Important Preliminary Checks
Before using this section, perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic
(OBD) System Check, refer to
Powertrain On Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check
, and verify all of the following
items:
| • | The PCM and MIL are operating correctly. |
| • | There are no DTC(s) stored. |
| • | Ensure that the engine coolant temperature is not above 128°C
(262°F). This condition will cause the PCM to operate in Coolant Hot Mode.
While in Coolant Hot Mode, the PCM will turn fuel OFF to three cylinders
to keep engine temperatures from reaching damaging levels. Coolant Hot Mode
will be perceived as a lack of power, miss, or rough idle. |
| • | Verify the customer complaint and locate the applicable symptoms.
Perform the procedure included in the symptom diagnostic table. |
Visual Physical Checks
Several of the symptom procedures call for a visual/physical inspection.
A careful visual/physical inspection can aid in correcting a problem without
further checks and can save valuable time. A visual/physical inspection
should include the following items:
| • | PCM grounds for being loose, corroded, or in an improper location. |
| • | Vacuum hoses for splits, kinks, and improper connections. The
proper connections are shown on the Vehicle Emission Control Information label.
Check the vacuum hoses for any type of leak or restriction. |
| • | Air intake ducts for collapsed or damaged areas. |
| • | Air leaks at throttle body mounting area, Mass Air Flow (MAF)
sensor and intake manifold sealing surfaces. |
| • | Ignition wires for cracking, hardness, proper routing and carbon
tracking. |
| • | Wiring for improper connections, pinches and cuts. |
Intermittent Condition
An intermittent condition may or may not store a DTC or illuminate
the Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) . DO NOT use the Diagnostic Trouble
Code (DTC) charts for intermittent problems. The fault must be present to
locate the problem.
Most intermittent problems are caused by loose electrical connections
or malfuctioning wiring. Perform a careful visual/physical check for the following
conditions:
| • | Poor mating of the connector halves or a terminal not fully seated
in the connector (backed out). |
| • | Improperly formed or damaged terminal. |
| • | All connector terminals in the problem circuit should be carefully
checked for proper contact tension. |
| • | Poor terminal to wire connection. This requires removing the
terminal from the connector body to check. |
Road test the vehicle with a J 39200
Use a scan tool to help detect intermittent conditions. The scan tool
has several features that can be used to locate an intermittent condition.
Use the following features to find intermittent faults:
| • | The Snapshot feature can be triggered to capture and store engine
parameters within the scan tool when the malfunction occurs. The stored information
then can be reviewed by the service technician to determine what caused
the malfunction. |
| • | Viewing the Freeze Frame data or Failure Records data can also
aid in locating an intermittent condition. Review and record the information
in the freeze frame or failure record associated with the intermittent DTC
being diagnosed. The vehicle can then be driven within the conditions that
were present when the DTC originally set. |
Loss of diagnostic code memory. To check, disconnect the MAF sensor
and idle engine until a DTC sets . DTC P0102 should be stored and kept in
memory when ignition is turned OFF. If DTC P0102 does not remain in memory,
the PCM is malfunctioning. When this test is completed, make sure that you
clear the DTC P0102 from memory.
An intermittent MIL with no stored DTC may be caused by the following
conditions:
| • | Ignition system secondary components arcing to wiring harnesses. |
| • | MIL control circuit wiring intermittently shorted to ground. |
Check for improper installation of electrical options such as lights,
cellular phones etc. Ensure that engine harness routing is correct. Check
all wiring between the PCM and the ignition control module for poor connections.
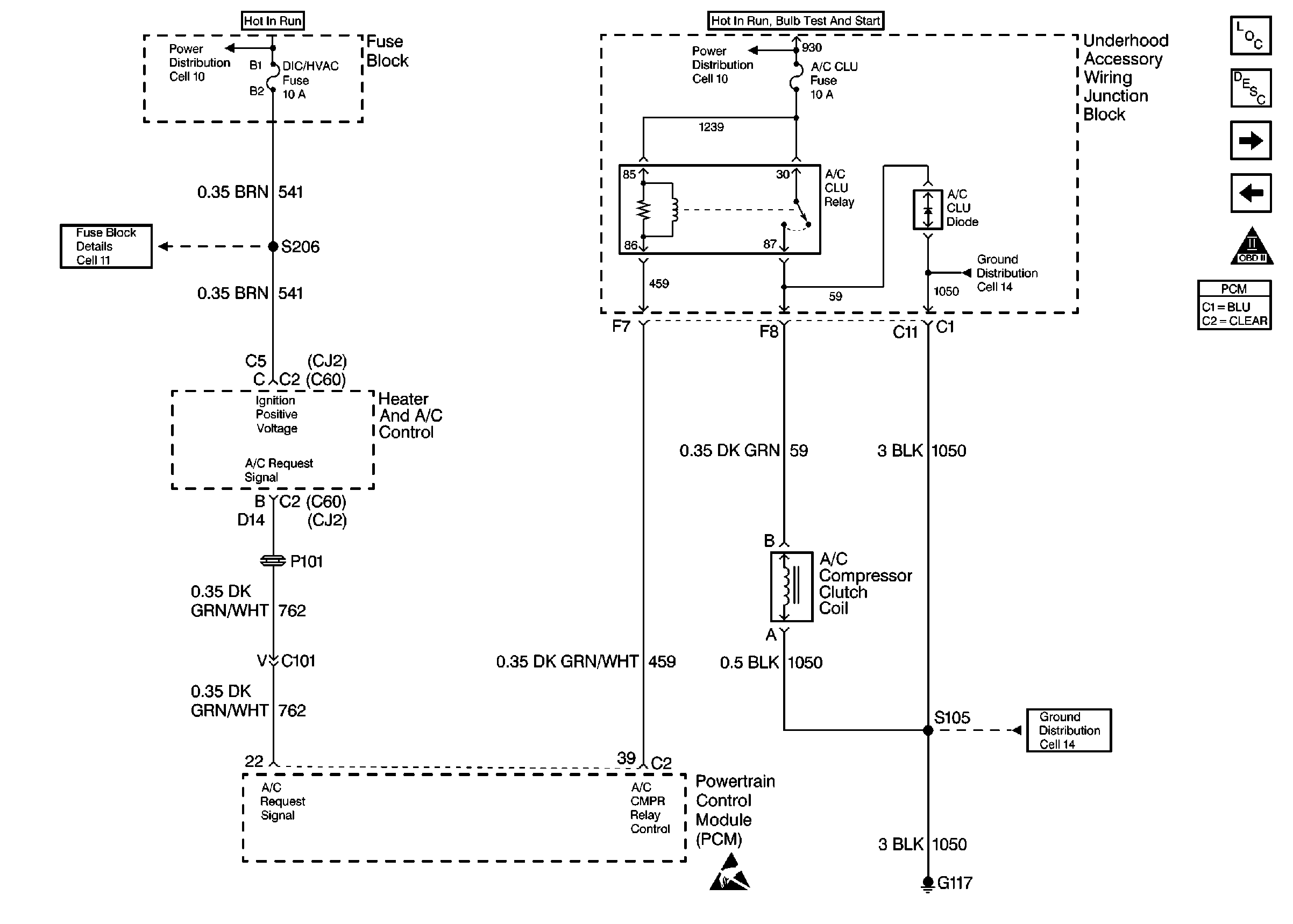
Check for open diode across A/C compressor clutch and check for other
open diodes. Refer to
A/C Controls
.
The following Symptom tables are located in this section:

