Refer to Engine Controls Schematics
PCM Power and Grounds
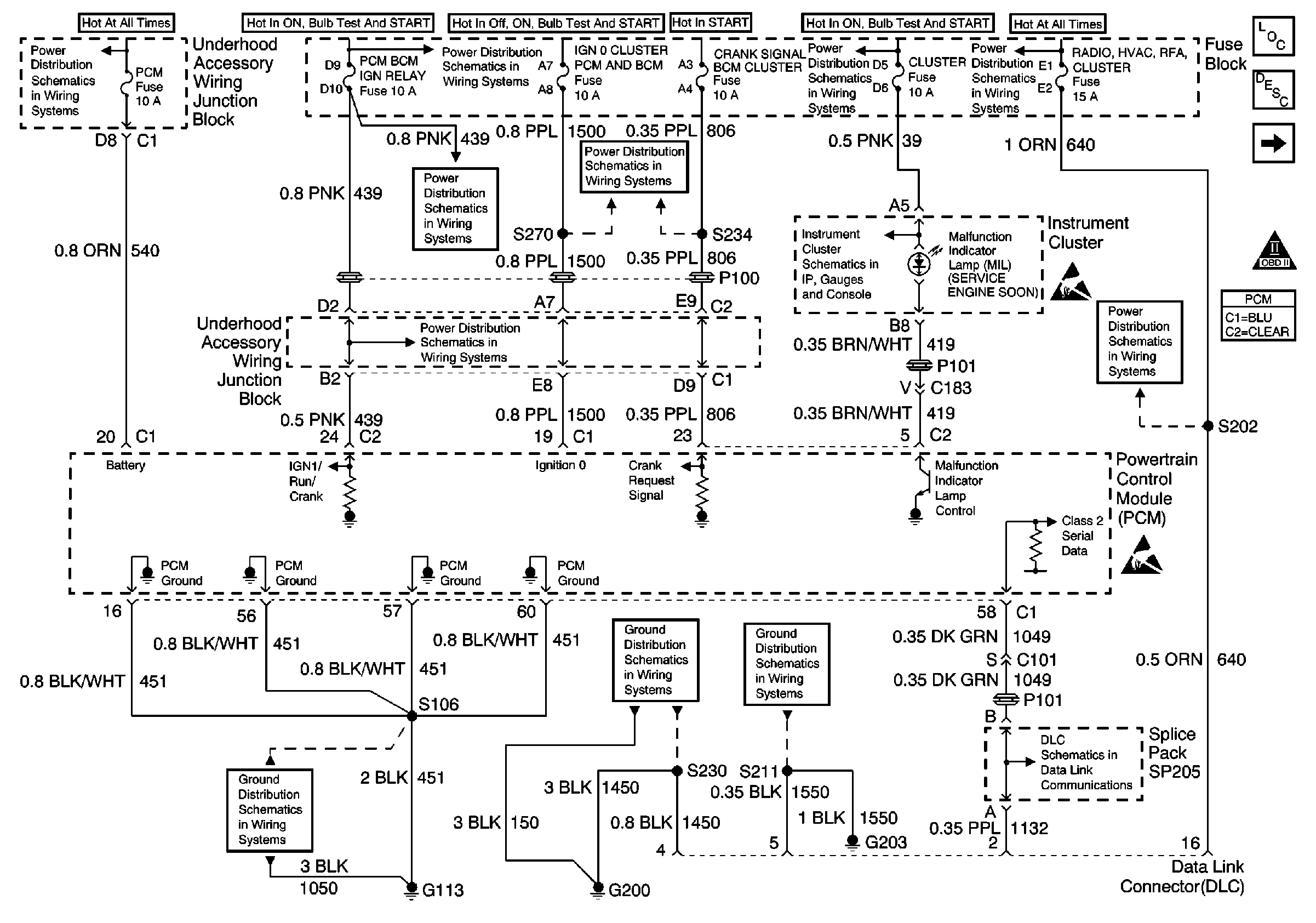
.
