The dual crankshaft position (CKP) sensor is secured in an aluminum
mounting bracket and bolted to the front left side of the engine timing chain
cover, partially behind the crankshaft balancer. A 4-wire harness connector
plugs into the sensor, connecting the sensor to the ignition control
module (ICM). The dual crankshaft position sensor contains 2 Hall-effect
switches with one shared magnet mounted between the switches. The magnet
and each Hall-effect switch are separated by an air gap. A Hall-effect
switch reacts like a solid state switch, grounding a low current signal
voltage when a magnetic field is present. When the magnetic field is
shielded from the switch by a piece of steel placed in the air gap between
the magnet and the switch, the signal voltage is not grounded. If the
piece of steel, called an interrupter, is repeatedly moved in and out
of the air gap, the signal voltage will appear to oscillate between on and
off. In the case of the electronic ignition system, the piece of steel
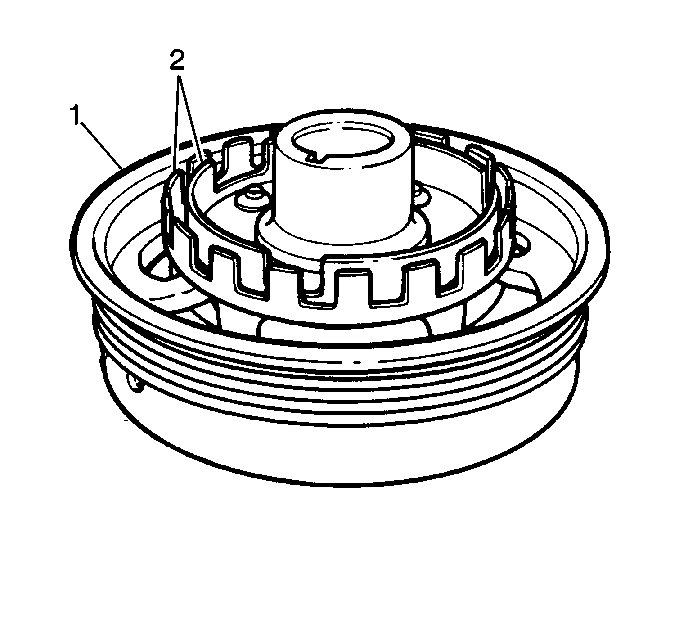
is 2 concentric interrupter rings mounted to the rear of the crankshaft
balancer (1).
Each interrupter ring (2) has blades and windows that either block the
magnetic field or allow the field to close one of the Hall-effect switches.
The outer Hall-effect switch produces a signal called the CKP 18X because
the outer interrupter ring has 18 evenly spaced blades and windows. The
CKP 18X portion of the crankshaft position sensor produces 18 on - off
pulses per crankshaft revolution. The Hall-effect switch closest to the
crankshaft, the CKP sync portion of the sensor, produces a signal that
approximates the inside interrupter ring. The inside interrupter ring
has 3 unevenly spaced blades and windows of different widths. The CKP
sync portion of the crankshaft position sensor produces 3 different length
ON - OFF pulses per crankshaft revolution. When a CKP sync interrupter
ring window is between the magnet and inner switch, the magnetic field
will cause the CKP sync Hall-effect switch to ground the CKP sync signal
voltage supplied from the ignition control module. The CKP 18X interrupter
ring and Hall-effect switch react similarly. The ignition control module
interprets the CKP 18X and CKP sync ON - OFF signals as an indication
of crankshaft position, and the ignition control module must have both
signals to fire the correct ignition coil. The ignition control module
determines crankshaft position for correct ignition coil sequencing by
counting how many CKP 18X signal transitions occur, i.e.; ON - OFF or
OFF - ON, during a CKP sync pulse.
The camshaft position sensor is located on the timing cover behind the
water pump near the camshaft sprocket. As the camshaft sprocket turns, a magnet
activates the Hall effect switch in the camshaft position sensor. When
the Hall-effect switch is activated, the switch grounds the signal line
to the ICM, pulling the camshaft position sensor signal circuit's applied
voltage low. This is interpreted as a CMP sensor signal. The CMP sensor
signal is created as piston #1 is approximately 25 degrees after top
dead center on the power stroke.