Refer to Emission Hose Routing Diagram
EVAP Control System Overview
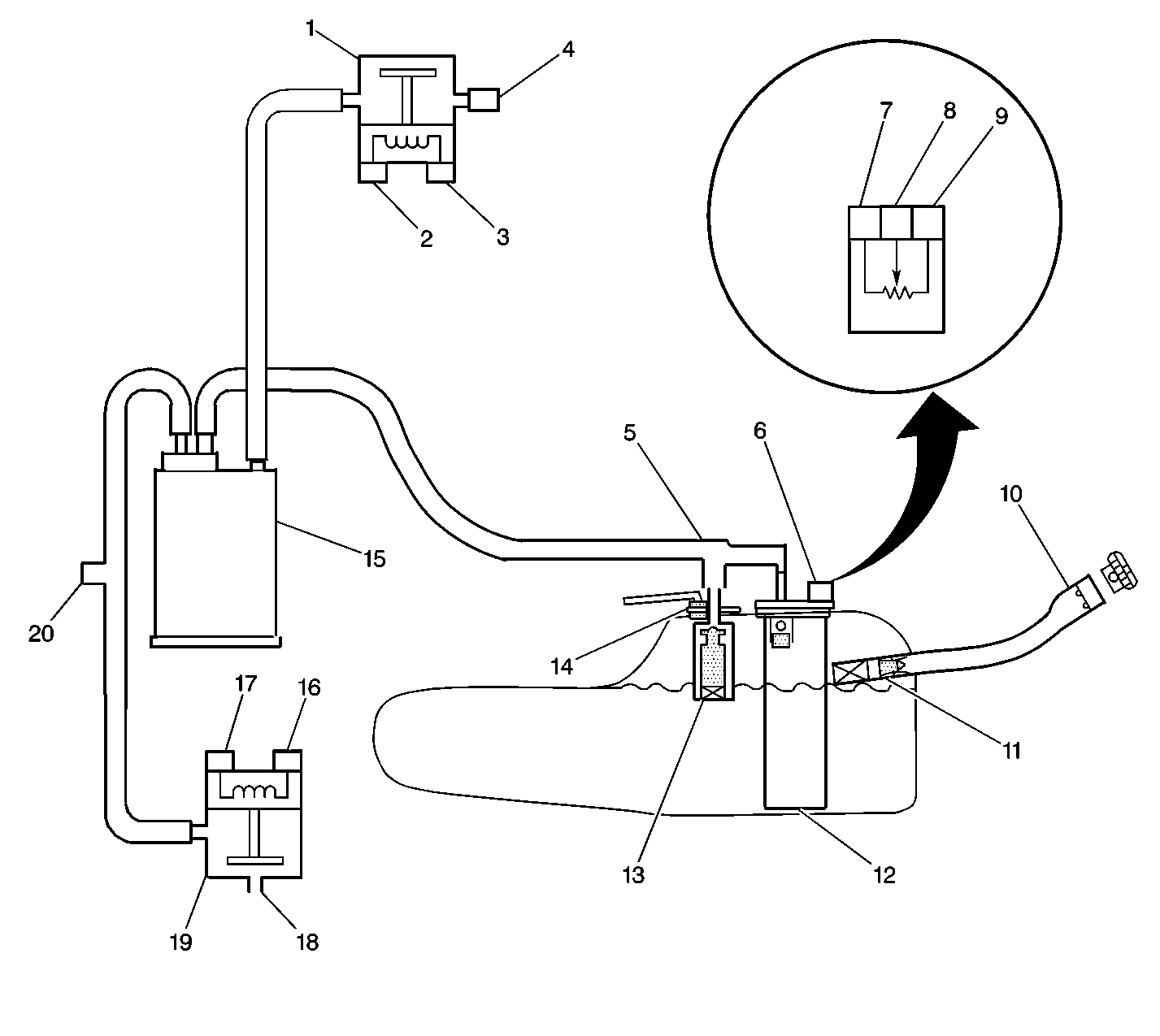
System Description
The evaporative emissions (EVAP) canister purge valve allows the manifold
vacuum to purge the canister. The powertrain control module (PCM) supplies
a ground in order to energize ON the purge valve. The EVAP purge valve
control is pulse-width modulated (PWM), or turned ON and OFF several
times per second. The engine operating conditions including
the load, the throttle position, the coolant temperature, and the ambient
temperature determine the duty cycle. The PCM calculates the duty cycle,
and the output is commanded when the appropriate conditions have
been met.
During diagnostic tests, the EVAP vent valve seals the EVAP system
tests. During the diagnostic tests, the fuel tank pressure sensor monitors
the vacuum in the system.
The following conditions can set DTC P0440:
| • | An EVAP canister purge valve that is stuck closed |
| • | An EVAP canister purge valve that is stuck open |
| • | An EVAP purge line or vent nose that is disconnected or damaged |
| • | A leaking fuel fill neck |
A small leak in the EVAP system can set DTC P0442.
