Refer to Engine Controls Schematics
Heated O2 Sensors
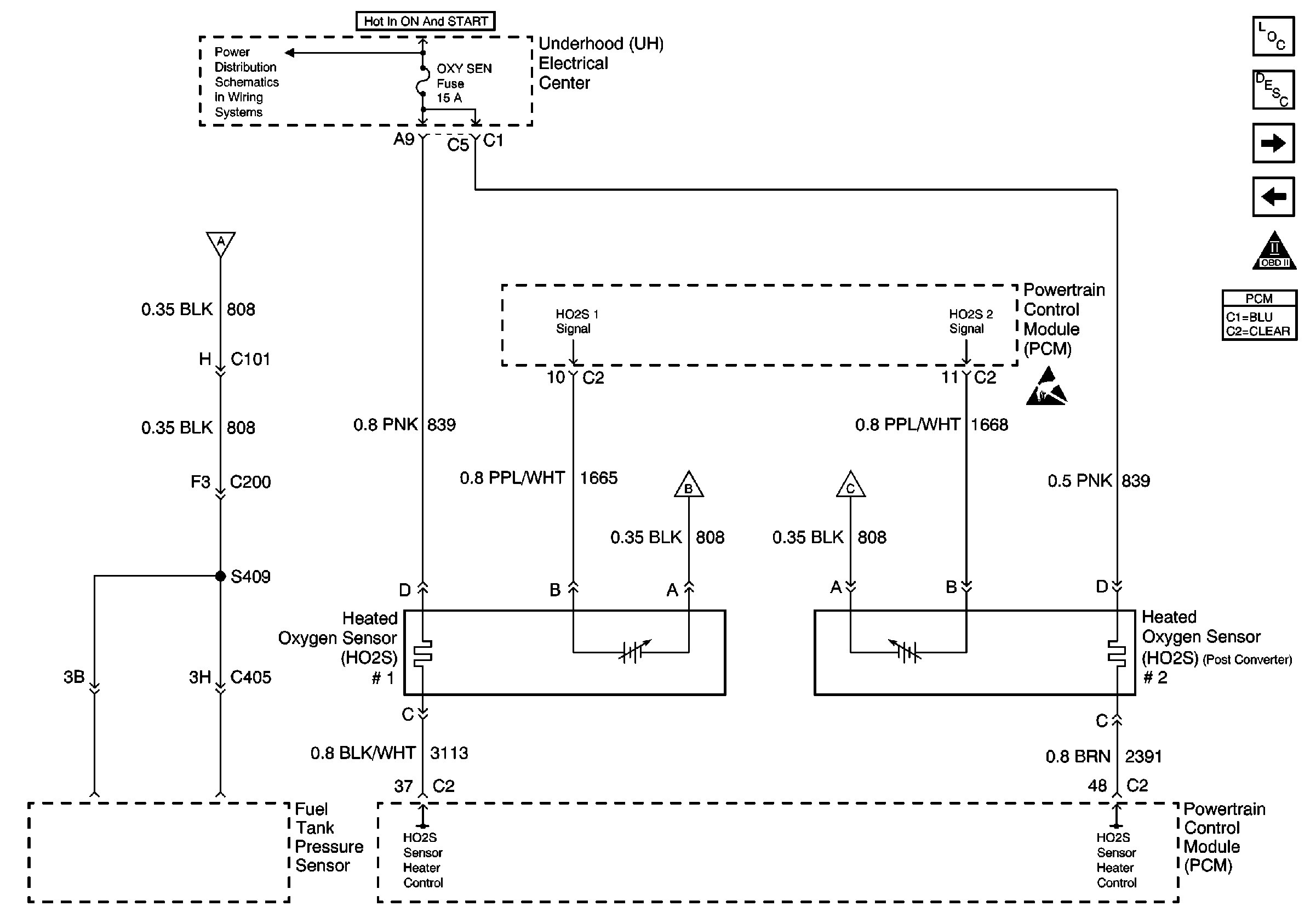
.
Circuit Description
Heated oxygen sensors are used to minimize the amount of time required for closed loop fuel control operation and to allow accurate catalyst monitoring. The oxygen sensor heater greatly decreases the amount of time required for fuel control sensor HO2S 1 to become active. The oxygen sensor heater is required by catalyst monitor sensor HO2S 2 to maintain a sufficiently high temperature. This allows accurate exhaust oxygen content readings at an increased distance from the engine.
