Tools Required
- Use the J 8089
in
order to clean the carbon from the combustion chambers and the valve parts.
Be careful not to scuff the chamber
- Clean the following areas:
| 2.1. | The carbon and the sludge from the valve pushrods and the valve
rocker arms |
| 2.2. | The valve stems and heads on a buffing wheel |
| 2.3. | The cylinder head and engine block gasket surfaces |
| 2.4. | The bolt hole threads in the cylinder heads and the engine block |
- Inspect the following areas:
| 3.1. | The cylinder head for cracks in the exhaust ports and combustion
chambers |
| 3.2. | The cylinder head for external cracks in the water chamber |
| 3.3. | The valves for burned heads, cracked faces, or damaged stems |
| 3.4. | The valve springs for squareness |
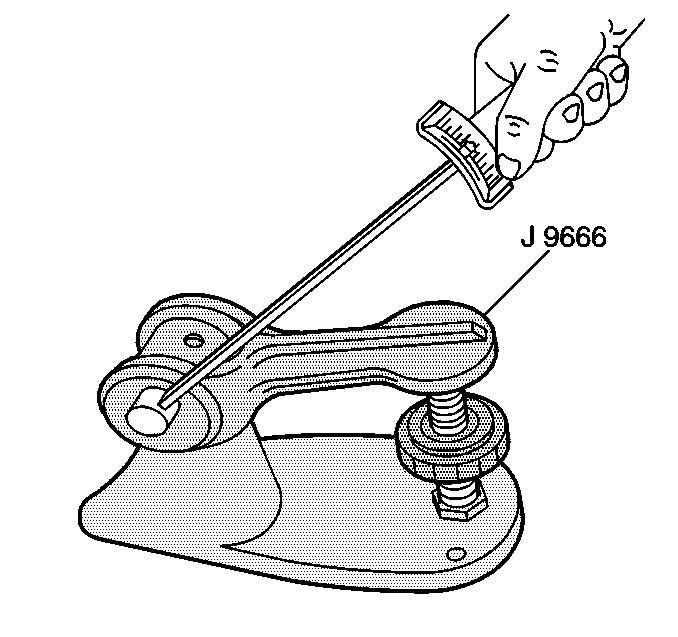
- Use the J 9666
in
order to measure the valve spring.
Replace the spring if the spring tension is less than 332-362 N·m
(75-81 lb) at 43.43 mm (1.710 in)
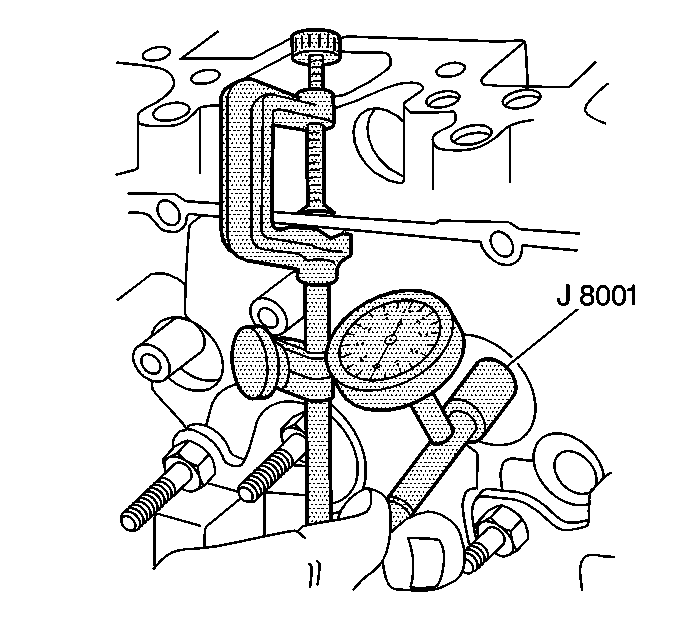
- Measure the valve stem-to-guide clearance.
| • | Excessive valve stem-to-guide clearance will cause an excessive
oil consumption and may case a valve to break. Insufficient clearance will
result in noisy and sticky functioning of the valve and will disturb the
engine assembly smoothness. |
| • | Clamp the J 8001
on
the exhaust port side of the cylinder head. |
| • | Locate the indicator so that the movement of the valve stem from
side to side (crosswise to the cylinder head) will cause a direct movement
of the indicator stem. |
| • | The indicator stem must contract the side of the valve stem just above
the valve guide. |
| • | Drop the valve head about 1.6 mm (0.0064 in) off
the valve seat. |
| • | Use light pressure when moving the valve stem from side to side
in order to obtain a clearance reading. |
| • | Ream the intake valve guides for oversize valves if the clearance
exceeds .069 mm (0.0027 in) on the intake valve. |
| • | Ream the exhaust valve guides for oversize valves if the clearance
exceeds .081 mm (0.0031 in) |


