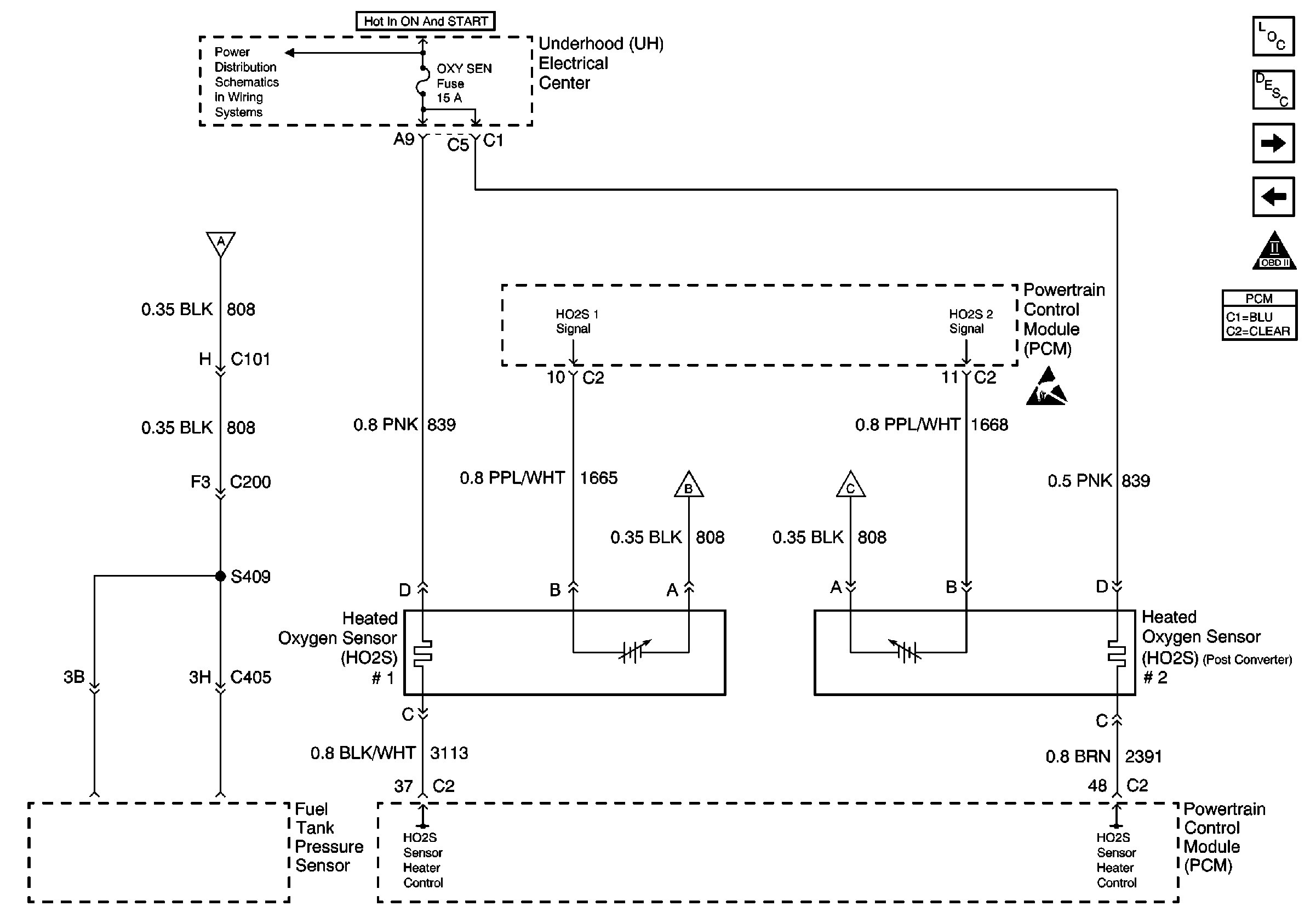
.
Circuit Description
The PCM uses a three-way catalytic converter to control emissions of hydrocarbons (HC), carbon monoxide (CO), and oxides of nitrogen (NOx). The catalyst within the converter promotes a chemical reaction that oxidizes the HC and CO present in the exhaust gas. After undergoing oxidation, the HC and CO are converted into harmless water vapor and carbon dioxide. The catalyst also reduces NOx emissions by converting the NOx into nitrogen. The PCM uses the heated oxygen sensors (HO2S 1 and HO2S 2) to monitor this process. HO2S 1 produces an output signal that indicates how much oxygen is present in the exhaust gas entering the three-way catalytic converter. HO2S 2 produces an output signal that indicates the oxygen storage capacity of the catalyst. The oxygen storage capacity of the catalyst is a measure of the catalyst's ability to convert exhaust gases efficiently. If the catalyst is operating efficiently, the HO2S 1 signal will be far more active than the HO2S 2 signal.. If the HO2S 2 signal voltage remains excessively low for an extended period of time, DTC P0137 will set.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | There are no active DTCs of the following types present: |
| • | Fuel trim |
| • | Fuel injector circuit |
| • | Misfire |
| • | Evaporative emissions (EVAP) |
| • | Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) |
| • | Throttle position (TP) sensor |
| • | Intake air temperature (IAT) sensor |
| • | Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor |
| • | Engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor |
| • | Crankshaft position (CKP) sensor |
| • | Mass air flow (MAF) sensor |
| • | The system voltage is more than 9 volts. |
| • | The closed loop commanded air-to-fuel ratio is between 14.4-14.9. |
| • | The throttle angle is between 3-40 percent. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The HO2S 2 signal voltage remains below 175 mV during normal closed loop operation.
