Piston, Connecting Rod, and Bearing Cleaning and Inspection Piston/Connecting Rod Inspect
Connecting Rod Measurement
- Clean the connecting rods
in solvent and dry with compressed air.
- Inspect the connecting rods for the following:
| • | Signs of being twisted, bent, nicked, or cracked |
| • | Scratches or abrasion on the rod bearing seating surface |
- If the connecting rod bores contain minor scratches or abrasions,
clean the bores in a circular direction with a light emery paper. DO NOT scrape
the rod or rod cap.
- Measure the piston pin to connecting rod bore using the following
procedure:
| 4.1. | Using an outside micrometer, take two measurements of the piston
pin in the area of the connecting rod contact. |
| 4.2. | Using an inside micrometer, measure the connecting rod piston
pin bore. |
| 4.3. | Subtract the piston pin diameter from the piston pin bore diameter. |
| 4.4. | The clearance should not be more than 0.05 mm (0.0020 in). |
- If there is excessive clearance, replace the piston pin.
- If there is still excessive clearance, replace the connecting
rod.
Piston Measurement
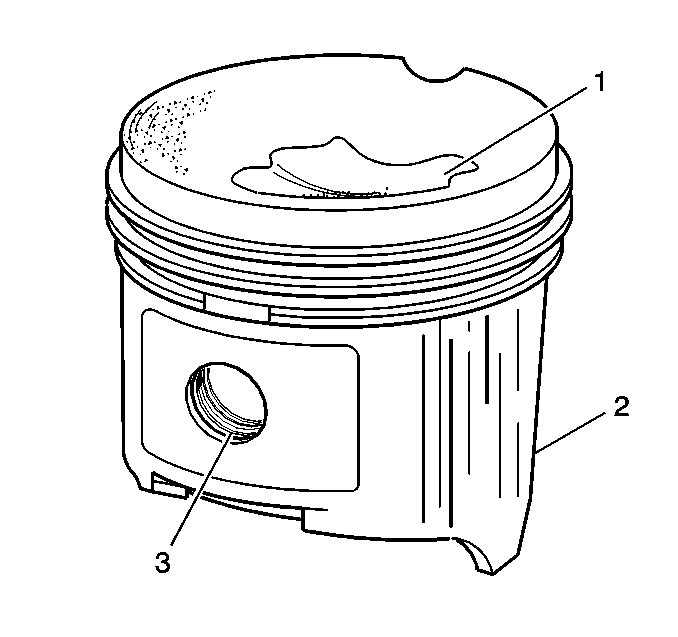
- Clean the piston skirts
and the pins with a cleaning solvent. DO NOT wire brush any part of the piston.
- Clean the piston ring grooves with a groove cleaner. Make sure
oil ring holes and slots are clean.
- Inspect the pistons for the following conditions:
| • | Cracked ring lands, skirts, or pin bosses |
| • | Ring grooves for nicks, burrs that may cause binding |
| • | Warped or worn ring lands |
| • | Eroded areas at the top of the piston (1) |
| • | Scuffed or damaged skirts (2) |
| • | Worn piston pin bores (3) |
- Replace pistons that show any signs or damage or excessive wear.
