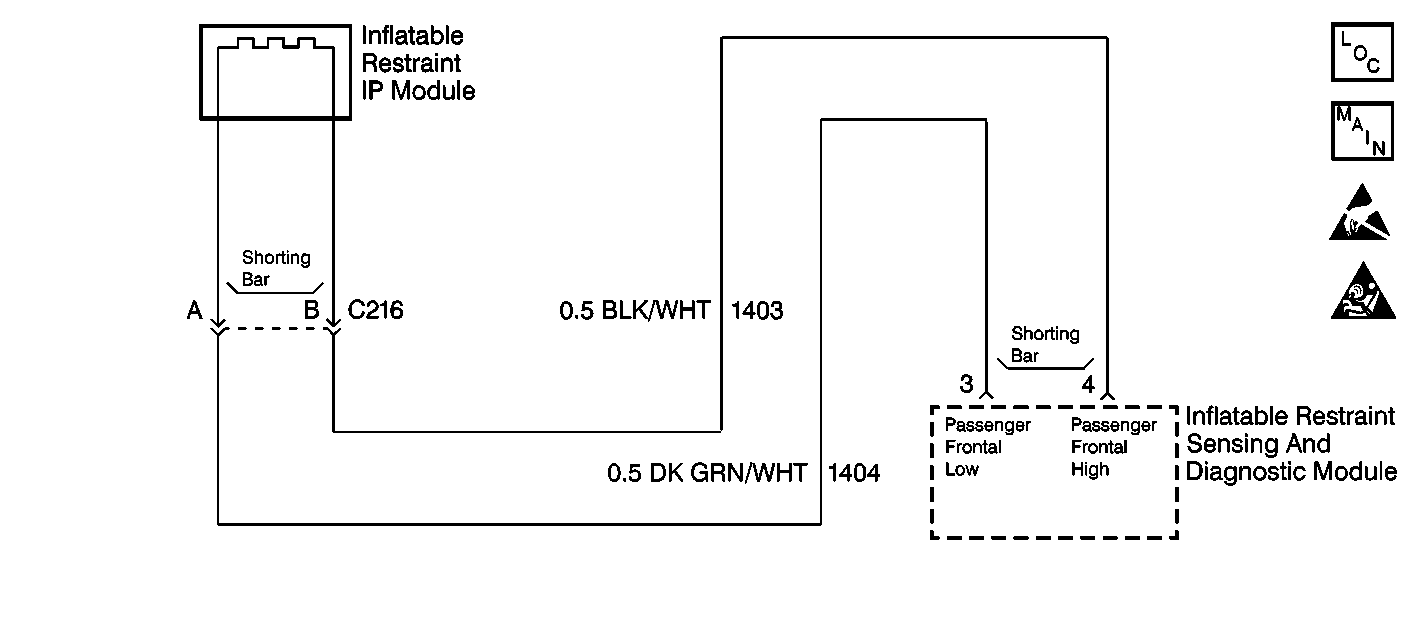
Circuit Description
When you first turn the ignition switch to the RUN position, the inflatable restraint sensing and diagnostic module (SDM) perform tests to diagnose critical malfunctions within itself. Next the SDM measures IGNITION and the deployment loop voltages to make sure they are within their respective normal voltage ranges. Then the SDM proceeds with the RESISTANCE MEASUREMENT test. During one portion of the RESISTANCE MEASUREMENT test, the SDM does the following:
| • | Grounds the Passenger Frontal Low terminal 3 through an internal current sink. |
| • | Connects the Passenger Frontal High terminal 4 to an internal constant current source. This current produces proportional voltage drops in the deployment loop. |
| • | Measures the voltage difference between Passenger Frontal High and Passenger Frontal Low. |
| • | Calculates the resistance of the passenger frontal air bag deployment loop using the measured voltage. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | The passenger frontal air bag deployment loop is not open. |
| • | The passenger frontal air bag deployment loop is not shorted to voltage. |
| • | The passenger frontal air bag deployment loop is not shorted to ground. |
| • | The passenger frontal air bag deployment loop resistance is more than 2.5 ohms. The passenger frontal air bag deployment loop consists of the following components: |
| - | Inflatable restraint IP module. |
| - | Harness wiring of CKT 1403. |
| - | Harness wiring of CKT 1404. |
| - | Connector terminal contact. |
The RESISTANCE MEASUREMENT test checks for this malfunction. This test only occurs once each ignition cycle when IGNITION is within the normal operating voltage range.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The SDM sets a DTC B1015. |
| • | The SDM turns ON the AIR BAG warning lamp. |
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
| • | Current DTC |
| The resistance of the passenger frontal air bag deployment loop is less than 2.25 ohms and the ignition switch is cycled. |
| • | History DTC |
| - | You issue a scan tool CLEAR CODES command. |
| - | Once 250 malfunction free ignition cycles have occurred. |
When you issue a scan tool CLEAR CODES command and the malfunction is still present, the DTC will not reappear until the next ignition cycle.