OR
The HO2S 2 signal voltage remains below 600 mV during power enrichment mode fuel control operation.
Either one of these condition exists for up to 50 seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) on the second consecutive ignition cycle that the diagnostic runs and fails. |
| • | The PCM records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The first time the diagnostic fails, the PCM stores this information in the Failure Records. If the diagnostic reports a failure on the second consecutive ignition cycle, the PCM records the operating conditions at the time of the failure. The PCM writes the conditions to the Freeze Frame and updates the Failure Records. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The PCM turns the MIL OFF after 3 consecutive drive trips during which the diagnostic runs and passes. |
| • | A last test failed, or the current DTC, clears when the diagnostic runs and passes. |
| • | A History DTC clears after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles, if no other emission related diagnostic failures are reported. |
| • | Use a scan tool in order to clear the MIL diagnostic trouble code. |
| • | Interrupting the PCM battery voltage may or may not clear DTCs. This practice is not recommended. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Description , Clearing Diagnostic Trouble Codes. |
Diagnostic Aids
Notice: Use the connector test adapter kit J 35616-A for any test that
requires probing the following items:
• The PCM harness connectors • The electrical center fuse/relay cavities • The component terminals • The component harness connector
Check for the following conditions
| • | Misrouted heated oxygen sensor wiring -- The HO2S pigtail may be mispositioned and contacting the exhaust system. |
| • | Faulty PCM to engine grounds -- Refer to Power Distribution Schematics in Wiring Systems. |
| • | Incorrect fuel pressure -- A condition that causes a lean exhaust can cause DTC P0137 to set. The system will go lean if the fuel pressure is too low. The PCM can compensate for some decrease. However, if fuel pressure falls too low, DTC P0137 may set. Refer to Fuel System Pressure Test . |
| • | Problems with the fuel injectors -- Refer to Fuel Injector Solenoid Coil Test - Engine Coolant Temperature Between 10-35 Degrees C (50-95 Degrees F) or Fuel Injector Solenoid Coil Test - Engine Coolant Temperature Outside 10-35 Degrees C (50-95 Degrees F) . |
| • | Vacuum leaks |
| • | Check for the following conditions: |
| - | Disconnected or damaged vacuum hoses |
| - | An incorrectly installed or malfunctioning crankcase ventilation valve. -- Refer to Crankcase Ventilation System Diagnosis |
| - | Vacuum leaks at the throttle body, EGR valve, and intake manifold mounting surfaces |
| • | Exhaust leaks -- An exhaust leak may cause outside air to be pulled into the exhaust gas stream past the HO2S, causing DTC P0137 to set. Check for exhaust leaks near the HO2S 2 sensor. |
| • | Fuel contamination -- Water can be delivered to the fuel injectors. Water, even in small amounts, can cause a lean exhaust to be indicated. Excessive alcohol in the fuel can also cause this condition. Refer to Alcohol/Contaminants-in-Fuel Diagnosis . |
If the problem is intermittent, refer to Intermittent Conditions .
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
Step | Action | Values | Yes | No | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||||||||||||||||||||||
2 |
Is the HO2S voltage less than the value specified? | 86 mV | ||||||||||||||||||||||
The condition that set this DTC is not present. This DTC may have been set by one of the following conditions:
Repair any of the above or similar engine conditions as necessary. Was a condition found and repaired? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids. | ||||||||||||||||||||||
4 |
Is the HO2S voltage within the value range specified? | 351-551 mV | ||||||||||||||||||||||
5 | The HO2S may be detecting a lean exhaust condition. Check for one of the following conditions:
Repair any of the above or similar engine conditions as necessary. Was a condition found and repaired? | -- | ||||||||||||||||||||||
6 |
Is infinite resistance measured on both tests? | ∞ | ||||||||||||||||||||||
7 | Repair the HO2S signal high circuit shorted to ground or shorted to the HO2S low circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||||||||||||
8 | Replace the HO2S. Refer to Heated Oxygen Sensor Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||||||||||||
9 |
Important: The replacement PCM must be programmed. Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement/Programming . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||||||||||||
10 |
Does the scan tool indicate that this test ran and passed? | -- | ||||||||||||||||||||||
11 | Review the Captured Info using the scan tool. Are there any DTCs that have not been diagnosed? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | System OK |