- Measure the piston pin bore to piston pin clearances using the
following procedure:
| 5.1. | Piston pin bores and pins must be free of varnish or scuffing. |
| 5.2. | If the clearance is excessive, determine which component is out
of specification. |
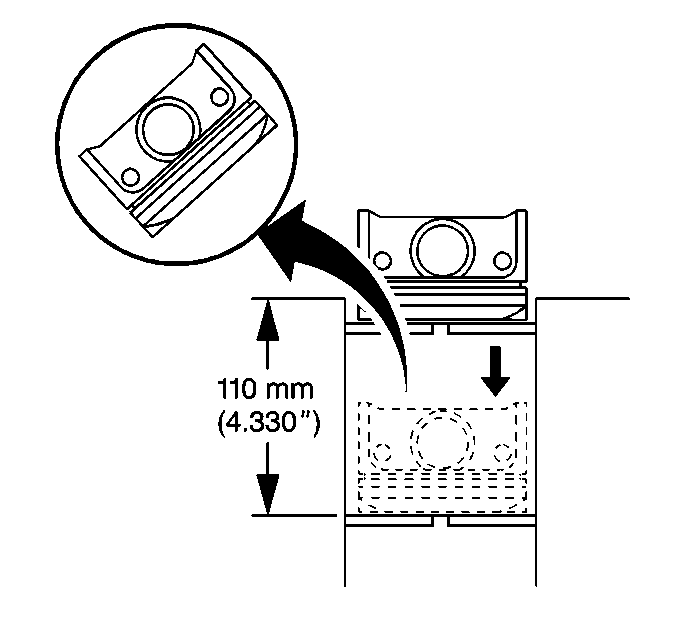
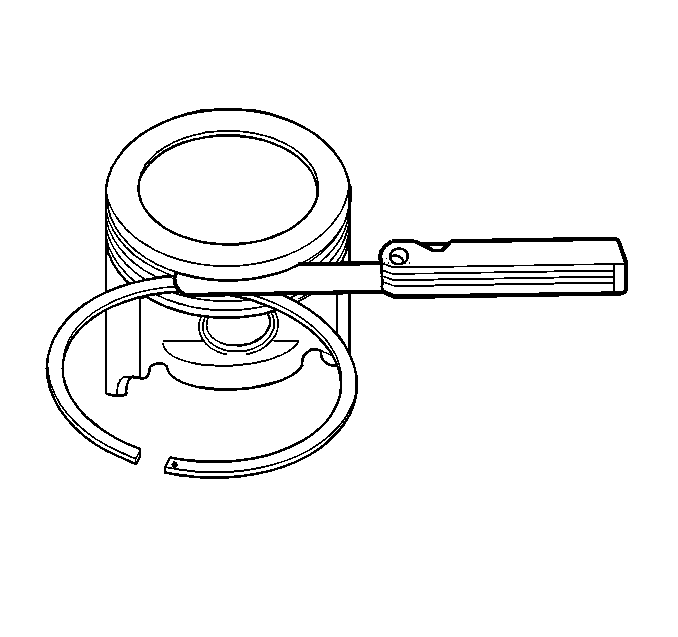
- Measure the piston ring
end gap using the following procedure:
| 6.1. | Place the piston ring in the area of the bore where the piston
ring will travel (approximately 110 mm (4 in) down from the
deck surface). |
| 6.2. | Be sure the ring is square with the cylinder bore by positioning
the ring with the piston head. |
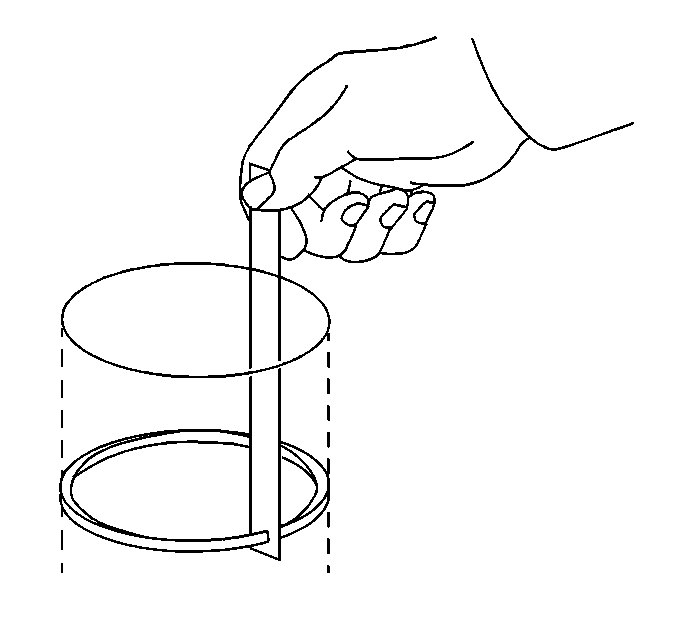
- Measure the end gap of
the piston ring with feeler gages. Compare the measurements with those provided
below:
| 7.1. | The top compression ring end gap should be 0.15-0.30 mm
(0.0098-0.0138 in). |
| 7.2. | The second compression ring end gap should be 0.20-0.35 mm
(0.0138-0.0197 in). |
| 7.3. | The oil ring end gap should be 0.20-0.60 mm (0.0059-0.0157 in). |
- Measure the piston ring
side clearance using the following procedure:
| 8.1. | Roll the top two piston rings entirely around the piston ring
groove. If any binding is caused by the ring groove, dress the groove with
a fine file. If any binding is caused by a distorted piston ring, replace
the ring. |
| 8.2. | With the piston ring on the piston, use feeler gages to check
clearance at multiple locations. |
| 8.3. | The clearance between the surface of the top piston rings and
the ring land should be no greater than 0.070 mm (0.0027 in). |
| 8.4. | If the clearance is greater than specifications, replace the piston
rings. |
| 8.5. | If the new ring does not reduce the top ring side clearance to
