Refer to Engine Controls Schematics
Crankshaft and Camshaft Position Sensor
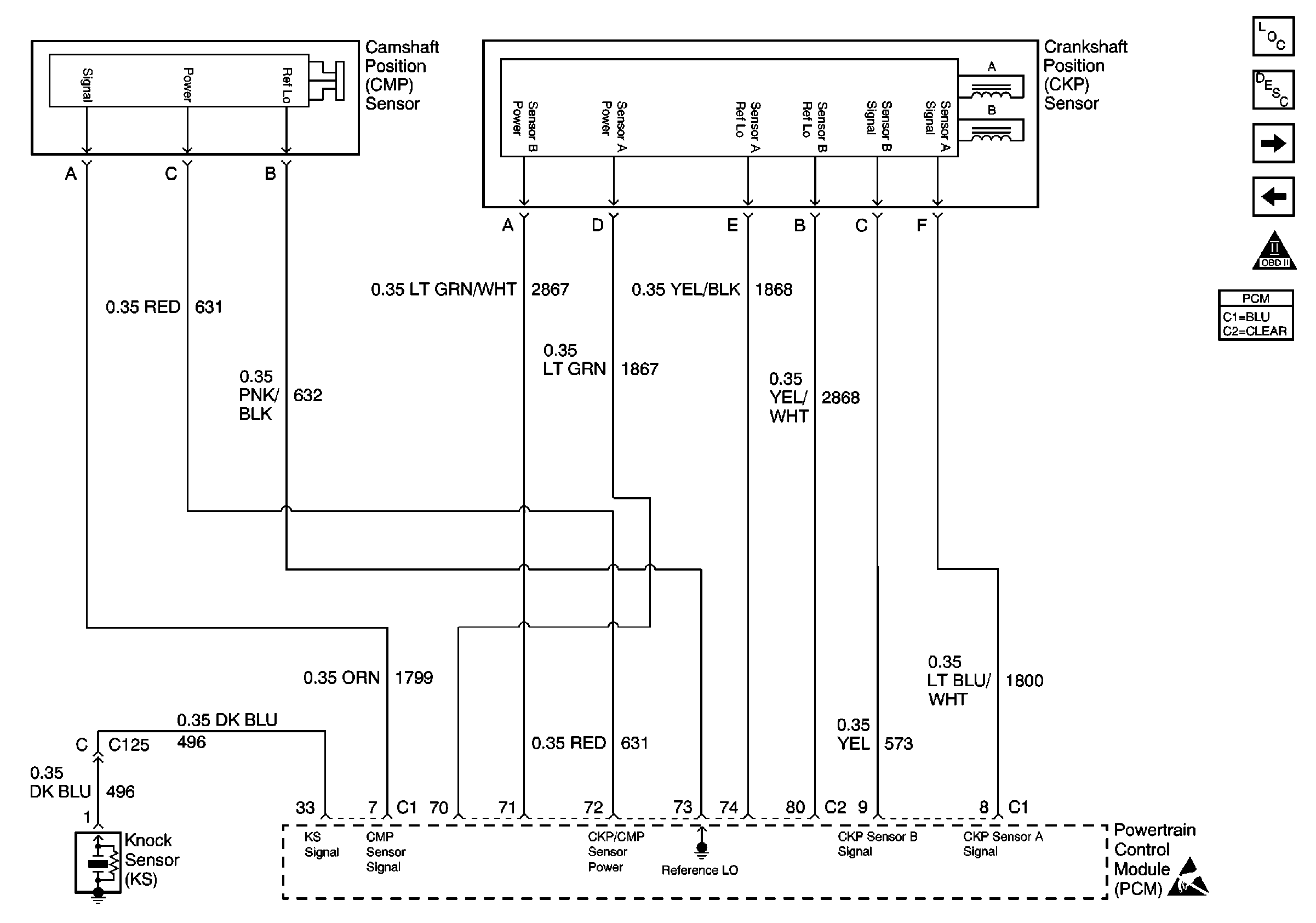
.
Circuit Description
The crankshaft position (CKP) sensor used on this engine is actually 2 sensors within a single housing. There are separate power, ground (reference low) and signal circuits connecting both sensors to the powertrain control module (PCM). The PCM supplies 12 volts to the CKP sensors.
The PCM can use three different modes of decoding crankshaft position. During normal operation, the PCM performs an Angle Based calculation using both signals to determine crankshaft position. The dual sensor allows the engine to run even if one signal is lost. If either signal is lost, the PCM switches to a Time Based method of calculating crankshaft position. If the system is operating in Time A mode, the PCM is using only the signal from sensor A. Time B indicates that the sensor B signal is being used. If the lost signal is restored, the PCM will continue to operate in Time A or B mode for the remainder of the current key cycle. The PCM will automatically revert back to the Angle mode on the next start up if the fault is not present. The scan tool can display the Crank Position Sensing Decode Mode.
