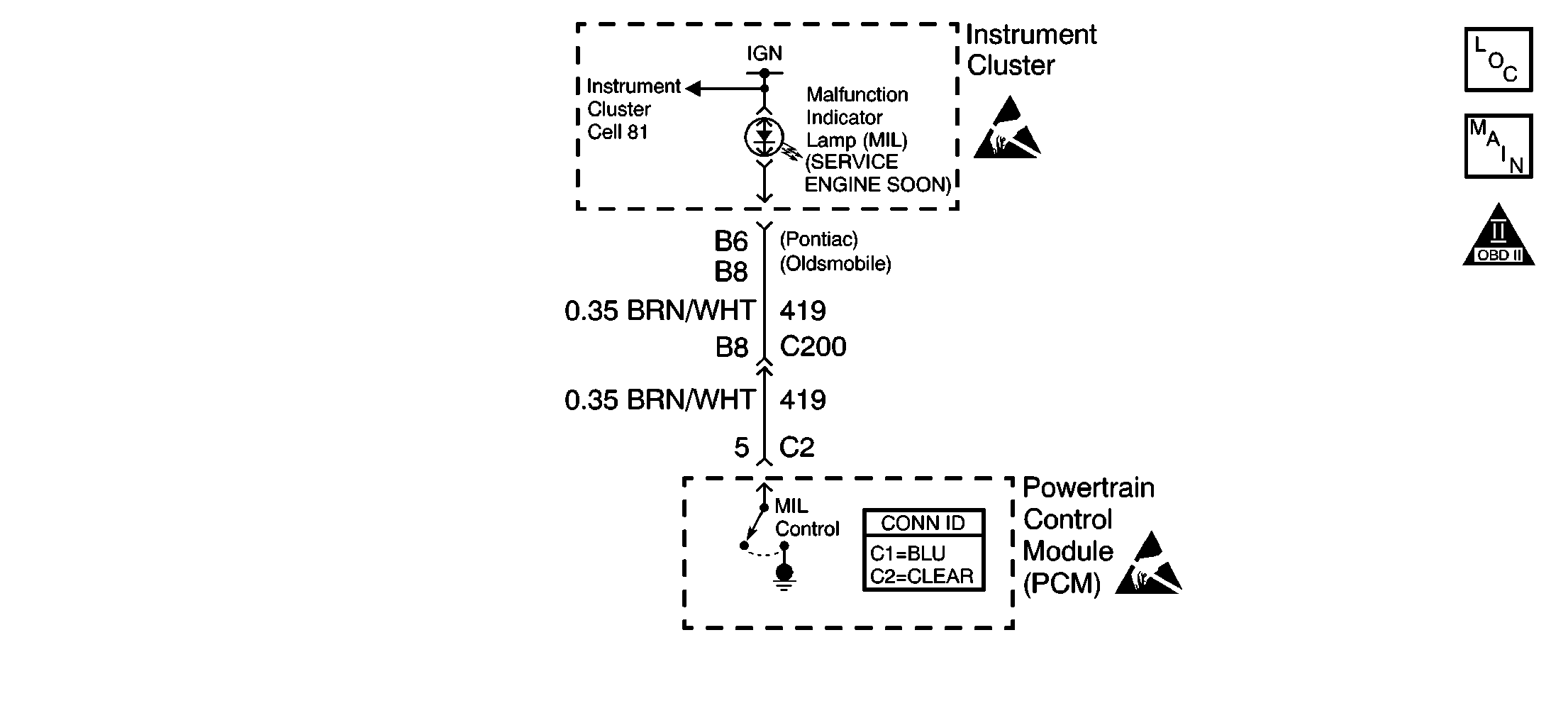
Circuit Description
Ignition voltage is supplied directly to the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL). The powertrain control module (PCM) controls the lamp by grounding the control circuit via an internal switch called a driver. The primary function of the driver is to supply the ground for the component being controlled. Each driver has a fault line which is monitored by the PCM. When the PCM is commanding a component on, the voltage of the control circuit should be low, near 0 volts. When the PCM is commanding the control circuit to a component off, the voltage potential of the circuit should be high, near battery voltage. If the fault detection circuit senses a voltage other than what is expected, the fault line status will change causing the DTC to set.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | The ignition is ON. |
| • | Ignition voltage is between 9.0-18.0 volts. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | An improper voltage level has been detected on the MIL control circuit. |
| • | The above condition is present for at least 30 seconds. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM will illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) during the second consecutive trip in which the diagnostic test has been run and failed. |
| • | The PCM will store conditions which were present when the DTC set as Freeze Frame/Failure Records data. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The PCM will turn OFF the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) during the third consecutive trip in which the diagnostic has run and passed. |
| • | The history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles have occurred without a malfunction. |
| • | The DTC can be cleared by using a scan tool. |
Diagnostic Aids
inspect for the following conditions:
If the ignition feed circuit is suspected of being open, observe if other lamps on that circuit illuminate.
Important: Remove any debris from the connector surfaces before servicing a component. Inspect the connector gaskets when diagnosing or replacing a component. Ensure that the gaskets are installed correctly. The gaskets prevent contaminate intrusion.
| • | Faulty terminal connection--Inspect the harness connectors for the following conditions: |
| - | Backed out terminals |
| - | Improper mating |
| - | Broken locks |
| - | Improperly formed or damaged terminals |
| - | Faulty terminal to wire connection--Use a corresponding mating terminal to test for proper tension. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections and Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems. |
| • | Damaged harness--Inspect the wiring harness for damage. |
| If the harness inspection does not reveal a problem, observe the display on the scan tool while moving connectors and wiring harnesses related to the sensor. A change in the scan tool display may indicate the location of the fault. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. |
| • | Clean and secure the connections at the PCM and the engine grounds. |
If the DTC is determined to be intermittent, reviewing the Failure Records can be useful in determining when the DTC was last set.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table:
-
Important: If the I/P is completely inoperative, refer to Body and Accessories for further diagnosis.
Command the MIL ON and OFF. Repeat the commands as necessary.
-
If you do not find trouble in the control circuit or the connection at the PCM, the PCM may be faulty. However, this is an extremely unlikely failure.
-
This DTC will not report a pass. The scan tool status for this DTC will never report a pass. The scan tool will only display when the diagnostic fails. The repair is not complete if the scan tool indicates that the diagnostic ran and failed.
Step | Action | Values | Yes | No | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||||||||
Does the MIL turn ON and OFF with each command? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | ||||||||
3 |
Is the MIL OFF? | -- | ||||||||
4 | Probe the MIL control circuit in the PCM harness connector with a fused jumper wire connected to ground. Is the MIL ON? | -- | ||||||||
5 | Repair the short to ground in the MIL control circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you complete the repair? | -- | -- | |||||||
6 | Test for faulty connections at the PCM. Refer to Testing for Continuity , and Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||
7 | Test for the following conditions:
Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you complete the repair? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check - Instrument Cluster in Instrument Panel, Gauges, and Console | |||||||
|
Important: : The replacement PCM must be programmed. Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement/Programming . Did you complete the repair? | -- | -- | ||||||||
Does the scan tool indicate that this test failed? | -- | |||||||||
10 | Using the scan tool, select the Capture Info option and the Review Info option. Does the scan tool display any DTCs that you have not diagnosed? | -- | Go to applicable DTCs | System OK |