0.070 mm (0.0027 in) or less, install a new piston. |
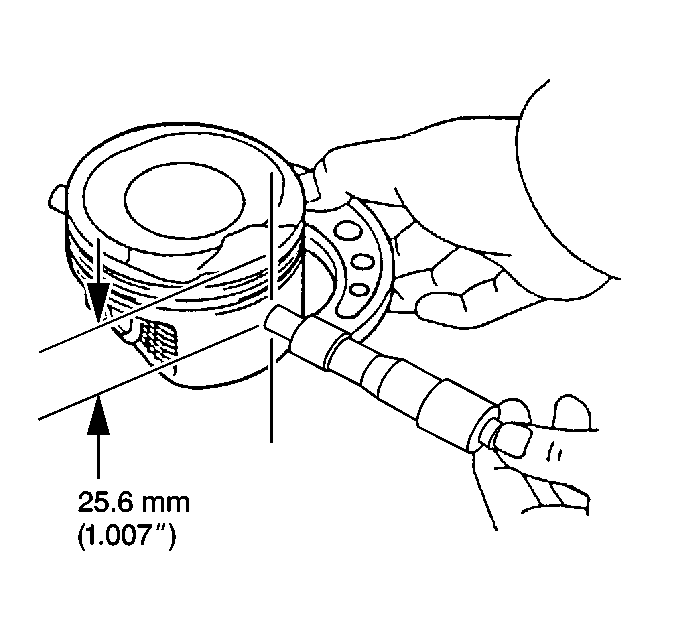
- Measure piston width using
the following procedure:
| 9.1. | Using an outside micrometer, measure the width of the piston 25 mm
(1 in) below the top of the piston at the thrust surface perpendicular
to the centerline of the piston pin. |
| 9.2. | Compare the measurement of the piston to its original cylinder
by subtracting the piston width from the cylinder diameter. |
| 9.3. | The proper clearance specification for the piston is 0.020-0.040 mm
(0.0008-0.0015 in). |
- If the clearance obtained through measurement is greater than
these specifications and the cylinder bores are within specification, replace
the piston.
Piston, Connecting Rod, and Bearing Cleaning and Inspection Bearing Selection
Connecting Rod Bearing Selection
Tool Required
J 36660-A Torque Angle
Meter
- The connecting rod bearings are of the precision insert type.
The connecting rod bearings are available in standard and 0.25 mm (0.0098 in)
undersize.
Important: If crankshaft bearing failure is due to other than normal wear, investigate
the cause. Inspect the crankshaft or connecting rod bearing bores.
- Inspect the connecting rod bearing bores or crankshaft main bearing
bores using the following procedure:
| 2.1. | Tighten the bearing cap to specification. |
| 2.2. | Measure the bearing bore for taper and out-of-round. |
| 2.3. | No taper or out-of-round should exist. |
Important: The crankshaft and the main bearing caps must be installed and properly
torqued before measuring the connecting rod clearances.
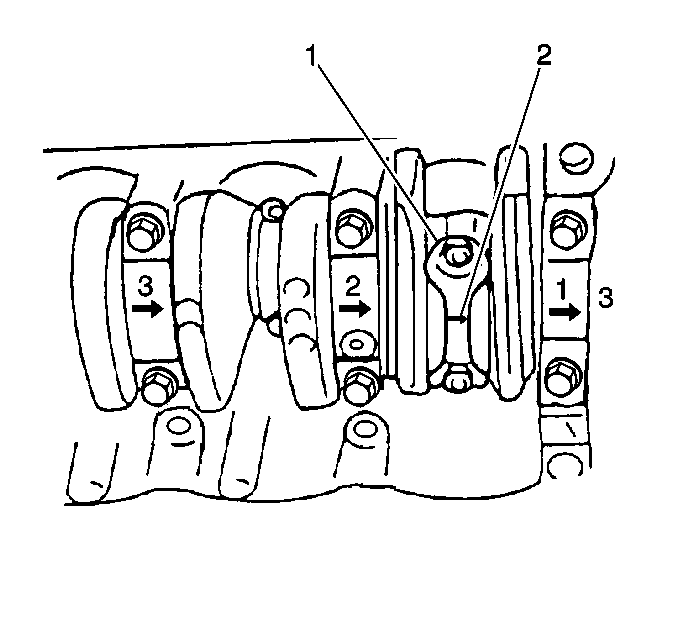
- Starting with the number one connecting rod, remove the connecting rod
cap nuts.