Conditions for Running the DTC
The engine is cranking or running
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The PCM detects a problem with the CKP sensor B signal.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) on the second consecutive ignition cycle that the diagnostic runs and fails. |
| • | The PCM records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The first time the diagnostic fails, the PCM stores this information in the Failure Records. If the diagnostic reports a failure on the second consecutive ignition cycle, the PCM records the operating conditions at the time of the failure. The PCM writes the conditions to the Freeze Frame and updates the Failure Records. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The PCM turns the MIL OFF after 3 consecutive drive trips during which the diagnostic runs and passes. |
| • | A last test failed, or the current DTC, clears when the diagnostic runs and passes. |
| • | A History DTC clears after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles, if no other emission related diagnostic failures are reported. |
| • | Use a scan tool in order to clear the MIL diagnostic trouble code. |
| • | Interrupting the PCM battery voltage may or may not clear DTCs. This practice is not recommended. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Description , Clearing Diagnostic Trouble Codes. |
Diagnostic Aids
Notice: Use the connector test adapter kit J 35616-A for any test that
requires probing the following items:
• The PCM harness connectors • The electrical center fuse/relay cavities • The component terminals • The component harness connector
If the problem is intermittent, refer to Intermittent Conditions .
CKP/CMP sensor DTCs may set if the key is turned to Start and the starter is inoperative. If P0335, P0340, and P0385 are set and no trouble is found, check for the following:
| • | Is there a no-crank condition or an intermittent no-crank condition? |
| • | Was an attempt made to crank the engine with the shift lever not in P/N? |
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
Step
| Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | Go to Step 2 | |
2 | Does the engine start and run? | -- | Go to Step 3 | Go to Step 5 |
Does the scan tool indicate CKP Sensor Status Angle? | -- | Go to Step 4 | Go to Step 5 | |
4 | Move the related harnesses and connectors, by hand only, while monitoring the scan tool display. Does CKP Sensor Status change to Time A or Time B or does an engine stall occur? | -- | Go to Step 12 | Go to Intermittent Conditions |
5 | The following steps apply to the sensor and related circuitry that is malfunctioning. For example, if the scan tool indicates Time A, the system is using the signal from CKP sensor A. CKP sensor B and related circuits should be diagnosed.
Does the DMM indicate the specified voltage? | B+ | Go to Step 6 | Go to Step 13 |
6 | Connect the DMM between the power circuit and the ground circuit in the CKP sensor harness connector. Does the DMM indicate the specified voltage? | B+ | Go to Step 7 | Go to Step 14 |
7 | For the following test, the PCM must be commanded to look at the sensor being tested. Set the Crank Position Sensing Decode Mode to Time A when testing sensor A, Time B when testing sensor B.
Is RPM indicated on the scan tool? | -- | Go to Step 19 | Go to Step 8 |
8 |
Is voltage indicated? | -- | Go to Step 17 | Go to Step 9 |
9 | Using the DMM, check the signal circuit for continuity between the CKP sensor harness connector and the PCM harness connector. Does the DMM display the value shown or lower? | 5 ohms | Go to Step 10 | Go to Step 15 |
10 | Using the DMM, check for continuity between the signal circuit and ground. The DMM should display infinite resistance. Does the DMM display infinite resistance? | -- | Go to Step 11 | Go to Step 16 |
11 | Using DMM J 39200 , check for continuity between the CKP sensor A and CKP sensor B signal circuits. The DMM should display infinite resistance. Does the DMM display infinite resistance? | -- | Go to Step 21 | Go to Step 18 |
12 | Repair the harness and connections as necessary. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | Go to Step 23 | -- |
13 | Repair the sensor power circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | Go to Step 23 | -- |
14 | Repair the open or high resistance sensor ground circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | Go to Step 23 | -- |
15 | Repair the open or high resistance sensor signal circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | Go to Step 23 | -- |
16 | Repair the sensor signal circuit shorted to ground. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | Go to Step 23 | -- |
17 | Repair the sensor signal circuit shorted to power. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | Go to Step 23 | -- |
18 | Repair the signal circuits shorted together. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | Go to Step 23 | -- |
19 | Check for poor connections and terminal tension at the CKP sensor. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections in Wiring Systems. Was a problem found and corrected? | -- | Go to Step 23 | Go to Step 20 |
20 |
Is the action complete? | -- | Go to Step 23 | -- |
21 | Check for poor connections and terminal tension at the PCM. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections in Wiring Systems. Was a problem found and corrected? | -- | Go to Step 23 | Go to Step 22 |
22 |
Important: The replacement PCM must be programmed. Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement/Programming . Is the action complete? | -- | Go to Step 23 | -- |
23 |
Does the scan tool indicate that this test ran and passed? | -- | Go to Step 24 | Go to Step 2 |
24 | Review Captured Info using the scan tool. Are there any DTCs that have not been diagnosed? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | System OK |