Diagnostic Aids
A poor connection can cause an intermittent condition. Check the following for a poor connection:
| • | The inflatable restraint IP module wiring harness connector terminal A and terminal B. |
| • | The SDM wiring harness connector terminal 3 and terminal 4. |
| • | The wire to terminal connections in CKT 1403. |
| • | The wire to terminal connections in CKT 1404. |
The diagnostic table directs the technician to note the entry value of PASS. FRONTAL RESIST.. Comparing the value of PASS. FRONTAL RESIST. over multiple ignition cycles can be helpful in determining if an intermittent condition exists.
When measurements are requested in this table, use J 39200 Digital Multimeter with the correct terminal adapter from J 35616 Connector Test Adapter Kit. When a check for proper connection is requested, refer to Intermittents and Poor Connections . When a wire, connector or terminal repair is requested, use J-38125 Terminal Repair Kit and refer to Wiring Repair .
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table:
-
This step checks the inflatable restraint IP module yellow 2-way wiring harness connector for corrosion or damaged terminals.
-
This step isolates the malfunction to one side of the inflatable restraint IP module yellow 2-way connector.
-
This step checks the SDM wiring harness connector for corrosion or damaged terminals.
-
This step checks to see if there is a high resistance in CKT 1404.
-
This step determines if there is a high resistance in CKT 1403 or if there is a malfunctioning SDM.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Was the SIR Diagnostic System Check performed? | -- | ||
2 |
Has PASS. FRONTAL RESIST. been read and recorded on the repair order? | -- | -- | |
Are the terminals damaged or corroded? | -- | |||
4 | Replace the inflatable restraint IP module yellow 2-way wiring harness connector. Refer to Wiring Repair . Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |
5 | Check for a proper connection at terminal A and terminal B of the inflatable restraint IP module yellow 2-way connector. Are the terminals damaged or corroded? | -- | ||
6 | Check for a proper connection at terminal A and terminal B of the inflatable restraint IP module yellow 2-way connector. Are the terminals damaged or corroded? | -- | ||
7 | Replace the inflatable restraint IP module. Refer to Inflatable Restraint Instrument Panel Module Replacement . Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |
8 |
Is PASS. FRONTAL RESIST. more than the specified value? | 2.5 ohms | ||
9 |
Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |
Is PASS. FRONTAL RESIST. more than the specified value? | 2.5 ohms | |||
11 |
Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |
Is the SDM wiring harness connector damaged or corroded? | -- | |||
13 | Replace the SDM wiring harness connector. Refer to Wiring Repair . Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |
14 | Check for a proper connection at terminal 3 and terminal 4 on the SDM. Are the terminals damaged or corroded? | -- | ||
15 | Check for a proper connection at terminal 3 and terminal 4 on the SDM. Are the terminals damaged or corroded? | -- | ||
16 | Replace the SDM. Refer to Inflatable Restraint Sensing and Diagnostic Module Replacement . Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |
Is the measured resistance within the specified value? | 0-0.5 ohms | |||
18 |
Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |
Use the J 39200 to measure the resistance between terminal 4 of the SDM wiring harness connector and terminal B of the inflatable restraint IP module yellow 2-way wiring harness connector. Is the measured resistance within the specified value? | 0-0.5 ohms | |||
20 |
Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |
21 | Reconnect all the SIR components, making sure all the components are properly mounted. Have all the SIR components been reconnected and properly mounted? | -- | -- | |
22 | Use the scan tool to clear all current and history SIR DTCs. Have all current and history SIR DTCs been cleared? | -- | -- |