The PCM will run the heater test only after a cold start, which is determined by the engine coolant temperature and the intake air temperature at the time of startup. The heater test will also run only once during an ignition cycle. When the engine is started, the PCM will monitor the HO2S voltage. When the HO2S voltage indicates that the sensor is sufficiently active, the PCM determines how much time has elapsed since startup. If the PCM determines that too much time was required for the HO2S 2 to become active, the DTC will set. The appropriate length of time for the HO2S to reach operating temperature is calculated based on the engine coolant temperature at start-up and the average mass air flow since startup. The more total airflow and the higher the startup engine coolant temperature, the less time should be required for HO2S activity.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | There are no active DTCs of any of the following types present: |
| • | Fuel trim |
| • | Fuel injector circuit |
| • | Misfire |
| • | Evaporative emissions (EVAP) |
| • | Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) |
| • | Throttle position (TP) sensor |
| • | Intake air temperature (IAT) sensor |
| • | Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor |
| • | Engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor |
| • | Crankshaft position (CKP) sensor |
| • | Mass air flow (MAF) sensor |
| • | Secondary air injection system (AIR) |
| • | DTC P0131 or P0132 is not set |
| • | The system voltage is between 9-18 volts. |
| • | The intake air temperature (IAT) is less than 45°C (113°F) at startup. |
| • | The engine coolant temperature (ECT) is less than 40°C (104°F) at startup. |
| • | The IAT and ECT are within 15°C (27°F) of each other at start-up. |
| • | The average mass airflow for the sample period is less than 26 g/s. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The HO2S 2 voltage remains within 150 mV of the bias voltage (approximately 450 mV) for more time than it should. The amount of time ranges between 50-130 seconds depending on the engine coolant temperature at startup and the average air flow since startup.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) on the second consecutive ignition cycle that the diagnostic runs and fails. |
| • | The PCM records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The first time the diagnostic fails, the PCM stores this information in the Failure Records. If the diagnostic reports a failure on the second consecutive ignition cycle, the PCM records the operating conditions at the time of the failure. The PCM writes the conditions to the Freeze Frame and updates the Failure Records. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The PCM turns the MIL OFF after 3 consecutive drive trips during which the diagnostic runs and passes. |
| • | A last test failed, or the current DTC, clears when the diagnostic runs and passes. |
| • | A History DTC clears after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles, if no other emission related diagnostic failures are reported. |
| • | Use a scan tool in order to clear the MIL diagnostic trouble code. |
| • | Interrupting the PCM battery voltage may or may not clear DTCs. This practice is not recommended. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Description , Clearing Diagnostic Trouble Codes. |
Diagnostic Aids
Notice: Use the connector test adapter kit J 35616-A for any test that
requires probing the following items:
• The PCM harness connectors • The electrical center fuse/relay cavities • The component terminals • The component harness connector
Reviewing the Failure Records vehicle mileage since the diagnostic test last failed may help determine how often the condition occurs that caused the DTC to set. This may assist in diagnosing the condition.
If the problem is intermittent, refer to Intermittent Conditions .
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
As the heater warms the oxygen sensor to operating temperature, the HO2S will generate an output voltage proportional to the amount of oxygen in the exhaust. With the ignition ON and the engine OFF, the exhaust usually contains a high oxygen content. With the engine OFF, the HO2S voltage will usually decrease from the initial, or bias, voltage due to the high oxygen content.
-
This step checks for a correct HO2S heater ignition feed and ground supply.
-
This step checks for proper PCM and signal circuit operation.
Step | Action | Values | Yes | No | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||||||||||
|
Important: The HO2S must be cool before proceeding with diagnosis. The Ignition must remain Off for at least one half hour before proceeding with diagnosis.
The ignition is ON and the engine is OFF. The ignition is ON and the engine is OFF. Does the HO2S voltage increase or decrease from the initial voltage by at least the value specified? | 150 mV | |||||||||||
3 | The condition that set this DTC is not present. This DTC may have been set by one of the following conditions:
Repair any of the above conditions as necessary. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Was a condition found and repaired? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids. | |||||||||
Start the engine. Is the test lamp illuminated? | -- | |||||||||||
Is the HO2S voltage less than the value specified? | 20 mV | |||||||||||
6 | Connect a test lamp J 35616-200 between the HO2S heater ignition feed circuit terminal on the engine harness side, and a known good ground. Ensure the ignition is ON while the engine is OFF. Is the test lamp illuminated? | -- | ||||||||||
7 |
Is the individual resistance of both circuits less than the value specified? | 5 ohms | ||||||||||
8 | Replace the HO2S. Refer to Heated Oxygen Sensor Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||
9 | Repair the open HO2S heater ground circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||
10 | Repair the lack of power on the HO2S heater ignition feed circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. If the fuse is blown repair the short to ground on the circuit. A blown fuse or lack of power to the fuse may cause other DTCs or symptoms to be present. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||
11 | Repair the circuit that measured high resistance. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||
12 |
Was a PCM terminal repair made? | -- | ||||||||||
13 |
Important: The replacement PCM must be programmed. Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement/Programming . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||
14 |
Important: The HO2S must be cool before proceeding with diagnosis. The Ignition must remain OFF for at least one half hour before proceeding with diagnosis.
The ignition is ON and the engine is OFF. The ignition is ON and the engine is OFF. Does the HO2S voltage increase or decrease from the initial voltage by at least the value specified? | 150 mV | ||||||||||
15 | Review the Captured Info using the scan tool. Are there any DTCs that have not been diagnosed? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | System OK |
