SIR System Overview
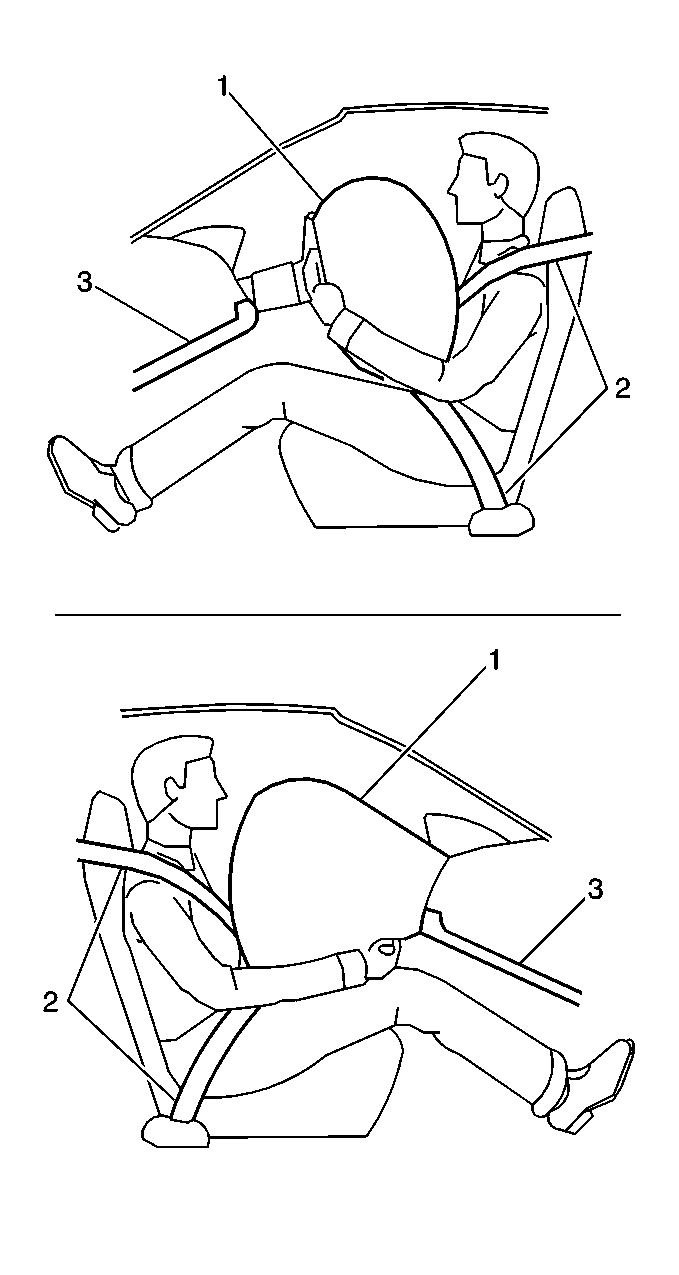
The supplemental inflatable restraint (SIR) system supplements the
protection offered by the occupant seat belt system (2). The SIR system
contains various inflator modules and seat belt pretensioners that are
located throughout the vehicle, i.e. inflatable restraint steering wheel
module (1), inflatable restraint IP module (1), inflatable restraint
side impact module - LF, inflatable restraint side impact module - RF,
seat belt pretensioner - LF, and seat belt pretensioner - RF. Each inflator
module and seat belt pretensioner has a deployment loop that is controlled
by the inflatable restraint sensing and diagnostic module (SDM), which
is mounted inside of the vehicle. The SDM determines the severity of a
collision and commands deployment of each inflator module and seat belt
pretensioner. The SDM performs continuous diagnostic monitoring of the
SIR system electrical components. Upon detection of a circuit malfunction,
the SDM will set a diagnostic trouble (DTC) and inform the driver by commanding
the instrument panel cluster (IPC) to turn the AIR BAG indicator ON. The
steering column and knee bolsters (3) are designed to absorb energy and
compress during frontal collisions in order to limit leg movement and
decrease the chance of injury to the driver and front passenger.
