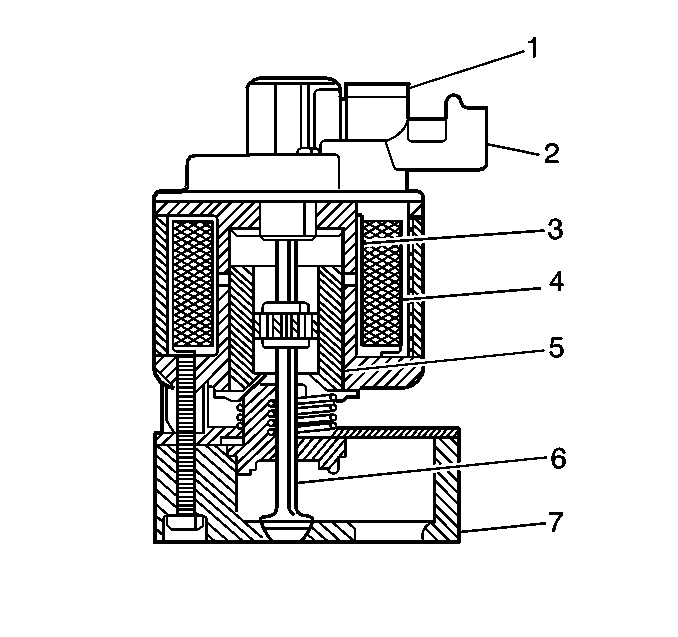
Purpose
The exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) system is used to lower oxides of
nitrogen (NOx) emission levels caused by high combustion temperature. The
EGR system does this by decreasing combustion temperature.
Linear EGR Valve
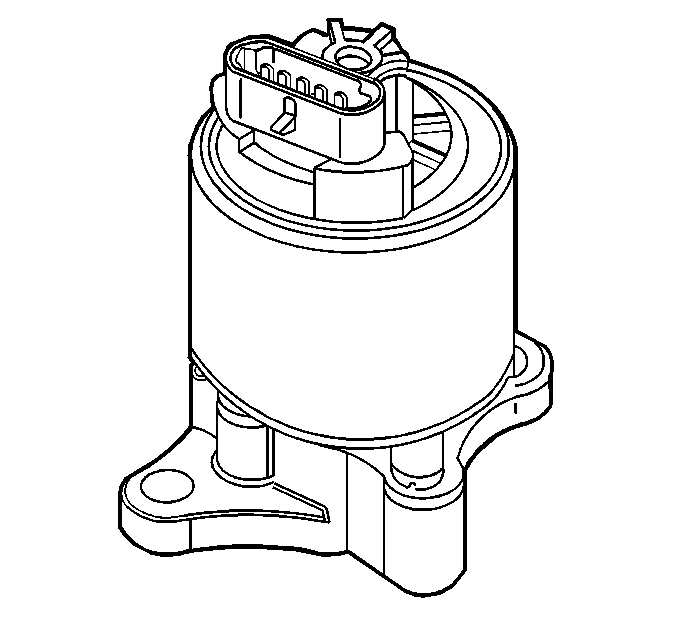
The main element of the system is the linear EGR valve.
The EGR valve feeds small amounts of exhaust gas back into the combustion
chamber. With the fuel/air mixture diluted by the exhaust gases, combustion
temperatures are reduced.
Operation