- Carefully remove the connecting rod bearing cap.
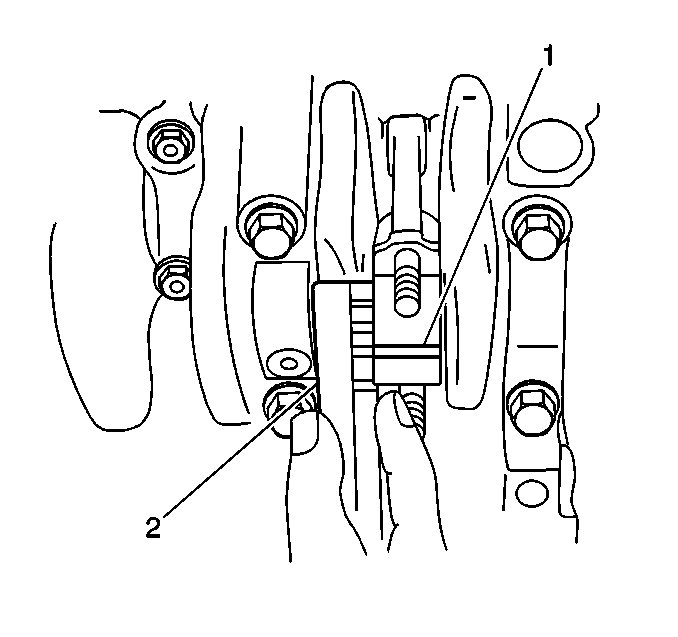
- Lay a piece of gaging
plastic across the crankshaft number one connecting rod journal.
- Carefully place the connecting rod cap onto the connecting rod.
Important: Do not turn the crankshaft while measuring the bearing clearance.
- Install the two connecting rod bearing cap nuts.
Tighten
Tighten the connecting rod bearing cap bolts to 35 N·m
(26 lb ft).
- After reaching the proper torque, remove the two crankshaft connecting
rod bearing cap nuts.
- Carefully remove the connecting rod bearing cap from the connecting
rod.

- Measure the gaging plastic
(1) at its widest point.
Standard Oil Clearance:
0.020-0.050 mm (0.0008-0.0019 in)
Maximum Oil Clearance:
0.080 mm (0.0031 in)
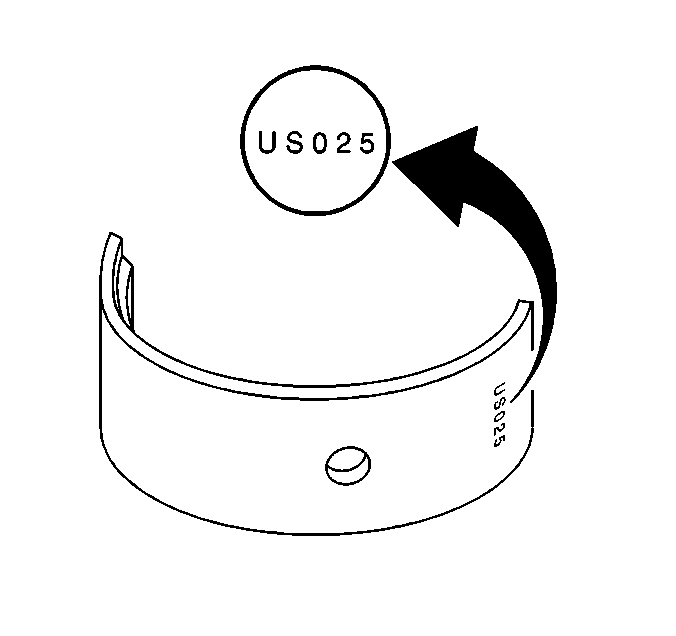
- If bearing replacement
is necessary, determine if a standard bearing or an undersized bearing is
needed. The undersized bearing is identifiable by a stamping on the backside
of the bearing.