The following conditions can set DTC P0446:
| • | An EVAP vent valve that is stuck closed |
| • | A blocked EVAP canister |
A continuous purge condition with no purge commanded by the PCM,
when the EVAP purge valve is stuck open or leaking, can set DTC P1441.
Refer to the DTC tables for further EVAP system diagnostic procedures.
The EVAP system includes the following components:
| • | The EVAP canister purge valve |
| • | The EVAP fresh air vent hose |
| • | The fuel pipes and hoses |
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
| • | A cracked or punctured EVAP canister |
| • | Damaged or disconnected components that are listed below: |
| - | The fuel tank vapor line |
| • | A poor connection at the PCM |
| • | Inspect all wiring and connections of the PCM harness. |
| • | The following conditions can cause an intermittent: |
| - | Rubbed-through wire insulation |
| - | Broken wire inside the insulation |
| - | Improperly formed or damaged terminals |
| - | Poor terminal-to-wire connections |
| • | Inspect the wiring harness for an intermittent, an open, or a
short circuit to the following components: |
| - | The fuel tank pressure sensor |
| • | Verify that the lines are not restricted. Inspect for the following
conditions: |
| - | Kinked or pinched lines |
| - | A plugged vacuum source, EVAP purge, or fuel tank vapor line |
| • | Inspect for carbon being released into the system. |
EVAP Control System Diagnosis
Step
| Action
| Value(s)
| Yes
| No
|
1
| Did you complete the Powertrain
On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check?
| --
|
Go to Step 2
| Go to
Powertrain On Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check
|
2
| Did any other DTC set?
| --
| Go to Applicable DTC
|
Go to Step 3
|
3
| Inspect the EVAP system for the
following conditions:
| • | A fuel fill cap that is: |
| • | EVAP system purge or vapor pipes that are: |
| • | A fresh air vent hose that is: |
| • | Damaged EVAP system components |
| • | A service port dust cap or schrader valve that is: |
Did you find and correct the condition?
| --
|
Go to Step 9
|
Go to Step 4
|
4
|
- Disconnect the EVAP vapor pipe from the fuel tank or the EVAP
canister.
- Turn ON the ignition, with the engine OFF.
- With a scan tool, observe the Fuel Tank Pressure Parameter.
Is the fuel tank pressure near the specified value?
| 0 in H2O
|
Go to Step 5
| Go to
DTC P0453 Fuel Tank Pressure Sensor Circuit High Voltage
|
5
|
- Reconnect all of the EVAP hardware that you previously disconnected.
- Install theJ 41415-40
fuel tank cap adapter to the fuel fill neck and the fuel fill cap.
- Connect the J 41413
EVAP pressure and purge diagnostic station to the fuel tank cap adaptor.
- Use a scan tool in order to seal the EVAP system.
Important: DO NOT exceed the pressure in the specified value.
- Use the EVAP station in order to pressurize the system to the specified
value by slowly turning the rotary switch to the Pressure position.
Did you achieve the specified value?
| 1.25 kPa (5 in. H2O)
|
Go to Step 6
| Go to
|
6
| Use the
EVAP service station in order to maintain the fuel tank pressure at the specified
value.
Is the fuel tank pressure at the specified value?
| 1.25 kPa (5 in
H2O)
|
Go to Step 7
| Go to
DTC P0452 Fuel Tank Pressure Sensor Circuit Low Voltage
|
7
| With a scan tool, command the vent valve OFF.
With the rotary switch in the Off/Hold position, does the pressure
decrease to near the specified value within 2 minutes ?
| 0 kPa (0 in.
H2O)
|
Go to Step 8
| Go to
DTC P0446 Evaporative Emission (EVAP) Vent System Performance
|
8
|
- With the EVAP station, increase the fuel tank pressure to the
specified value.
- Use a scan tool in order to observe the Fuel Tank Pressure Parameter.
Does the scan tool indicate a fuel tank pressure decrease to the specified
lower value within 15 Seconds?
| 1.25 kPa (5 in H2O)
0 kPa (0 in H2O)
| Go to
DTC P1441 Evaporative Emission (EVAP) System Flow During Non-Purge
|
Go to Step 9
|
9
|
- Reconnect all of the EVAP hardware that you previously disconnected.
- Turn ON the ignition, with the engine OFF.
- With scan tool, select the Seal option in order to seal the EVAP
system.
Important: Do not exceed the pressure in the specified value.
- With the EVAP station, pressurize the system to the first specified,
or higher, value by slowly turning the rotary switch to the Pressure position.
- Monitor the pressure with the gauge on the cart with the rotary
switch in the Off/Hold position.
Does the EVAP pressure decrease to less than the second specified value
within 2 minutes?
| 15 in H2O
10 in H2O
| Go to
DTC P0442 Evaporative Emission (EVAP) System Small Leak Detected
| System OK
|

