For 1990-2009 cars only
Completely inspect the turbocharger and all other engine components that may cause similar conditions before replacing the turbocharger.
Use the following information to diagnose problems caused by the turbocharger.
The turbocharger is serviced as a complete unit.
- Clean mating surfaces.
- Inspect for damage to the compressor wheel, compared to a normal compressor wheel.
- Inspect for damage to the compressor wheel, by a soft object.
- Inspect for damage to the compressor wheel, by a hard object.
- Inspect for damage to the turbine wheel, compared to a normal turbine wheel.
- Inspect for damage to the turbine wheel, by a soft object.
- Inspect for damage to the turbine wheel, by a hard object.
- Inspect compressor and turbine blades for heavy rubbing.
- Check the turbocharger housing for signs of rubbing.
- Clean the turbocharger inlet duct.
- Clean the turbocharger inlet duct mating surfaces.
- Inspect the turbocharger inlet duct for cracks.
- Inspect the turbocharger inlet duct mating surfaces for damage.
- Clean the turbocharger outlet duct.
- Clean the turbocharger outlet duct mating surfaces.
- Inspect the turbocharger outlet duct for cracks.
- Inspect the turbocharger outlet duct mating surfaces for damage.
- Inspect the turbocharger Wastegate Flap (3) for Cracks and Bends
- Inspect the Wastegate Regulator Valve (1).
- Ensure that the following components are moving correctly by using a vacuum pump connected to the Wastegate Regulator Valve:
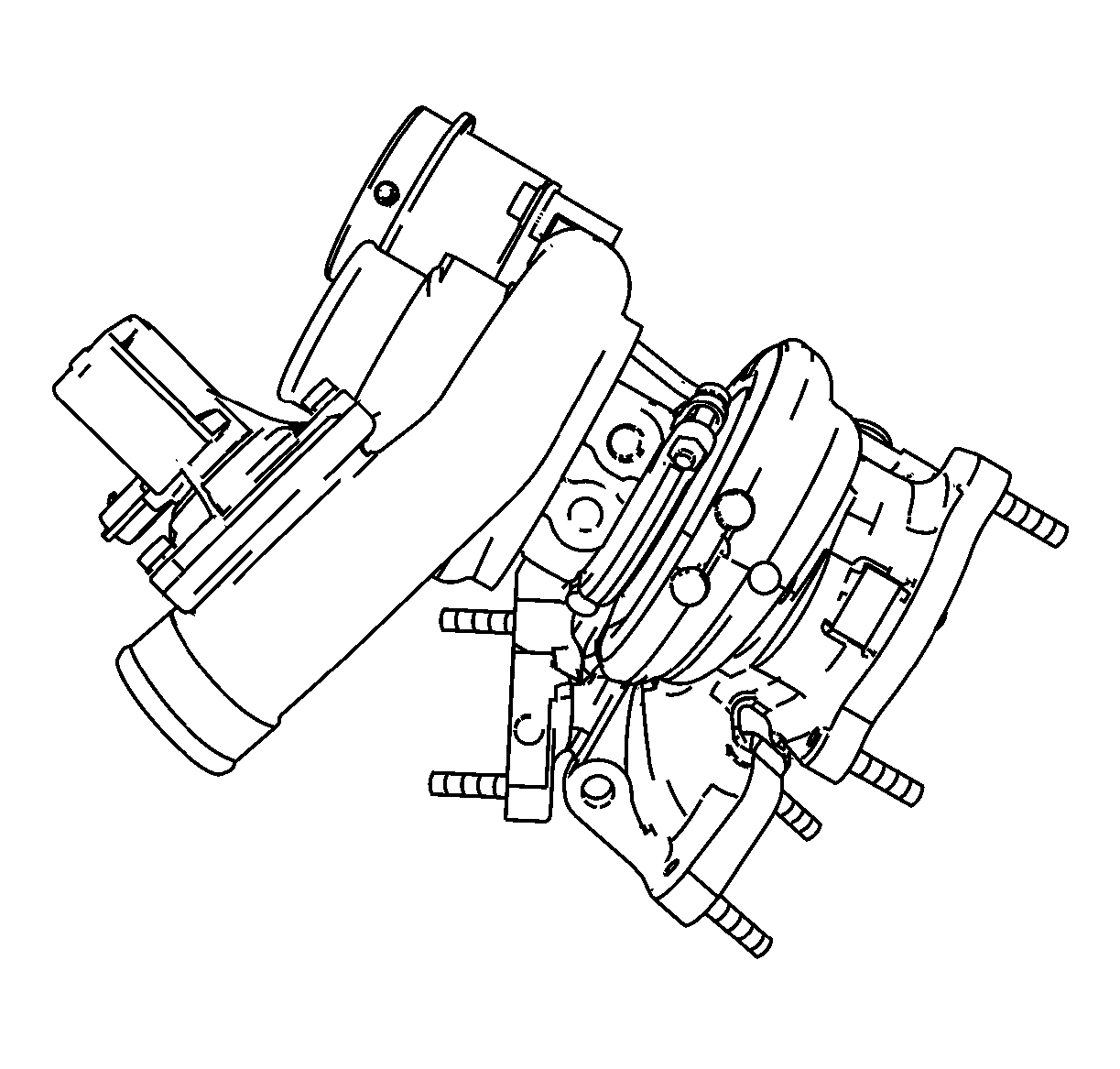
Note: Oil residue on the turbocharger compressor wheel is normal with a closed PCV system.
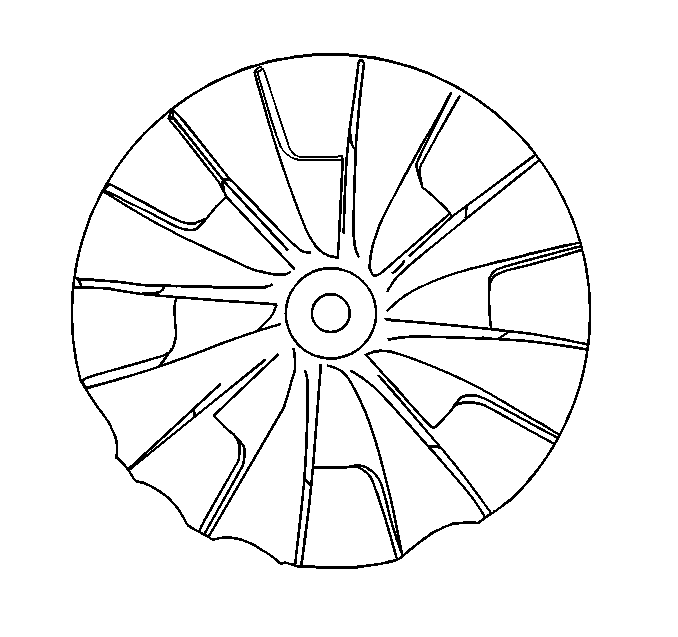
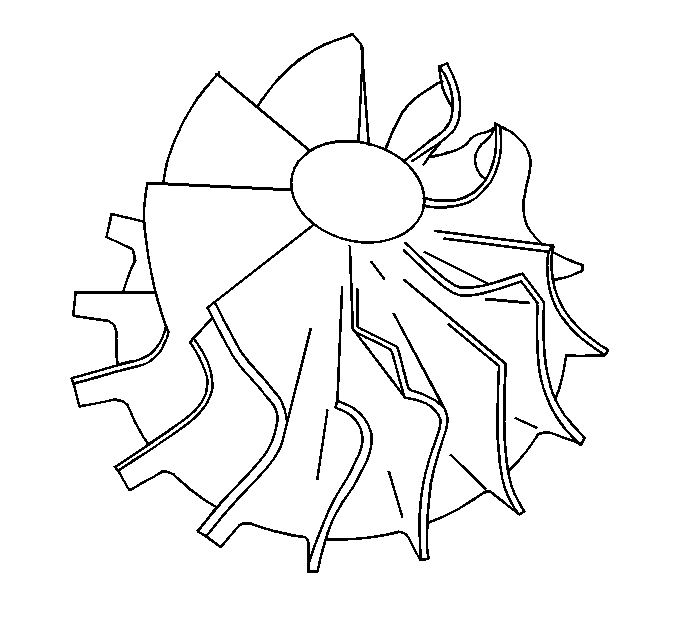
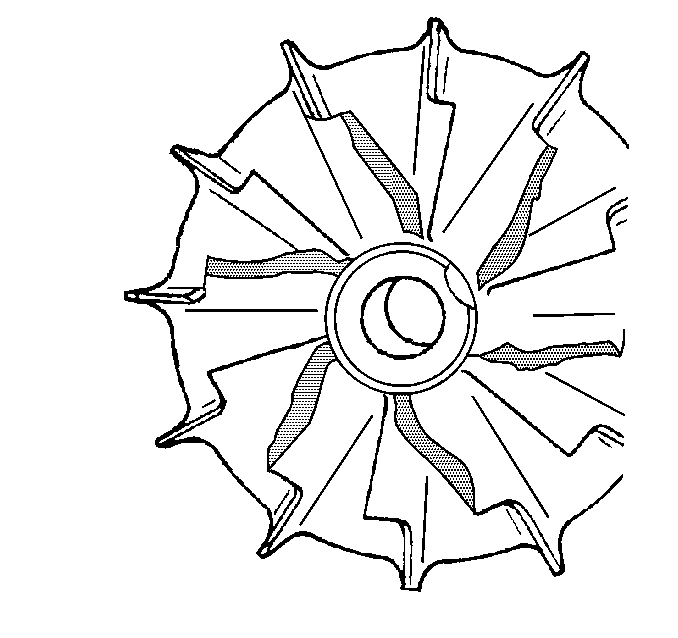
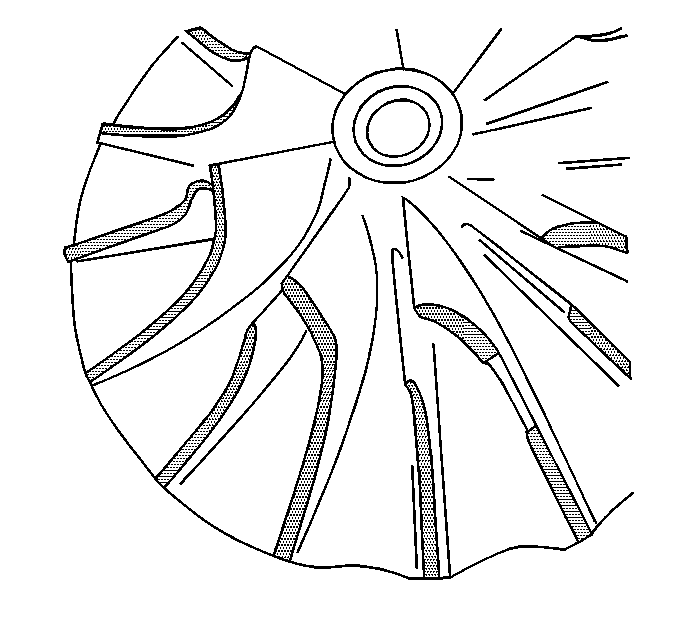
Ensure that the following conditions do not exist on the compressor and turbine wheel blades:
| • | Cracks |
| • | Bends |
| • | Erosion of the blades |
| • | Broken blades |

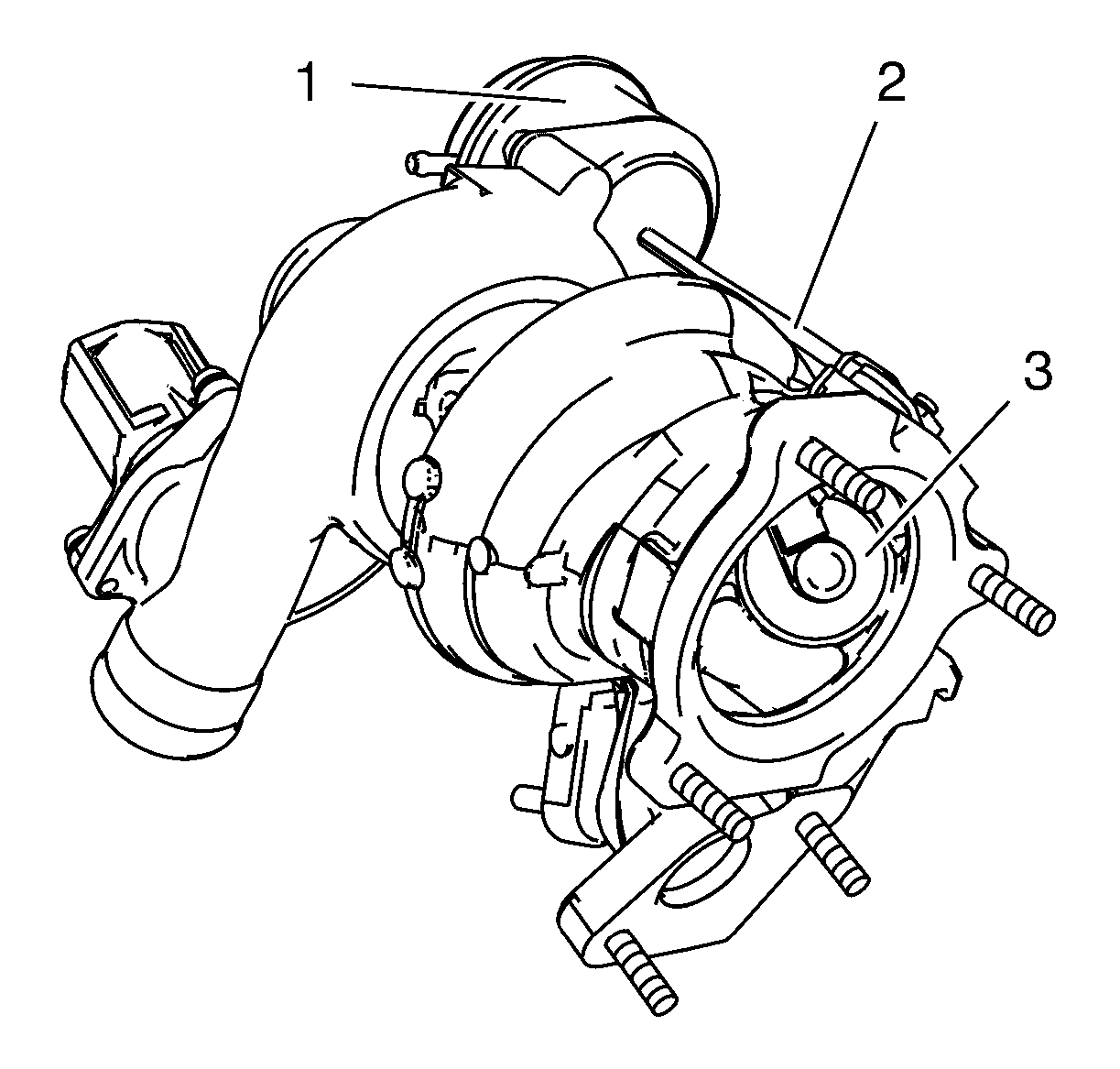
| • | Wastegate Regulator Valve rod (2) |
| • | Wastegate Flap |