Circuit Description
Ignition voltage is supplied directly to the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL). The powertrain control module (PCM) controls the lamp by grounding the control circuit via an internal solid state device called a driver. The primary function of the driver is to supply the ground for the component being controlled. Each driver has a fault line which is monitored by the PCM. When the PCM is commanding a component ON, the voltage of the control circuit should be near 0 volts. When the PCM is commanding the control circuit to a component OFF, the voltage potential of the circuit should be near battery voltage. If the fault detection circuit senses a voltage other than what is expected, this DTC will set.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | The ignition voltage is between 9-18 volts. |
| • | The engine speed is more than 80 RPM. |
| • | The PCM driver transitions from ON to OFF or from OFF to ON. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | A short to ground, an open circuit, or a short to battery voltage is detected on the control circuit. |
| • | The condition is present for at least 30 seconds. |
Action Taken When The DTC Sets
| • | The PCM enables the MIL when the diagnostic runs and fails. The MIL may not be able to illuminate depending on the nature of the problem. |
| • | The PCM records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The PCM stores this information in the Freeze Frame and/or the Failure Records. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The PCM turns the MIL OFF after 3 consecutive drive trips during which the diagnostic runs and passes. |
| • | A last test failed, or the current DTC, clears when the diagnostic runs and passes. |
| • | A History DTC clears after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles, if no other emission related diagnostic failures are reported. |
| • | Use a scan tool in order to clear the MIL diagnostic trouble code. |
| • | Interrupting the PCM battery voltage may or may not clear DTCs. This practice is not recommended. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Description , Clearing Diagnostic Trouble Codes. |
Diagnostic Aids
Notice: Use the connector test adapter kit J 35616-A for any test that
requires probing the following items:
• The PCM harness connectors • The electrical center fuse/relay cavities • The component terminals • The component harness connector
Important: The MIL is actually a lamp emitting diode (LED). An LED requires a parallel dropping resistor in order to operate on a 12 volt system. If the LED burns out, the dropping resistor will still pass voltage on to the PCM, and the MIL diagnostic trouble code (DTC) may not set even though the MIL is inoperative. If the power supply circuit to the indicator lamps and the MIL control circuit check out OK, the instrument panel (IP) cluster needs to be checked for a faulty LED. Refer to Diagnostic System Check - Instrument Cluster in Instrument Panel, Gauges and Console.
If the problem is intermittent, refer to Intermittent Conditions .
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
Normally, ignition feed voltage should be present on the control circuit with the PCM disconnected and the ignition turned ON.
-
Checks for a shorted component or a short to B+ on the control circuit. Either condition would result in a measured current of over 500 milliamps. Also checks for a component that is causing an open circuit while being operated, resulting in a measured current of 0 milliamps.
-
Checks for a short to voltage on the control circuit.
-
This vehicle is equipped with a PCM which utilizes an electrically erasable programmable read only memory (EEPROM). When the PCM is being replaced, the new PCM must be programmed.
Step | Action | Values | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||
2 | Turn the MIL ON and OFF with the scan tool. Does the MIL turn ON and OFF? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | |
Is voltage near the specified value? | B+ | |||
Does the current reading remain between the specified values? | 5-50 mA | |||
Is voltage at the specified value? | 0 V | |||
6 | Locate and repair short to voltage in the MIL control circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
7 | Check the ignition feed fuse for the instrument panel indicators. Is the fuse blown? | -- | ||
8 |
Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
9 |
Is the voltage near the specified value? | B+ | ||
10 |
Was a problem found and corrected? | -- | ||
11 |
Was a problem found and corrected? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check - Instrument Cluster in Instrument Panel, Gauges and Console | |
12 |
Does the test lamp turn ON and OFF? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | |
13 |
Was a problem found and corrected? | -- | ||
14 | Locate and repair open in the ignition feed circuit to the IP indicators. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
|
Important: The replacement PCM must be programmed. Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement/Programming . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | ||
16 |
Does the scan tool indicate that this test ran and passed? | -- | ||
17 | Review Captured Info using the scan tool. Are there any DTCs that have not been diagnosed? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | System OK |
