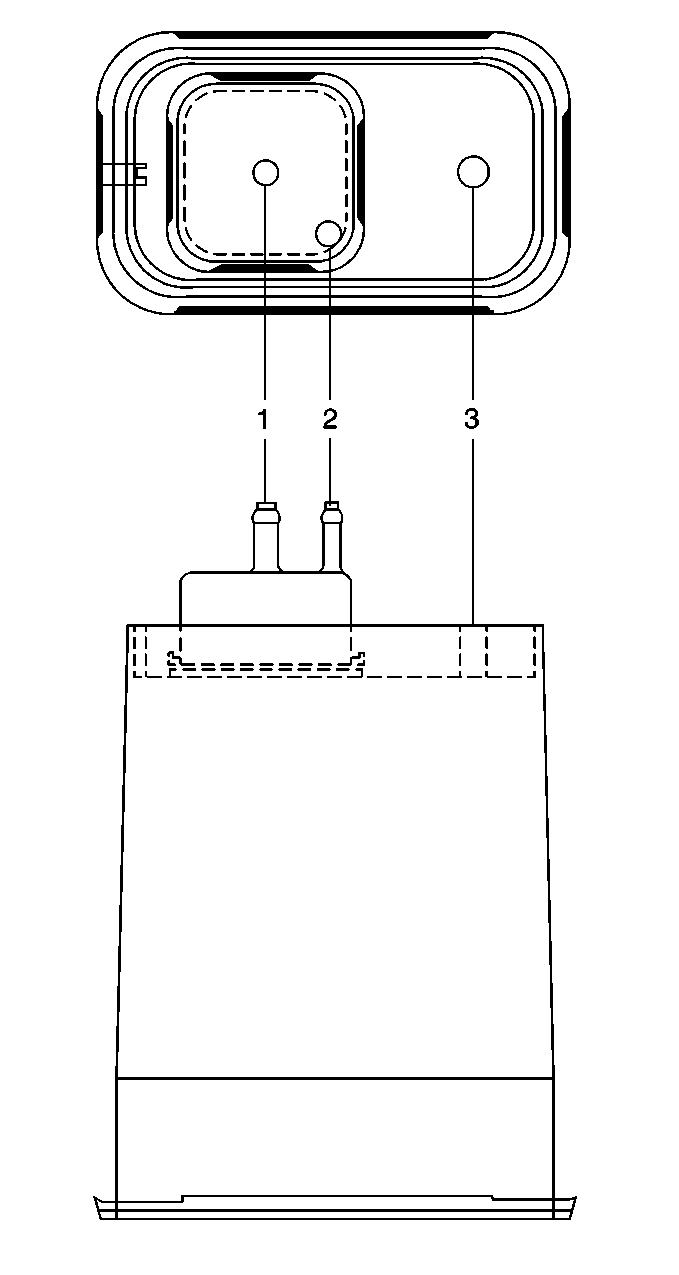
The Evaporative Emission (EVAP) Control system
used on all vehicles is the charcoal canister storage method. This method
transfers fuel vapor from the fuel tank to an activated carbon
storage canister in order to hold the vapors when the vehicle is
not operating. When the engine is operating, the fuel vapor is
purged from the carbon element by intake air flow, and consumed in
the normal combustion process.