Frontal SIR System Description
The frontal SIR system consists of the following components:
| • | AIR BAG indicator in the instrument panel cluster (IPC) |
| • | Driver and front passenger knee bolsters |
| • | Inflatable restraint instrument panel (IP) module |
| • | Inflatable restraint seat belt pretensioner - LF |
| • | Inflatable restraint seat belt pretensioner - RF |
| • | Inflatable restraint sensing and diagnostic module (SDM) |
| • | Inflatable restraint steering wheel module |
| • | Inflatable restraint steering wheel module coil |
| • | Inflatable restraint wiring harness |
| • | Steering wheel and column |
A frontal collision of sufficient force will deploy the frontal inflator
modules and the seat belt pretensioners. The SDM contains a sensing device
(accelerometer) that converts vehicle velocity changes to an electrical
signal. The SDM contains a microprocessor, which performs calculations
using the measured accelerations and compares these calculations to a
value stored in memory. When the generated calculations exceed the stored
value, the SDM will cause current to flow through the frontal inflator
module and seat belt pretensioner deployment loops, deploying the frontal
inflator modules and the seat belt pretensioners. Once the inflator modules
are inflated, they quickly deflate through the air bag vent holes and/or
the bag fabric. After the inflator modules and seat belt pretensioners
are deployed, the SDM sets a deployment commanded DTC and then commands
the IPC to turn the AIR BAG indicator ON. The SDM, IP module, steering
wheel module, steering wheel module coil, seat belt pretensioner - LF,
seat belt pretensioner - RF and the connecting wires make up the frontal
deployment loops. The SDM continuously monitors the deployment loops for
malfunctions and commands the IPC to turn the AIR BAG indicator ON if
a fault is detected.
AIR BAG Indicator
The AIR BAG indicator, located in the IPC is used to notify the driver
of SIR system malfunctions and to verify that the SDM is communicating with
the IPC. When the ignition is turned ON, the SDM and the IPC are supplied
with ignition 1 voltage. The IPC responds by flashing the AIR BAG
indicator seven times. While the IPC is flashing the AIR BAG indicator,
the SDM conducts tests on all SIR system components and circuits. If no
malfunctions are detected, the SDM will command the IPC to turn the AIR
BAG indicator OFF via Class 2 serial data. The SDM provides continuous
monitoring of the inflator module circuits by conducting a sequence of
checks. If a malfunction is detected, the SDM will store a diagnostic
trouble code (DTC) and command the IPC to turn the AIR BAG indicator
ON via Class 2 serial data. The presence of a SIR system malfunction
could result in non-deployment of the inflator modules in the event of
a collision, or deployment of the inflator modules without the event of
a collision. The AIR BAG indicator will remain ON until the malfunction
has been repaired.
Driver and Front Passenger Knee Bolsters
The knee bolsters are designed to help restraint the lower torso of
front seat occupants by absorbing the energy through the front seat occupant's
upper legs. In a collision, the front seat occupant legs may come in
contact with the knee bolsters. The knee bolsters are designed to crush
and deform, absorbing some of the impact and helping to reduce bodily
injuries. the driver and passenger knee bolsters are located in the
lower part of the instrument panel and must be inspected for damages
after a collision.
Inflatable Restraint Inflator Modules
The inflator modules contain a housing, an inflatable air bag, the initiator,
a canister of gas generating materials, and in some cases, stored compressed
gas. The initiator is part of the inflator module deployment loop. When
the vehicle is involved in a collision of sufficient force, the SDM
causes current to flow through the deployment loops to the initiator.
Current passing through the initiator ignites the material in the
canister producing a rapid generation of gas and the release of compressed
gas, if present. The gas produced from this reaction rapidly inflates
the inflator module. Once the inflator module is inflated, it quickly
deflates through the vent holes and/or the fabric. Each inflator module
is equipped with a shorting bar that is located in the connector of
the inflator module. The shorting bar shorts the inflator modules circuitry
to prevent unwanted deployment of the inflator module when the connector
is disconnected.
Inflatable Restraint Seat Belt Pretensioners
The seat belt pretensioners contain a housing, an initiator, a canister
of gas generating materials, a routing cable with a piston attached, and
a piston tube. The initiator is part of the seat belt pretensioner deployment
loop. When the vehicle is involved in a collision of sufficient force,
the SDM causes current to flow through the seat belt pretensioner deployment
loops to the initiator. Current passing through the initiator ignites
the material in the canister producing a rapid generation of gas.
The gas produced from this reaction deploys the seat belt pretensioner
and shortens the seat belt pretensioner height, which removes all of the
slack in the seat belts. The seat belt pretensioners will deploy immediately
before the frontal inflator modules deploy. Each seat belt pretensioner
is equipped with a shorting bar that is located in the connector of
the seat belt pretensioner. The shorting bar shorts the seat belt pretensioner
circuitry to prevent unwanted deployment of the seat belt pretensioner
when the connector is disconnected.
Inflatable Restraint Sensing and Diagnostic Module (SDM)
The inflatable restraint sensing and diagnostic module (SDM) is a microprocessor
and the control center for the SIR system. The SDM contains internal sensors
along with external sensors, if equipped, mounted at various locations,
depending on vehicle. In the event of a collision, the SDM performs
calculations using the signals received from the internal and external
sensors, if equipped. The SDM compares the result of the calculations
to values stored in memory. When these calculations exceed the stored
value, the SDM will cause current to flow through the deployment loops,
deploying the inflator modules and/or the seat belt pretensioners. The
SDM records the SIR system status when a deployment occurs and commands
the IPC to turn the AIR BAG indicator ON. The SDM performs continuous
diagnostic monitoring of the SIR system electrical components and circuitry
when the ignition is ON. If the SDM detects a malfunction, a DTC will
be stored and the SDM will turn the AIR BAG indicator ON. In the event
that ignition 1 voltage is lost during a collision, the SDM
maintains a 36 volt loop reserve (36 VLR) for deployment
of the inflator modules and seat belt pretensioners. It is important
to note, when disabling the SIR system for service or rescue operations,
to allow the 36 VLR to dissipate, which could take up to 1 minute.
Inflatable Restraint Steering Wheel Module Coil
The steering wheel module coil is attached to the steering column and
is located under the steering wheel. The steering wheel module coil consists
of two or more current - carrying coils. The coils allow the rotation
of the steering wheel while maintaining continuous electrical contact
between the steering wheel module deployment loop and the steering wheel
module. Two coil wires are used for the steering wheel module deployment
loop. Additional coil wires are used for accessories that are attached
to the steering wheel, depending on the vehicle model. The steering
wheel module coil connector is located near the base of the steering
column. The connector contains a shorting bar that shorts the steering
wheel module coil deployment loop circuitry to prevent unwanted deployment
of the steering wheel module when the connector is disconnected.
Inflatable Restraint Wiring Harness
The inflatable restraint wiring harness connects the inflator modules,
the SDM, the deployment loops, and the serial data circuit together using
weather - packed connectors. SIR system connectors are yellow for easy
identification. When repairing SIR wiring harnesses, follow the proper
testing and repair procedures listed in the service manual.
Steering Wheel and Column
The steering wheel and column are designed to absorb energy when driver
contact is made with steering wheel or inflated module. In a collision, the
driver may contact the steering wheel directly or load the steering
wheel and column through the inflated module. When the driver applies
load to the inflator module or the steering wheel, the column will compress
downward, absorbing some of the impact and helping to reduce bodily
injuries to the driver. The steering wheel and column must be inspected
for damages after a collision.
Side SIR System Description
The side impact SIR system consists of the following components:
| • | AIR BAG indicator in the instrument panel cluster (IPC) |
| • | Inflatable restraint seat belt pretensioner - LF |
| • | Inflatable restraint seat belt pretensioner - RF |
| • | Inflatable restraint sensing and diagnostic module (SDM) |
| • | Inflatable restraint side impact modules - LF |
| • | Inflatable restraint side impact modules - RF |
| • | Inflatable restraint side impact sensors (SIS) - LH |
| • | Inflatable restraint side impact sensors (SIS) - RH |
| • | Inflatable restraint wiring harness |
The side impact modules are located in the outside portion for the front
seat backs. The side impact modules contain a housing, inflatable air bag,
initiating device, and a canister of gas generating material. The initiator
is part of the side impact module deployment loop. When a side impact
of sufficient force occurs, the SIS detects the impact and sends a signal
to the SDM. The SDM compares the signal received from the SIS to a value
stored in memory. When the generated signal exceeds the stored value,
the SDM will cause current to flow through the side deployment loop, deploying
the inflator module. The SDM, side impact modules and the connecting wires
make up the side deployment loops. The SDM continuously monitors the side
deployment loops for malfunctions and commands the IPC to turn the AIR
BAG indicator ON if a fault is present.
Inflatable Restraint Side Impact Sensor (SIS)
The side impact sensors (SIS) contains a sensing device (accelerometer)
which monitors vehicle acceleration and velocity changes to detect side collisions
that are severe enough to warrant side inflator module deployment. The
SIS is not part of the deployment loop, but instead provides an input
to the SDM. The SDM contains a microprocessor that performs calculations
using the measured accelerations and compares these calculations to a
value stored in memory. When the generated calculations exceed the stored
value, the SDM will cause current to flow through the deployment loops,
deploying the side inflator module(s).

